Cho các PT sau: 3x2-4x+1=0; -x2+6x-5=0 a, Giải các PT trên bằng công thức nghiệm hoặc công thức nghiệm thu gọn.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



\(3x^2-2\left(x^2+4x\right)+3x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-2x^2-8x+3x+2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-5x+2=0\)

a. Em tự giải
b.
\(\Delta=4-3\left(m+5\right)>0\Rightarrow m< -\dfrac{11}{3}\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{4}{3}\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{m+5}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để biểu thức đề bài xác định \(\Rightarrow x_1x_2\ne0\Rightarrow m\ne-5\)
\(\dfrac{1}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_2}=\dfrac{4}{7}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x_1+x_2}{x_1x_2}=\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4}{m+5}=\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\(\Rightarrow m+5=7\)
\(\Rightarrow m=2\) (ktm)
Vậy ko tồn tại m thỏa mãn yêu cầu đề bài
Có cả điều kiện delta lúc đầu nữa em, \(m< -\dfrac{11}{3}\) mà \(m=2>-\dfrac{11}{3}\) nên không thỏa mãn

Lời giải:
$\Delta'=4-6m$
a. Để pt có nghiệm thì $\Delta'=4-6m\geq 0\Leftrightarrow m\leq \frac{2}{3}$
b/ Để pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thì $\Delta'=4-6m>0\Leftrightarrow m< \frac{2}{3}$
c. Để pt có nghiệm kép thì $\Delta'=4-6m=0\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{2}{3}$
d. Để pt vô nghiệm thì $\Delta'=4-6m< 0\Leftrightarrow m> \frac{2}{3}$
a: \(\text{Δ}=\left(-4\right)^2-4\cdot3\cdot2m=-24m+16\)
Để phương trình có nghiệm thì \(\text{Δ}\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-24m+16\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-24m\ge-16\)
hay \(m\le\dfrac{2}{3}\)
b: Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì Δ>0
hay \(m< \dfrac{2}{3}\)
c: Để phương trình có nghiệm kép thì Δ=0
hay \(m=\dfrac{2}{3}\)

a: ĐKXĐ: x<>0
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2+10x-3x-10=0\)
=>(3x+10)(x-1)=0
=>x=-10/3 hoặc x=1
b: ĐKXĐ: \(x\in R\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-17=0\)
hay x=17/4
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-5\)
=>2x-5=0
hay x=5/2
d: ĐKXĐ: x<>-2/3
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x-1\right)\left(3x+2\right)=5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+4x-3x-2-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2+x-7=0\)
=>(6x+7)(x-1)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=-7/6

\(1,\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta=\left(-3\right)^2-4\left(-2\right)\left(-m+1\right)>0\\x_1+x_2=\dfrac{3}{-2}< 0\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{-m+1}{-2}>0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}17-8m>0\\-m+1< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< \dfrac{17}{8}\\m>1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow1< m< \dfrac{17}{8}\)
\(2,\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta=\left(-4\right)^2-4\left(-3\right)\left(-2m+1\right)\ge0\\x_1+x_2=\dfrac{4}{-3}< 0\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{-2m+1}{-3}>0\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}28-24m\ge0\\-2m+1< 0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\le\dfrac{7}{6}\\m>\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}< m\le\dfrac{7}{6}\)
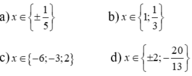
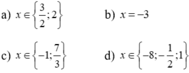
a: 3x^2-4x+1=0
a=3; b=-4; c=1
Vì a+b+c=0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm là:
x1=1 và x2=c/a=1/3
b: -x^2+6x-5=0
=>x^2-6x+5=0
a=1; b=-6; c=5
Vì a+b+c=0 nên phương trình có hai nghiệm là;
x1=1; x2=5/1=5