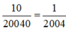Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 1:
a) x≠2x≠2
Bài 2:
a) x≠0;x≠5x≠0;x≠5
b) x2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5xx2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5x
c) Để phân thức có giá trị nguyên thì x−5xx−5x phải có giá trị nguyên.
=> x=−5x=−5
Bài 3:
a) (x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45)(x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45)
=(x+12(x−1)+3(x−1)(x+1)−x+32(x+1))⋅2(2x2−2)5=(x+12(x−1)+3(x−1)(x+1)−x+32(x+1))⋅2(2x2−2)5
=(x+1)2+6−(x−1)(x+3)2(x−1)(x+1)⋅2⋅2(x2−1)5=(x+1)2+6−(x−1)(x+3)2(x−1)(x+1)⋅2⋅2(x2−1)5
=(x+1)2+6−(x2+3x−x−3)(x−1)(x+1)⋅2(x−1)(x+1)5=(x+1)2+6−(x2+3x−x−3)(x−1)(x+1)⋅2(x−1)(x+1)5
=[(x+1)2+6−(x2+2x−3)]⋅25=[(x+1)2+6−(x2+2x−3)]⋅25
=[(x+1)2+6−x2−2x+3]⋅25=[(x+1)2+6−x2−2x+3]⋅25
=[(x+1)2+9−x2−2x]⋅25=[(x+1)2+9−x2−2x]⋅25
=2(x+1)25+185−25x2−45x=2(x+1)25+185−25x2−45x
=2(x2+2x+1)5+185−25x2−45x=2(x2+2x+1)5+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+25+185−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+25+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+2+185−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+2+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+205−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+205−25x2−45x
c) tự làm, đkxđ: x≠1;x≠−1

x2−10x=x(x−10)≠0x2−10x=x(x−10)≠0 khi x≠0;x−10≠0x≠0;x−10≠0
Hay x≠0;x≠10x≠0;x≠10
x2+10x=x(x+10)≠0x2+10x=x(x+10)≠0 khi x≠0;x+10≠0x≠0;x+10≠0
Hay x≠0;x≠−10x≠0;x≠−10
x2+4≥4x2+4≥4
Vậy điều kiện của biến x để biểu thức đã cho được xác định là
x≠−10,x≠0,x≠10x≠−10,x≠0,x≠10
Để việc tính giá trị của biểu thức được đơn giản hơn ta rút gọn biểu thức trước :
(5x+2x2−10x+5x−2x2+10x).x2−100x2+4(5x+2x2−10x+5x−2x2+10x).x2−100x2+4
= [
ĐKXĐ: x2 - 10x khác 0, x2 + 10x khác 0
<=> x khác 0 và x khác +-10.
\((\dfrac{5x + 2}{x^2-10x}+\dfrac{5x-2}{x^2+10x}).\dfrac{x^2-100}{x^2+4}\)
= \(\dfrac{(5x+2)(x+10)+(5x-2)(x-10)}{x(x-10)(x+10)} .\dfrac{(x-10)(x+10)}{x^2+4}\)
= \(\dfrac{5x^2+12x+20+5x^2-12x+20}{x(x^2+4)}\)
= \(\dfrac{10x^2+40}{x(x^2+4)}\)
= \(\dfrac{10(x^2-4)}{x(x^2-4)}\)
= \(\dfrac{10}{x}\)
Thay x = 20040 vào biểu thức, ta có:
\(\dfrac{10}{20040}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2004}\)

Dài quá trôi hết đề khỏi màn hình: nhìn thấy câu nào giải cấu ấy
Bài 4:
\(A=\frac{\left(x-1\right)+\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\frac{2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\frac{2\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\)
a) DK x khác +-1
b) \(dk\left(a\right)\Rightarrow A=\frac{2}{\left(x+1\right)}\)
c) x+1 phải thuộc Ước của 2=> x=(-3,-2,0))
1. a) Biểu thức a có nghĩa \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+2\ne0\\x^2-4\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x+2\ne0\\x-2\ne0\\x+2\ne0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne-2\\x\ne2\end{cases}}\)
Vậy vs \(x\ne2,x\ne-2\) thì bt a có nghĩa
b) \(A=\frac{x}{x+2}+\frac{4-2x}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\frac{4-2x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2-2x+4-2x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^2-4x+4}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{\left(x-2\right)^2}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x-2}{x+2}\)
c) \(A=0\Leftrightarrow\frac{x-2}{x+2}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=\left(x+2\right).0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=2\)(ko thỏa mãn điều kiện )
=> ko có gía trị nào của x để A=0

thiếu đề : \(\left(\frac{x+1}{2x-2}+\frac{3}{x^2-1}-\frac{x+3}{2x+2}\right).\frac{4x^2-4}{5}.\)
Bài 2 :
a, Để \(B=\left(\frac{x+1}{2x-2}+\frac{3}{x^2-1}-\frac{x+3}{2x+2}\right)\frac{4^2-4}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x-2\ne0\\x^2-1\ne0\\2x+2\ne0\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x\ne1\\x\ne-1\end{cases}}\)
b,\(B=\left(\frac{x+1}{2x-2}+\frac{3}{x^2-1}-\frac{x+3}{2x+2}\right)\frac{4x^2-4}{5}\)
\(B=\left[\frac{x+1}{2\left(x-1\right)}+\frac{3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\frac{x+3}{2\left(x+1\right)}\right].\frac{4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{5}\)
\(B=\left[\frac{x^2+2x+1}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{6}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\frac{x^2+2x-3}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right]\frac{4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{5}\)
\(B=\left[\frac{x^2+2x+1+6-x^2-2x+3}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right]\frac{4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{5}\)
\(B=\frac{4}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}.\frac{4\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{5}\)
\(B=\frac{8}{5}\)
=> giá trị của B ko phụ thuộc vào biến x
bài 1
=\(^{\left(2x+1\right)^2+2\left(2x+1\right)\left(2x-1\right)+\left(2x+1\right)^2}\)
=\(\left(2x+1+2x-1\right)^2\)
=\(\left(4x\right)^2\)
=\(16x^2\)
Tại x=100 thay vào biểu thức trên ta có:
16*100^2=1600000

bài1 A=\(\left(\frac{3-x}{x+3}\cdot\frac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}+\frac{x}{x+3}\right):\frac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
=\(\left(-\frac{x-3\cdot\left(x+3\right)^2}{\left(x+3\right)^2\cdot\left(x-3\right)}+\frac{x}{x+3}\right):\frac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
=\(-\frac{x}{x+3}\cdot\frac{x+3}{3x^2}=\frac{-1}{3x}\)
b) thế \(x=-\frac{1}{2}\)vào biểu thức A
\(-\frac{1}{3\cdot\left(-\frac{1}{2}\right)}=\frac{2}{3}\)
c) A=\(-\frac{1}{3x}< 0\)
VÌ (-1) <0 nên 3x>0
x >0

a. ĐK \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x+5\ne0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-5\end{cases}}}\)
b. \(A=\frac{x^2+2x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x^2+2x\right)+2\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x-1}{2}\)
Để \(A=1\Rightarrow\frac{x-1}{2}=1\Rightarrow x=3\)
Để \(A=-3\Rightarrow\frac{x-1}{2}=-3\Rightarrow x=-5\)
Vậy với x=3 thì A=1 ; với x=-5 thì A=-3

a) ĐKXĐ: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+2\ne0\\x^2-4\ne0\\2-x\ne0\end{cases}}\) => \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne-2\\x\ne\pm2\\x\ne2\end{cases}}\) => \(x\ne\pm2\)
Ta có:Q = \(\frac{x-1}{x+2}+\frac{4x+4}{x^2-4}+\frac{3}{2-x}\)
Q = \(\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\frac{4x+4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{3\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
Q = \(\frac{x^2-2x-x+2+4x+4-3x-6}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
Q = \(\frac{x^2-2x}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{x}{x+2}\)
b) ĐKXĐ P: x - 3 \(\ne\)0 => x \(\ne\)3
Ta có: P = 3 => \(\frac{x+2}{x-3}=3\)
=> x + 2 = 3(x - 3)
=> x + 2 = 3x - 9
=> x - 3x = -9 - 2
=> -2x = -11
=> x = 11/2 (tm)
Với x = 11/2 thay vào Q => Q = \(\frac{\frac{11}{2}}{\frac{11}{2}+2}=\frac{11}{15}\)
c) Với x \(\ne\)\(\pm\)2; x \(\ne\)3
Ta có: M = PQ = \(\frac{x+2}{x-3}\cdot\frac{x}{x+2}=\frac{x}{x-3}=\frac{x-3+3}{x-3}=1+\frac{3}{x-3}\)
Để M \(\in\)Z <=> 3 \(⋮\)x - 3
=> x - 3 \(\in\)Ư(3) = {1; -1; 3; -3}
Lập bảng:
| x - 3 | 1 | -1 | 3 | -3 |
| x | 4 | 2 (ktm) | 6 | 0 |
Vậy ...
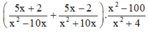
+ Tìm điều kiện xác định:
Biểu thức xác định khi tất cả các phân thức đều xác định.
⇔ x(x – 10) ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ 0 và x – 10 ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ 0 và x ≠ 10
⇔ x(x + 10) ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ 0 và x + 10 ≠ 0
⇔ x ≠ 0 và x ≠ -10
Vậy điều kiện xác định của biểu thức là x ≠ 0 và x ≠ ±10
+ Rút gọn biểu thức:
+ Tại x = 20040, giá trị biểu thức bằng