
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



Câu 1:
Để ý rằng \((2-\sqrt{3})(2+\sqrt{3})=1\) nên nếu đặt
\(\sqrt{2+\sqrt{3}}=a\Rightarrow \sqrt{2-\sqrt{3}}=\frac{1}{a}\)
PT đã cho tương đương với:
\(ma^x+\frac{1}{a^x}=4\)
\(\Leftrightarrow ma^{2x}-4a^x+1=0\) (*)
Để pt có hai nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1,x_2\) thì pt trên phải có dạng pt bậc 2, tức m khác 0
\(\Delta'=4-m>0\Leftrightarrow m< 4\)
Áp dụng hệ thức Viete, với $x_1,x_2$ là hai nghiệm của pt (*)
\(\left\{\begin{matrix} a^{x_1}+a^{x_2}=\frac{4}{m}\\ a^{x_1}.a^{x_2}=\frac{1}{m}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow \left\{\begin{matrix} a^{x_2}(a^{x_1-x_2}+1)=\frac{4}{m}\\ a^{x_1+x_2}=\frac{1}{m}(1)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay \(x_1-x_2=\log_{2+\sqrt{3}}3=\log_{a^2}3\) :
\(\Rightarrow a^{x_2}(a^{\log_{a^2}3}+1)=\frac{4}{m}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a^{x_2}(\sqrt{3}+1)=\frac{4}{m}\Rightarrow a^{x_2}=\frac{4}{m(\sqrt{3}+1)}\) (2)
\(a^{x_1}=a^{\log_{a^2}3+x_2}=a^{x_2}.a^{\log_{a^2}3}=a^{x_2}.\sqrt{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow a^{x_1}=\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{m(\sqrt{3}+1)}\) (3)
Từ \((1),(2),(3)\Rightarrow \frac{4}{m(\sqrt{3}+1)}.\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{m(\sqrt{3}+1)}=\frac{1}{m}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow \frac{16\sqrt{3}}{m^2(\sqrt{3}+1)^2}=\frac{1}{m}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=\frac{16\sqrt{3}}{(\sqrt{3}+1)^2}=-24+16\sqrt{3}\) (thỏa mãn)
Câu 2:
Nếu \(1> x>0\)
\(2017^{x^3}>2017^0\Leftrightarrow 2017^{x^3}>1\)
\(0< x< 1\Rightarrow \frac{1}{x^5}>1\)
\(\Rightarrow 2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}> 2017^1\Leftrightarrow 2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}>2017\)
\(\Rightarrow 2017^{x^3}+2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}> 1+2017=2018\) (đpcm)
Nếu \(x>1\)
\(2017^{x^3}> 2017^{1}\Leftrightarrow 2017^{x^3}>2017 \)
\(\frac{1}{x^5}>0\Rightarrow 2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}>2017^0\Leftrightarrow 2017^{\frac{1}{5}}>1\)
\(\Rightarrow 2017^{x^3}+2017^{\frac{1}{x^5}}>2018\) (đpcm)

\(I=\int\dfrac{x^3dx}{\left(x^8-4\right)^2}\)
Đặt \(x^4=t\Rightarrow x^3dx=\dfrac{1}{4}dt\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{1}{4}\int\dfrac{dt}{\left(t^2-2\right)^2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\int\dfrac{dt}{\left(t-\sqrt{2}\right)^2\left(t+\sqrt{2}\right)^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{32}\int\left(\dfrac{1}{t-\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{1}{t+\sqrt{2}}\right)^2dt=\dfrac{1}{32}\int\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(t-\sqrt{2}\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\left(t+\sqrt{2}\right)^2}-\dfrac{2}{\left(t+\sqrt{2}\right)\left(t-\sqrt{2}\right)}\right)dt\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{32}\int\left(\dfrac{1}{\left(t-\sqrt{2}\right)^2}+\dfrac{1}{\left(t+\sqrt{2}\right)^2}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\dfrac{1}{t-\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{1}{t+\sqrt{2}}\right)\right)dt\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{32}\left(\dfrac{-1}{t-\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{1}{t+\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}ln\left|\dfrac{t-\sqrt{2}}{t+\sqrt{2}}\right|\right)+C\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{32}\left(\dfrac{-1}{x^4-\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{1}{x^4+\sqrt{2}}-\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}ln\left|\dfrac{x^4-\sqrt{2}}{x^4+\sqrt{2}}\right|\right)+C\)
2/ \(I=\int\dfrac{\left(2x+1\right)dx}{\left(x^2+x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+3\right)}=\dfrac{1}{4}\int\left(\dfrac{1}{x^2+x-1}-\dfrac{1}{x^2+x+3}\right)\left(2x+1\right)dx\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\int\left(\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+x-1}-\dfrac{2x+1}{x^2+x+3}\right)dx\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\int\dfrac{d\left(x^2+x-1\right)}{x^2+x-1}-\int\dfrac{d\left(x^2+x+3\right)}{x^2+x+3}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}ln\left|\dfrac{x^2+x-1}{x^2+x+3}\right|+C\)
3/ Đặt \(\sqrt[3]{x}=t\Rightarrow x=t^3\Rightarrow dx=3t^2dt\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int\dfrac{3t^2.sint.dt}{t^2}=3\int sint.dt=-3cost+C=-3cos\left(\sqrt[3]{x}\right)+C\)
4/ \(I=\int\dfrac{dx}{1+cos^2x}=\int\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}dx}{\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}+1}\)
Đặt \(t=tanx\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}dt=\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}dx\\\dfrac{1}{cos^2x}=1+tan^2x=1+t^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int\dfrac{dt}{1+t^2+1}=\int\dfrac{dt}{t^2+2}=\dfrac{1}{2}\int\dfrac{dt}{\left(\dfrac{t}{\sqrt{2}}\right)^2+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{2}.\sqrt{2}.arctan\left(\dfrac{t}{\sqrt{2}}\right)+C=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}arctan\left(\dfrac{tanx}{\sqrt{2}}\right)+C\)
5/ \(I=\int\dfrac{sinx+cosx}{4+2sinx.cosx-sin^2x-cos^2x}dx=\int\dfrac{sinx+cosx}{4-\left(sinx-cosx\right)^2}dx\)
Đặt \(sinx-cosx=t\Rightarrow\left(cosx+sinx\right)dx=dt\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int\dfrac{dt}{4-t^2}=-\int\dfrac{dt}{\left(t-2\right)\left(t+2\right)}=\dfrac{1}{4}\int\left(\dfrac{1}{t+2}-\dfrac{1}{t-2}\right)dt\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{4}ln\left|\dfrac{t+2}{t-2}\right|+C=\dfrac{1}{4}ln\left|\dfrac{sinx-cosx+2}{sinx-cosx-2}\right|+C\)
Ơ bài 1 nhầm số 4 thành số 2 rồi, bạn sửa lại 1 chút nhé :D
Còn 1 cách làm khác nữa là lượng giác hóa
Đặt \(x^4=2sint\Rightarrow x^3dx=\dfrac{1}{2}cost.dt\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{1}{2}\int\dfrac{cost.dt}{\left(4sin^2t-4\right)^2}=\dfrac{1}{32}\int\dfrac{cost.dt}{cos^4t}=\dfrac{1}{32}\int\dfrac{dt}{cos^3t}\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=\dfrac{1}{cost}\\dv=\dfrac{dt}{cos^2t}\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=\dfrac{sint.dt}{cos^2t}\\v=tant\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow32I=\dfrac{tant}{cost}-\int\dfrac{tant.sint.dt}{cos^2t}=\dfrac{sint}{cos^2t}-\int\dfrac{sin^2t.dt}{cos^3t}\)
\(=\dfrac{sint}{1-sin^2t}-\int\dfrac{1-cos^2t}{cos^3t}dt=\dfrac{sint}{1-sin^2t}-\int\dfrac{dt}{cos^3t}+\int\dfrac{1}{cosx}dx\)
Chú ý rằng \(\int\dfrac{dt}{cos^3t}=32I\)
\(\Rightarrow32I=\dfrac{sint}{1-sin^2t}-32I+\int\dfrac{cost.dt}{cos^2t}\)
\(\Rightarrow64I=\dfrac{sint}{1-sin^2t}-\int\dfrac{d\left(sint\right)}{sin^2t-1}=\dfrac{sint}{1-sin^2t}-\dfrac{1}{2}ln\left|\dfrac{sint-1}{sint+1}\right|+C\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\dfrac{1}{64}\left(\dfrac{2x^4}{4-x^8}-\dfrac{1}{2}ln\left|\dfrac{x^4-2}{x^4+2}\right|\right)+C\)




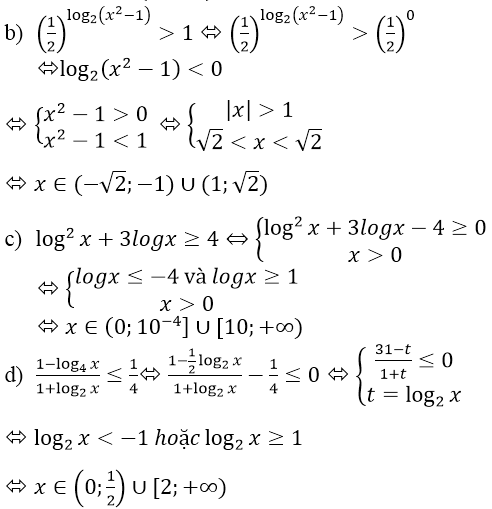



\(\Leftrightarrow1+8^{\dfrac{x}{2}}=9^{\dfrac{x}{2}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{1}{9}\right)^{\dfrac{x}{2}}+\left(\dfrac{8}{9}\right)^{\dfrac{x}{2}}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{1}{9}\right)^{\dfrac{x}{2}}+\left(\dfrac{8}{9}\right)^{\dfrac{x}{2}}-1=0\)
Nhận thấy \(\dfrac{x}{2}=1\Leftrightarrow x=2\) là 1 nghiệm của pt đã cho
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=\left(\dfrac{1}{9}\right)^{\dfrac{x}{2}}+\left(\dfrac{8}{9}\right)^{\dfrac{x}{2}}-1\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}.\left(\dfrac{1}{9}\right)^{\dfrac{x}{2}}.ln\left(\dfrac{1}{9}\right)+\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{8}{9}\right)^{\dfrac{x}{2}}.ln\left(\dfrac{8}{9}\right)< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) nghịch biến trên R
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) có tối đa 1 nghiệm
\(\Rightarrow x=2\) là nghiệm duy nhất của pt đã cho