
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



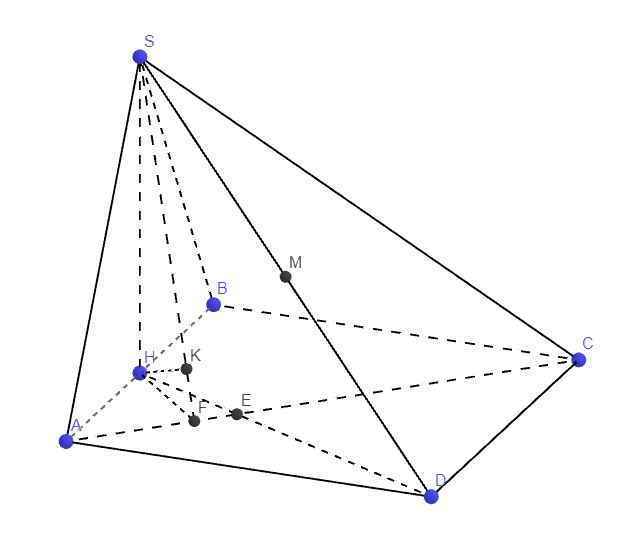
Gọi H là trung điểm AB, có lẽ từ 2 câu trên ta đã phải chứng minh được \(SH\perp\left(ABCD\right)\)
Do \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}DM\cap\left(SAC\right)=S\\MS=\dfrac{1}{2}DS\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow d\left(M;\left(SAC\right)\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}d\left(D;\left(SAC\right)\right)\)
Gọi E là giao điểm AC và DH
Talet: \(\dfrac{HE}{DE}=\dfrac{AH}{DC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\Rightarrow HE=\dfrac{1}{2}DE\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}DH\cap\left(SAC\right)=E\\HE=\dfrac{1}{2}DE\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow D\left(H;\left(SAC\right)\right)=\dfrac{1}{2}d\left(D;\left(SAC\right)\right)=d\left(M;\left(SAC\right)\right)\)
Từ H kẻ HF vuông góc AC (F thuộc AC), từ H kẻ \(HK\perp SF\)
\(\Rightarrow HK\perp\left(SAC\right)\Rightarrow HK=d\left(H;\left(SAC\right)\right)\)
ABCD là hình vuông \(\Rightarrow\widehat{HAF}=45^0\Rightarrow HF=AH.sin45^0=\dfrac{a\sqrt{2}}{4}\)
\(SH=\dfrac{a\sqrt{3}}{2}\), hệ thức lượng:
\(HK=\dfrac{SH.HF}{\sqrt{SH^2+HF^2}}=\dfrac{a\sqrt{21}}{14}\)
\(\Rightarrow d\left(M;\left(SAC\right)\right)=\dfrac{a\sqrt{21}}{14}\)

a.
\(sin\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{\pi}{8}+k\pi\) (1)
\(-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\le x\le\dfrac{7\pi}{3}\Rightarrow-\dfrac{\pi}{3}\le-\dfrac{\pi}{8}+k\pi\le\dfrac{7\pi}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow-\dfrac{5}{24}\le k\le\dfrac{59}{24}\Rightarrow k=\left\{0;1;2\right\}\)
Thế vào (1) \(\Rightarrow x=\left\{-\dfrac{\pi}{8};\dfrac{7\pi}{8};\dfrac{15\pi}{8}\right\}\)


1.
\(\lim\left(\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}-3^n+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\lim\left(\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}-3^n\right)\left(\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}+3^n\right)}{\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}+3^n}+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\lim\left(\dfrac{-2.3^n}{\sqrt{9^n-2.3^n}+3^n}+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\lim\left(\dfrac{-2.3^n}{3^n\left(\sqrt{1-\dfrac{2}{3^n}}+1\right)}+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\lim\left(\dfrac{-2}{\sqrt{1-\dfrac{2}{3^n}}+1}+\dfrac{1}{2021}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{-2}{1+1}+\dfrac{1}{2021}=-\dfrac{2020}{2021}\)
2.
\(AP=4PB=4\left(AB-AP\right)=4AB-4AP\)
\(\Rightarrow5AP=4AB\Rightarrow AP=\dfrac{4}{5}AB\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AP}=\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{AB}\)
\(CD=5CQ=5\left(CD-DQ\right)\Rightarrow5DQ=4CD\Rightarrow DQ=\dfrac{4}{5}CD\)
\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{DQ}=-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CD}\)
Ta có:
\(\overrightarrow{PQ}=\overrightarrow{PA}+\overrightarrow{AD}+\overrightarrow{DQ}=-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CD}\)
\(=-\dfrac{4}{5}\left(\overrightarrow{AD}+\overrightarrow{DB}\right)+\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CD}=-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{DB}+\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CD}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\left(\overrightarrow{CD}+\overrightarrow{DB}\right)=\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{AD}-\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{CB}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{5}\overrightarrow{AD}+\dfrac{4}{5}\overrightarrow{BC}\)
Mà \(\overrightarrow{AD};\overrightarrow{BC}\) không cùng phương\(\Rightarrow\overrightarrow{AD};\overrightarrow{BC};\overrightarrow{PQ}\) đồng phẳng


1.
\(u_{n+1}=4u_n+3.4^n\)
\(\Leftrightarrow u_{n+1}-\dfrac{3}{4}\left(n+1\right).4^{n+1}=4\left[u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n\right]\)
Đặt \(u_n-\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n=v_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}v_1=2-\dfrac{3}{4}.4=-1\\v_{n+1}=4v_n\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow v_n=-1.4^{n-1}\)
\(\Rightarrow u_n=\dfrac{3}{4}n.4^n-4^{n-1}=\left(3n-1\right)4^{n-1}\)
2.
\(a_n=\dfrac{a_{n-1}}{2n.a_{n-1}+1}\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=2n+\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=\dfrac{1}{a_{n-1}}-\left(n-1\right)^2-\left(n-1\right)\)
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{a_n}-n^2-n=b_n\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b_1=2-1-1=0\\b_n=b_{n-1}=...=b_1=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{a_n}=n^2+n\Rightarrow a_n=\dfrac{1}{n^2+n}\)

c.
\(\Leftrightarrow sin4x=sin\left(3x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=3x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\4x=\dfrac{3\pi}{2}-3x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}+k2\pi\\x=\dfrac{3\pi}{14}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d.
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(2x+30^0\right)=sin\left(30^0+x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x+30^0=30^0+x+k360^0\\2x+30^0=150^0-x+k360^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=k360^0\\x=40^0+k120^0\end{matrix}\right.\)
e.
\(\Leftrightarrow cos3x=-sinx\)
\(\Leftrightarrow cos3x=cos\left(\dfrac{\pi}{2}+x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}3x=\dfrac{\pi}{2}+x+k2\pi\\3x=-\dfrac{\pi}{2}-x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{4}+k\pi\\x=-\dfrac{\pi}{8}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
f.
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\left(sin2x+cos5x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow sin\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)\left(sin2x-sin\left(5x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}sin\left(2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}\right)=0\\sin\left(5x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}\right)=sin2x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-\dfrac{\pi}{4}=k\pi\\5x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}=2x+k2\pi\\5x-\dfrac{\pi}{2}=\pi-2x+k2\pi\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{\pi}{8}+\dfrac{k\pi}{2}\\x=\dfrac{\pi}{6}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{3}\\x=\dfrac{3\pi}{14}+\dfrac{k2\pi}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)








Tham khảo:
CHÚC BẠN HỌC TỐT NHA
9.
Gọi D là trung điểm BC \(\Rightarrow AD\perp BC\) (do tam giác ABC đều)
Mặt khác \(SA\perp\left(ABC\right)\Rightarrow SA\perp BC\)
\(\Rightarrow BC\perp\left(SAD\right)\)
Mà BC là giao tuyến (SAB) và (SBC)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{SDA}\) là góc giữa (ABC) và (SBC)
\(AD=\dfrac{AB\sqrt{3}}{2}=\dfrac{a\sqrt{3}}{2}\) (trung tuyến tam giác đều)
\(\Rightarrow tan\widehat{SDA}=\dfrac{SA}{AD}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{SDA}=30^0\)
b.
Câu b nhìn không rõ, đề yêu cầu tính diện tích tam giác SBC đúng không nhỉ?
Từ câu a ta có \(BC\perp\left(SAD\right)\Rightarrow SD\perp BC\)
Pitago tam giác SAD: \(SD=\sqrt{SA^2+AD^2}=a\)
\(\Rightarrow S_{\Delta SBC}=\dfrac{1}{2}SD.BC=\dfrac{a^2}{2}\)