Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

ính giá trị của các biểu thức sau:
A=827−(349+427)A=827−(349+427)
B=(1029+235)−629B=(1029+235)−629
Giải:
A=827−(349+427)A=827−(349+427)
=587−(319+307)=58−307−319=4−319=587−(319+307)=58−307−319=4−319
= 36−319=5936−319=59
B=(1029+235)−629B=(1029+235)−629
=1029−629+235=4+235=635
ính giá trị của các biểu thức sau:
A
=
8
2
7
−
(
3
4
9
+
4
2
7
)
A=827−(349+427)
B
=
(
10
2
9
+
2
3
5
)
−
6
2
9
B=(1029+235)−629
Giải:
A
=
8
2
7
−
(
3
4
9
+
4
2
7
)
A=827−(349+427)
=
58
7
−
(
31
9
+
30
7
)
=
58
−
30
7
−
31
9
=
4
−
31
9
=587−(319+307)=58−307−319=4−319
=
36
−
31
9
=
5
9
36−319=59
B
=
(
10
2
9
+
2
3
5
)
−
6
2
9
B=(1029+235)−629
=
10
2
9
−
6
2
9
+
2
3
5
=
4
+
2
3
5
=
6
3
5
Xem thêm tại: http://loigiaihay.com/bai-100-trang-47-sgk-toan-6-tap-2-c41a24737.html#ixzz4eUGN0ooE

\(A=\dfrac{6}{7}+\dfrac{1}{7}.\dfrac{2}{7}+\dfrac{1}{7}.\dfrac{5}{7}.\)
\(A=\dfrac{6}{7}+\dfrac{1}{7}\left(\dfrac{2}{7}+\dfrac{5}{7}\right).\)
\(A=\dfrac{6}{7}+\dfrac{1}{7}.1.\)
\(A=\dfrac{6}{7}+\dfrac{1}{7}=1.\)
Vậy \(A=1.\)
\(B=\dfrac{40}{9}.\dfrac{13}{3}-\dfrac{4}{3}.\dfrac{40}{9}.\)
\(B=\dfrac{4}{9}.\dfrac{13}{3}-\dfrac{4}{9}.\dfrac{40}{3}.\)
\(B=\dfrac{4}{9}\left(\dfrac{13}{3}-\dfrac{40}{3}\right).\)
\(B=\dfrac{4}{9}.\left(-9\right).\)
\(B=-4.\)
Vậy \(B=-4.\)

Áp dụng tính chất phân phối, rồi tính giá trị biểu thức.
Chẳng hạn,
Với , thì
ĐS. ; C = 0.
Xem thêm tại: http://loigiaihay.com/bai-77-trang-39-phan-so-hoc-sgk-toan-6-tap-2-c41a5943.html#ixzz4eU1fQCGw

\(A=11\dfrac{3}{13}-\left(2\dfrac{4}{7}+5\dfrac{3}{13}\right)\)
\(A=11\dfrac{3}{13}-5\dfrac{3}{13}-2\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\(A=6-2\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\(A=5\dfrac{7}{7}-2\dfrac{4}{7}\)
\(A=3\dfrac{3}{7}\)
\(B=\left(6\dfrac{4}{9}+3\dfrac{7}{11}\right)-4\dfrac{4}{9}\)
\(B=\left(6\dfrac{4}{9}-4\dfrac{4}{9}\right)+3\dfrac{7}{11}\)
\(B=2+3\dfrac{7}{11}\)
\(B=5\dfrac{7}{11}\)
\(C=\dfrac{-5}{7}.\dfrac{2}{11}+\dfrac{-5}{7}-\dfrac{9}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{-5}{7}.\left(\dfrac{2}{11}+1\right)-\dfrac{9}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{-5}{7}.\dfrac{13}{11}-\dfrac{9}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{-65}{77}-\dfrac{9}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{4}{11}+1\dfrac{5}{7}\)
\(C=\dfrac{160}{11}\)
\(D=0,7.2\dfrac{2}{3}.20.0,375.\dfrac{5}{28}\)
\(D=\dfrac{7}{10}.\dfrac{8}{3}.20.\dfrac{375}{1000}.\dfrac{5}{28}\)
\(D=\dfrac{7}{28}=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
\(E=\left(-6,17+3\dfrac{5}{9}-2\dfrac{36}{97}\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{3}-0,25-\dfrac{1}{12}\right)\)
\(E=\left(-6,17+3\dfrac{5}{9}-2\dfrac{36}{97}\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{3}-\dfrac{1}{4}-\dfrac{1}{12}\right)\)
\(E=\left(-6,17+3\dfrac{5}{9}-2\dfrac{36}{97}\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{12}-\dfrac{1}{12}\right)\)
\(E=\left(-6,17+3\dfrac{5}{9}-2\dfrac{36}{97}\right).0\)
\(\Rightarrow E=0\)

Bài 2:
a: Để A là phân số thì x+6<>0
hay x<>-6
b: Để A là sốnguyen thì \(x+6-13⋮x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+6\in\left\{1;-1;13;-13\right\}\)
hay \(x\in\left\{-5;-7;7;-19\right\}\)

Bài 1:
a: =>13x+8=9x+20
=>4x=12
hay x=3
b: \(\Leftrightarrow5x-7=-8-11-3x\)
=>5x-7=-3x-19
=>8x=-12
hay x=-3/2
c: \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}12x-7=5\\12x-7=-5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x=\dfrac{1}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
e: =>3x+1=-5
=>3x=-6
hay x=-2

Gợi ý: Sử dụng tính chất phân phối của phép nhân đối với phép cộng để nhóm thừa số chung ra ngoài.

a)<=>\(\dfrac{\left(2x-3\right).2}{6}-\dfrac{3.3}{6}=\dfrac{5-2x}{6}-\dfrac{1.3}{6}\)
<=>\(\dfrac{4x-6}{6}-\dfrac{9}{6}=\dfrac{5-2x}{6}-\dfrac{3}{6}\)
<=>\(\dfrac{4x-6}{6}-\dfrac{9}{6}-\dfrac{5-2x}{6}+\dfrac{3}{6}=0\)
<=>\(\dfrac{4x-6-9-5+2x+3}{6}=\dfrac{4x-17}{6}=0\)
<=>\(4x-17=0\)
<=>\(4x=17\)<=>\(x=\dfrac{17}{4}\)
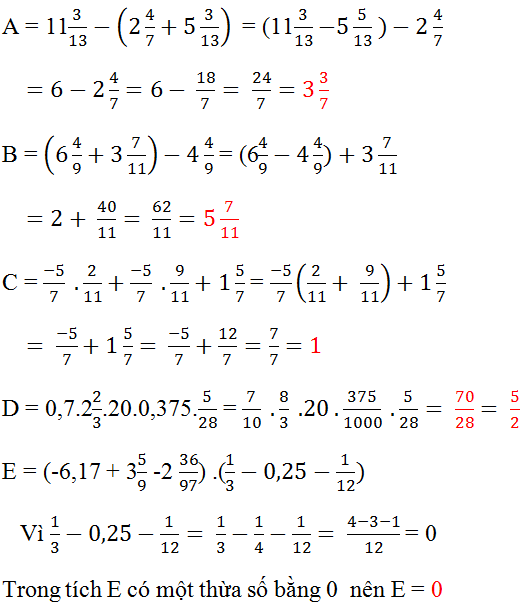
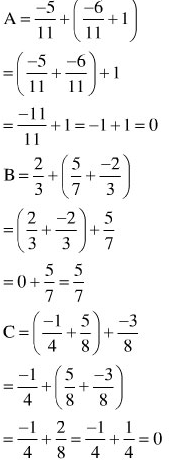
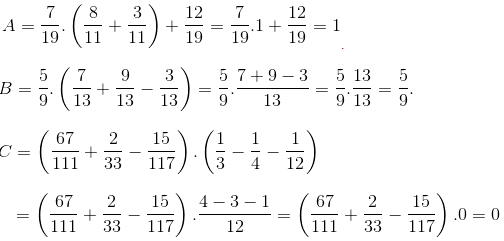

\(A=\dfrac{1}{3}x+x-\dfrac{4}{3}x=0\)