\(14-|\dfrac{3x}{2}-1=9;17-|\dfrac{2}{3}-4x|=9\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(x^2-\dfrac{1}{5}.\dfrac{5}{4}=\dfrac{3}{4}\\ \Rightarrow x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{3}{4}\\ \Rightarrow x^2=1\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-1\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{9}\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{2}-x=-\dfrac{1}{3}\\\dfrac{1}{2}-x=\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{6}\\x=\dfrac{1}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x^2-5=5\\ \Rightarrow x^2=10\\ \Rightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{10}\)
\(3x^2-1=14\\ \Rightarrow3x^2=15\\ \Rightarrow x^2=5\\ \Rightarrow x=\pm\sqrt{5}\)
1. x2 - \(\dfrac{1}{5}.\dfrac{5}{4}=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
<=> x2 - \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) = \(\dfrac{3}{4}\)
<=> x2 = \(\dfrac{3}{4}+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
<=> x2 = 1
<=> x = \(\pm\)1
2. \(\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-x\right)^2=\dfrac{1}{9}\)
<=> \(\dfrac{1}{4}-x+x^2=\dfrac{1}{9}\)
<=> x2 - x = \(\dfrac{1}{9}-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
<=> x2 - x = \(\dfrac{-5}{36}\)
<=> x2 - x - \(\dfrac{-5}{36}\) = 0
Đoạn này dài, mik giải ngoài rồi viết vào nha:
<=> x = \(\dfrac{5}{6}\)
3. x2 - 5 = 5
<=> x2 = 10
<=> x = \(\sqrt{10}\)
4. 3x2 - 1 = 14
<=> 3x2 = 15
<=> x2 = 15 : 3
<=> x2 = 5
<=> x = \(\sqrt{5}\)

1/ \(\dfrac{4x+7}{x-1}=\dfrac{12x+5}{3x+4}\) (1)
Điều kiện: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1\ne0\\3x+4\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne1\\x\ne-\dfrac{4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
(1) \(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+7\right)\left(3x+4\right)=\left(12x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)\\\Leftrightarrow12x^2+16x+21x+28=12x^2-12x+5x-5\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(16+21+12-5\right)x=-5-28\\ \Leftrightarrow44x=-33\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{4}\) (Thỏa mãn)
Vậy \(x=-\dfrac{3}{4}\).
2/ \(\dfrac{x}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{x^2-1}=0\) (2)
Điều kiện: \(x\ne\pm1\)
(2)\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)-2x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x+1\right)-2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2+x-2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-x=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
So sánh với điều kiện \(\Rightarrow x=0\) là nghiệm của PT.
3/ \(\dfrac{1}{3-x}-\dfrac{14}{x^2-9}=1\) (3)
Điều kiện: \(x\ne\pm3\)
(3)\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{3-x}-\dfrac{14}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow-\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{14}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow-\left(x+3\right)-14=\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow-x-17=x^2-9\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+8=0\) (Vô nghiệm do \(x^2+x+8>0\qquad\forall x\)).
Vậy PT vô nghiệm.
4/ \(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{4}{x^2-1}\) (4)
Điều kiện: \(x\ne\pm1\)
(4)\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x-1\right)^2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+2x+1\right)-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=4\Leftrightarrow4x=4\Leftrightarrow x=1\) (loại)
Vậy PT vô nghiệm.
5/ \(x+\dfrac{1}{x}=x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\) (5)
Điều kiện: \(x\ne0\)
(5)\(\Leftrightarrow x+\dfrac{1}{x}=\left(x+\dfrac{1}{x}\right)^2-2\)
Đặt \(t=x+\dfrac{1}{x}\), ta có: \(t=t^2-2\\ \Leftrightarrow t^2-t-2=0\Leftrightarrow\left(t-2\right)\left(t+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=2\\t=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Với \(t=2\) ta có: \(x+\dfrac{1}{x}=2\Leftrightarrow x^2+1=2x\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\) (thỏa mãn)
Với \(t=-1\) ta có: \(x+\dfrac{1}{x}=-1\Leftrightarrow x^2+1=-x\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+1=0\) (vô nghiệm).
Vậy \(x=1\) là nghiệm PT.
6/ \(\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+4}=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\) (6)
Điều kiện: \(x\ne-1\)
(6)\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+4}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{x^2+4}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=0\\\dfrac{1}{x^2+4}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\) (Thỏa mãn)
\(\dfrac{1}{x^2+4}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}=0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x^2+4}=\dfrac{1}{x+1}\Leftrightarrow x^2+4=x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-x+3=0\) (vô nghiệm).
Vậy \(x=1\) là nghiệm PT.
1) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-\dfrac{4}{3}\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{4x+7}{x-1}=\dfrac{12x+5}{3x+4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4x+7\right)\left(3x+4\right)=\left(12x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2+16x+21x+28=12x^2+12x+5x-5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2+37x+28-12x^2-17x+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20x+33=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20x=-33\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{33}{20}\)(nhận)
Vậy: \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{33}{20}\right\}\)
2) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x}{x-1}-\dfrac{2x}{x^2-1}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{2x}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=0\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+x-2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(nhận\right)\\x=1\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: S={0}
3) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{3;-3\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{1}{3-x}-\dfrac{14}{x^2-9}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-1}{x-3}-\dfrac{14}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}-\dfrac{14}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(-x-3-14=x^2-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9=-x-17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9+x+17=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+x+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2\cdot x\cdot\dfrac{1}{2}+\dfrac{1}{4}+\dfrac{31}{4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2+\dfrac{31}{4}=0\)(vô lý)
Vậy: \(S=\varnothing\)
4) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{4}{x^2-1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
Suy ra: \(x^2+2x+1-\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+2x+1-x^2+2x-1=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=4\)
hay x=1(loại)
Vậy: \(S=\varnothing\)
5) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne0\)
Ta có: \(x+\dfrac{1}{x}=x^2+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x^2+1}{x}=\dfrac{x^4+1}{x^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x^2+1\right)=x\left(x^4+1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4+x^2=x^5+x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^5+x-x^4-x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^4-x^3-x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left[x^3\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)^2\cdot\left(x^2+x+1\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2+x+1>0\)
nên \(x\cdot\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(loại\right)\\x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Vậy: S={1}
6) ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
Ta có: \(\dfrac{x-1}{x^2+4}=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)=\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1-x^2-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(-x^2+x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2-x+3\right)=0\)
mà \(x^2-x+3>0\)
nên x-1=0
hay x=1(nhận)
Vậy: S={1}

f: =>\(\dfrac{14}{3\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{x+2}{x-4}=\dfrac{-3}{2\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
=>28-6(x+2)=-9-5(x-4)
=>28-6x-12=-9-5x+20
=>-6x+16=-5x+11
=>-x=-5
=>x=5
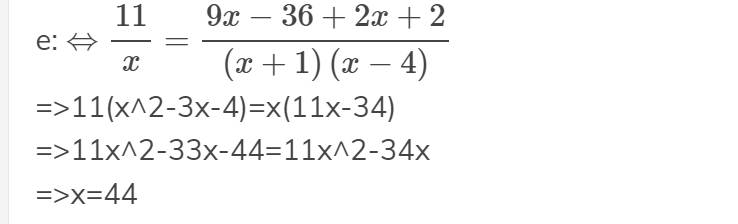

d: =>\(\dfrac{12x+1}{11x-4}=\dfrac{20x+17-20x+8}{18}=\dfrac{25}{18}\)
=>25(11x-4)=18(12x+1)
=>275x-100=216x+18
=>59x=118
=>x=2
f: =>\(\dfrac{14}{3\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{x+2}{x-4}=\dfrac{-3}{2\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{5}{6}\)
=>28-6(x+2)=-9-5(x-4)
=>28-6x-12=-9-5x+20
=>-6x+16=-5x+11
=>-x=-5
=>x=5
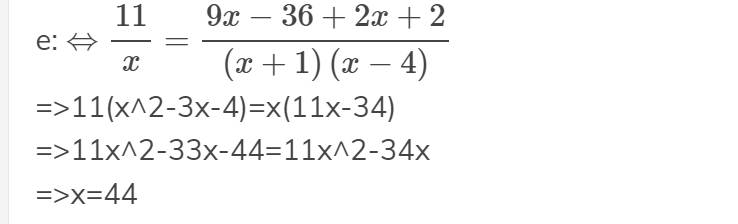

a: \(A=\left|3x-9\right|+1.5\ge1.5\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=3
b: \(B=\left|x-7\right|-14\ge-14\forall x\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra khi x=7

Để giải phương trình, ta sẽ thực hiện các bước sau: Bước 1: Giải các phép tính trong phương trình. 32x^(-1) + 2.9x^(-1) = 405(13)^(-1) + 5.(13)^2 + 1 = 1493(31)^(-1) + 5.(31)^2 + 1 = 9314(35)^(-1) Bước 2: Rút gọn các số hạng. 32x^(-1) + 2.9x^(-1) = 405/13 + 5.(13)^2 + 1 = 1493/31 + 5.(31)^2 + 1 = 9314/35 Bước 3: Đưa các số hạng về cùng mẫu số. 32x^(-1) + 2.9x^(-1) = (405/13).(31/31) + 5.(13)^2 + 1 = (1493/31).(13/13) + 5.(31)^2 + 1 = 9314/35 Bước 4: Tính toán các số hạng. 32x^(-1) + 2.9x^(-1) = 405.(31)/13.(31) + 5.(13)^2 + 1 = 1493.(13)/31.(13) + 5.(31)^2 + 1 = 9314/35 Bước 5: Tính tổng các số hạng. 32x^(-1) + 2.9x^(-1) = 405.(31)/403 + 5.(13)^2 + 1 = 1493.(13)/403 + 5.(31)^2 + 1 = 9314/35 Bước 6: Đưa phương trình về dạng chuẩn. 32x^(-1) + 2.9x^(-1) - 9314/35 = 0 Bước 7: Giải phương trình. Để giải phương trình này, ta cần biến đổi nó về dạng tương đương. Nhân cả hai vế của phương trình với 35 để loại bỏ mẫu số. 35.(32x^(-1) + 2.9x^(-1) - 9314/35) = 0 1120x^(-1) + 101.5x^(-1) - 9314 = 0 Bước 8: Tìm giá trị của x. Để tìm giá trị của x, ta cần giải phương trình này. Tuy nhiên, phương trình này không thể giải được vì x có mũ là -1.

\(a,5\left(x+2\right)^3+7=2\\ \Leftrightarrow5\left(x+2\right)^3=-5\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)^3=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x+2=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=-3\\ b,14-\left|\dfrac{3}{2}x-1\right|=9\\ \Leftrightarrow\left|\dfrac{3}{2}x-1\right|=5\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{2}x-1=5\\\dfrac{3}{2}x-1=-5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{2}x=6\\\dfrac{3}{2}x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-\dfrac{8}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(a,\Leftrightarrow5\left(x+2\right)^3=-5\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+2\right)^3=-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x+2=-1\Leftrightarrow x=-3\\ b,\Leftrightarrow\left|\dfrac{3}{2}x-1\right|=5\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{2}x-1=5\\1-\dfrac{3}{2}x=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3}{2}x=6\\\dfrac{3}{2}x=-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=4\\x=-\dfrac{8}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(1,\left(dk:x\ne0,-1,4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{9}{x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x-4}-\dfrac{11}{x}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{9x\left(x-4\right)+2x\left(x+1\right)-11\left(x+1\right)\left(x-4\right)}{x\left(x+1\right)\left(x-4\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x^2-36x+2x^2+2x-11x^2+44x-11x+44=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=-44\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=44\left(tm\right)\)
\(2,\left(đk:x\ne4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14}{3\left(x-4\right)}-\dfrac{2+x}{x-4}-\dfrac{3}{2\left(x-4\right)}+\dfrac{5}{6}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{14.2-6\left(2+x\right)-3.3+5\left(x-4\right)}{6\left(x-4\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow28-12-6x-9+5x-20=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x=13\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-13\left(tm\right)\)
Lời giải:
$14-|\frac{3x}{2}-1|=9$
$|\frac{3x}{2}-1|=14-9=5$
$\Rightarrow \frac{3x}{2}-1=5$ hoặc $\frac{3x}{2}-1=-5$
$\Rightarrow \frac{3x}{2}=6$ hoặc $\frac{3x}{2}=-4$
$\Rightarrow x=4$ hoặc $x=\frac{-8}{3}$
----------------
$17-|\frac{2}{3}-4x|=9$
$|\frac{2}{3}-4x|=17-9=8$
$\Rightarrow \frac{2}{3}-4x=8$ hoặc $\frac{2}{3}-4x=-8$
$\Rightarrow x=\frac{-11}{6}$ hoặc $x=\frac{13}{6}$