
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-2y=4\\2x+y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3x-2y=4\\4x+2y=10\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x=-6\\2x+y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=6\\y=5-2x=5-12=-7\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-y=m\left(1\right)\\2x+y=4\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow x=y+m\)
Thay \(x=y+m\) vào (2) ta được:
\(2\left(y+m\right)+y=4\\ \Leftrightarrow2y+2m+y=4\\ \Leftrightarrow3y=4-2m\\ \Leftrightarrow y=\dfrac{4-2m}{3}\)
Thay \(y=\dfrac{4-2m}{3}\) vào (1) ta được:
\(x-\dfrac{4-2m}{3}=m\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3x}{3}-\dfrac{4-2m}{3}=\dfrac{3m}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow3x-4+2m=3m\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=m+4\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{m+4}{3}\)
Vậy hpt có nghiệm là \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(\dfrac{m+4}{3};\dfrac{4-2m}{3}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=x-m\\2x+y=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=x-m\\2x+x-m=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=x-m\\3x=m+4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=x-m\\x=\dfrac{m+4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{m+4}{3}\\y=\dfrac{-2m+4}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a ) \(\begin{cases}3x-y=5\\5x+2y=23\end{cases}\)
Từ phương trình \(\left(1\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow y=3x-5\) \(\left(3\right)\)
Thế \(\left(3\right)\) vào phương trình \(\left(2\right)\) : \(5x+2\left(3x-5\right)=23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x+6x-10=23\Leftrightarrow11x=33\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
Từ đó \(y=3.3-5=4\)
Vậy hệ có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(3;4\right)\)
b ) \(\begin{cases}3x+5y=1\\2x-y=-8\end{cases}\)
Từ hệ phương trình \(\left(2\right)\) \(\Leftrightarrow y=3x+8\)
Thế (3) vào (1): \(3x+5\left(2x+8\right)=1\Leftrightarrow3x+10x+40=1\Leftrightarrow13x=-39\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=-3\)
Từ đó \(y=2\left(-3\right)+8=2\)
Vậy hệ có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(-3;2\right)\)

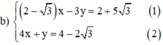
Từ (2) ta rút ra được y = -4x + 4 - 2 √3 (*)
Thế (*) vào phương trình (1) ta được:
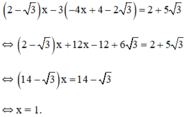
Thay x = 1 vào (*) ta được y = -4.1 + 4 - 2√3 = -2√3
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (1; -2√3)
Cách 2
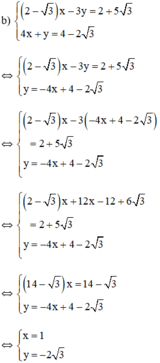
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (1; -2√3)

\(1,\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2y+4\\-4y-8+5y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2\cdot5+4=14\\y=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ 2,\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5x-30+6x=3\\y=10-2x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\y=4\end{matrix}\right.\\ 3,\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=4-2y\\6y-12+y=7\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{10}{7}\\y=\dfrac{19}{7}\end{matrix}\right.\)

Đáp án D
Ta có:
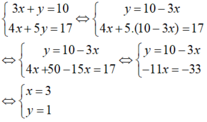
Vậy nghiệm của hệ phương trình đã cho là: (3; 1).

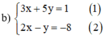
Từ (2) ta rút ra được y = 2x + 8 (*)
Thế (*) vào phương trình (1) ta được :
3x + 5(2x + 8) = 1 ⇔ 3x + 10x + 40 = 1 ⇔ 13x = -39 ⇔ x = -3.
Thay x = - 3 vào (*) ta được y = 2.(-3) + 8 = 2.
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (-3 ; 2).

Cách 1
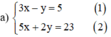
Từ (1) ta rút ra được y = 3x – 5 (*)
Thế (*) vào phương trình (2) ta được :
5x + 2(3x – 5) = 23 ⇔ 5x + 6x – 10 = 23 ⇔ 11x = 33 ⇔ x = 3.
Thay x = 3 vào (*) ta được y = 3.3 – 5 = 4.
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm duy nhất (3 ; 4).
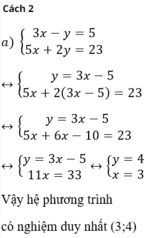
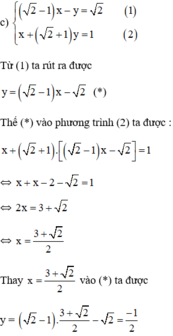
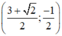

2x+y=-4
\(\Leftrightarrow2x=-4-y\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{-y-4}{2}\)
Ta có: 3x+|y|=-1
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-3y-12}{2}+\left|y\right|=-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|y\right|=\dfrac{-2+3y+12}{2}=\dfrac{3y+10}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{3}{2}y+5\left(y\ge0\right)\\y=-\dfrac{3}{2}y+5\left(y< 0\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{-1}{2}y=5\\\dfrac{5}{2}y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow y\in\varnothing\)
x=-1 ,y=-2