Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\Delta=\left[-2\left(m+1\right)\right]^2-4\left(m^2-3\right)\)
\(=4m^2+8m+4-4m^2+12=8m+16\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm thì 8m+16>=0
hay m>=-2
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et, ta được:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=m^2-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Theo đề, ta có: \(x_1^2+x_2^2+1=3x_1x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-5x_1x_2+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m+2\right)^2-5\left(m^2-3\right)+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2+8m+4-5m^2+15+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-m^2+8m+20=0\)
=>(m-10)(m+2)=0
=>m=10 hoặc m=-2
a, \(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(m^2-3\right)=m^2+2m+1-m^2+3=2m+4\)
Để pt có 2 nghiệm x1 ; x2 khi \(\Delta'\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge-2\)
Theo Vi et \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m+2\\x_1x_2=m^2-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có : \(\dfrac{x_1}{x_2}+\dfrac{x_2}{x_1}+\dfrac{1}{x_1x_2}=3\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2+1}{x_1x_2}=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4\left(m^2+2m+1\right)-2\left(m^2-3\right)+1}{m^2-3}=3\)
\(\Rightarrow2m^2+8m+11=3m^2-9\Leftrightarrow m^2-8m-20=0\Leftrightarrow m=10;m=-2\)(tm)

b) phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1-m^2-3m+m+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le1\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_1x_2+x_2^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=1\)
Theo viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m-1\right)^2\right]-2\left(m+3\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-2m-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-10m-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(ktm\right)\\m_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)

Cách ngắn ngọn nhất:
\(x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+4m=0\left(1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-2mx+4m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)-2m\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)\left(x-2m\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Phương trình (1) có 2 nghiệm là \(x=2;x=2m\). Mặt khác phương trình (1) cũng có 2 nghiệm là x1, x2 nên ta chia làm 2 trường hợp:
TH1: \(x_1=2;x_2=2m\).
Có \(2x_1-x_2=-2\Rightarrow2.2-2m=-2\Leftrightarrow m=3\)
TH2: \(x_1=2m;x_2=2\)
Có \(2x_1-x_2=-2\Rightarrow2.\left(2m\right)-2=-2\Leftrightarrow m=0\)
Vậy m=0 hay m=3

Cách ngắn ngọn nhất:
x2−2(m+1)x+4m=0(1)�2−2(�+1)�+4�=0(1)
⇔x2−2x−2mx+4m=0⇔�2−2�−2��+4�=0
⇔x(x−2)−2m(x−2)=0⇔�(�−2)−2�(�−2)=0
⇔(x−2)(x−2m)=0⇔(�−2)(�−2�)=0
⇔[x=2x=2m⇔[�=2�=2�
Phương trình (1) có 2 nghiệm là x=2;x=2m�=2;�=2�. Mặt khác phương trình (1) cũng có 2 nghiệm là x1, x2 nên ta chia làm 2 trường hợp:
TH1: x1=2;x2=2m�1=2;�2=2�.
Có 2x1−x2=−2⇒2.2−2m=−2⇔m=32�1−�2=−2⇒2.2−2�=−2⇔�=3
TH2: x1=2m;x2=2�1=2�;�2=2
Có 2x1−x2=−2⇒2.(2m)−2=−2⇔m=02�1−�2=−2⇒2.(2�)−2=−2⇔�=0
Vậy m=0 hay m=3

\(\text{Δ}=\left[-\left(m+1\right)\right]^2-4\cdot1\cdot m\)
\(=\left(m+1\right)^2-4m\)
\(=\left(m-1\right)^2>=0\forall m\)
=>Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm
Theo Vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=m+1\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=\left(x_1-1\right)\left(x_2-1\right)-x_1-x_2+5\)
=>\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=x_1x_2-2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+6\)
=>\(\left(m+1\right)^2-2m=m-2\left(m+1\right)+6\)
=>\(m^2+1=m-2m-2+6\)
=>\(m^2+1=-m+4\)
=>\(m^2+m-3=0\)
=>\(m=\dfrac{-1\pm\sqrt{13}}{2}\)
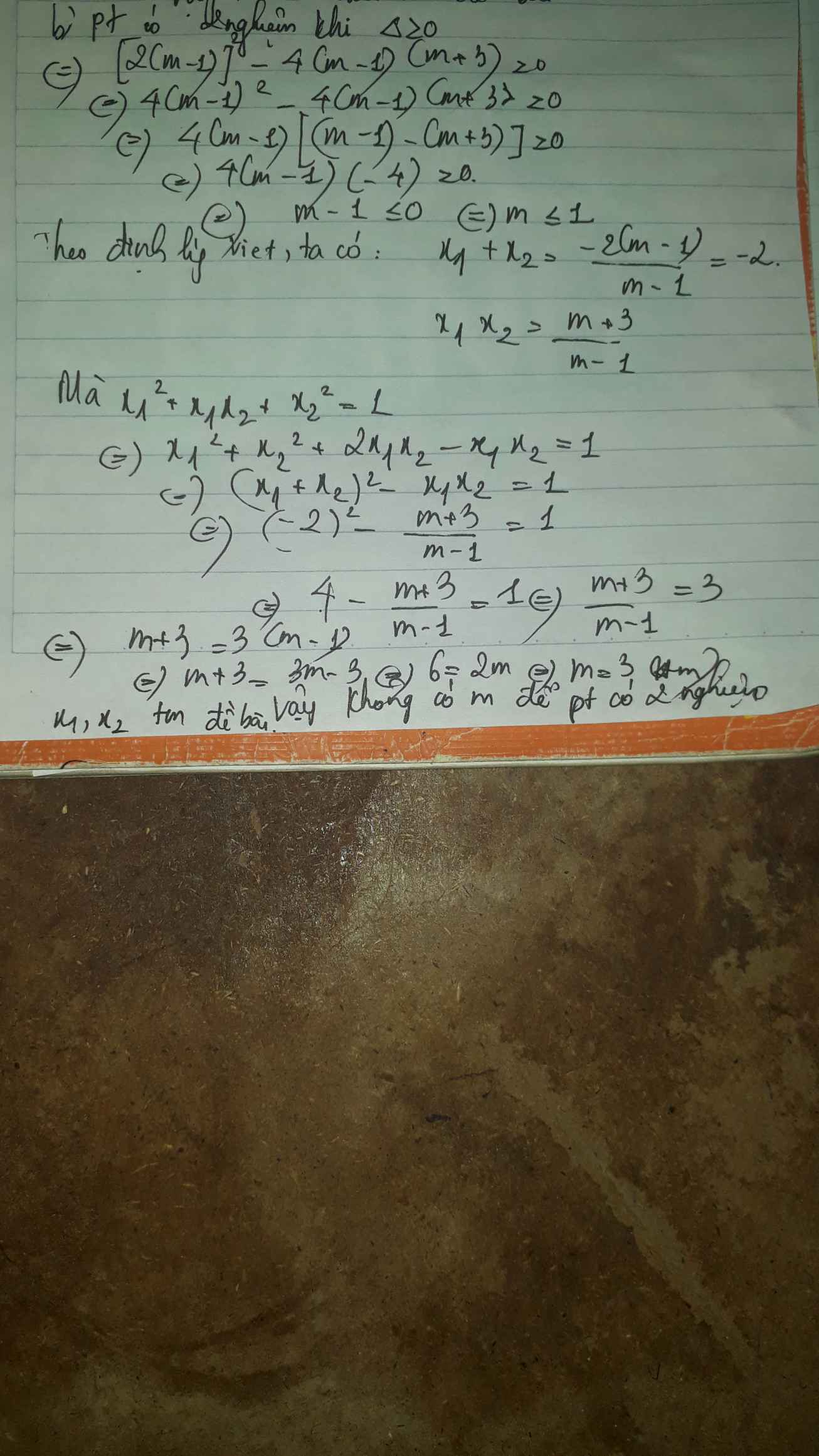
\(\Delta'=\left[-\left(m+1\right)\right]^2-\left(m^2+m\right)=m^2+2m+1-m^2-m\)
\(=m+1\)
pt có nghiệm x1,x2 \(< =>m+1\ge0< =>m\ge-1\)
vi ét \(=>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x1+x2=2m+2\\x1x2=m^2+m\end{matrix}\right.\)
a,\(=>2m+2=m^2+m< =>m^2-m-2=0\)
\(a-b+c=0=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}m1=-1\\m2=2\end{matrix}\right.\left(tm\right)\)
b,\(< =>3\left(2m+2\right)-2\left(m^2+m\right)-1=0\)
\(< =>-2m^2+4m+5=0\)
\(ac< 0\) pt có 2 nghiệm pbiet \(=>\left[{}\begin{matrix}m1=...\\m2=...\end{matrix}\right.\) thay số vào tính m1,m2 đối chiếu đk