Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: \(y=-x^3-\left(m+1\right)x^2+3\left(m+1\right)x\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2-\left(m+1\right)\cdot2x+3\left(m+1\right)\)
=>\(y'=-3x^2+x\cdot\left(-2m-2\right)+\left(3m+3\right)\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(-2m-2\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-3\right)\left(3m+3\right)< =0\\-3< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(4m^2+8m+4+12\left(3m+3\right)< =0\)
=>\(4m^2+8m+4+36m+36< =0\)
=>\(4m^2+44m+40< =0\)
=>\(m^2+11m+10< =0\)
=>\(\left(m+1\right)\left(m+10\right)< =0\)
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1>=0\\m+10< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=-1\\m< =-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m+1< =0\\m+10>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< =-1\\m>=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-10<=m<=-1
b: \(y=-\dfrac{1}{3}x^3+mx^2-\left(2m+3\right)x\)
=>\(y'=-\dfrac{1}{3}\cdot3x^2+m\cdot2x-\left(2m+3\right)\)
=>\(y'=-x^2+2m\cdot x-\left(2m+3\right)\)
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên R thì \(y'< =0\forall x\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\text{Δ}< =0\\a< 0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1< 0\\\left(2m\right)^2-4\cdot\left(-1\right)\cdot\left(-2m-3\right)< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(4m^2+4\left(-2m-3\right)< =0\)
=>\(m^2-2m-3< =0\)
=>(m-3)(m+1)<=0
TH1: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3>=0\\m+1< =0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>=3\\m< =-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(m\in\varnothing\)
TH2: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-3< =0\\m+1>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< =3\\m>=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-1<=m<=3

1: TXĐ: D=R\{3}
\(y=\dfrac{x^2-6x+10}{x-3}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(x^2-6x+10\right)'\left(x-3\right)-\left(x^2-6x+10\right)\left(x-3\right)'}{\left(x-3\right)^2}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{\left(2x-6\right)\left(x-3\right)-\left(x^2-6x+10\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{2x^2-12x+18-x^2+6x-10}{\left(x-3\right)^2}\)
=>\(y'=\dfrac{x^2-6x+8}{\left(x-3\right)^2}\)
Đặt y'<=0
=>\(\dfrac{x^2-6x+8}{\left(x-3\right)^2}< =0\)
=>\(x^2-6x+8< =0\)
=>(x-2)(x-4)<=0
=>2<=x<=4
Vậy: Khoảng đồng biến là [2;3) và (3;4]

- Nếu m = -1,hàm số trở thành y=-2x2-x+4 và y'=-4x-1.Dễ thấy hàm số đồng biến trên \(\left(-\infty;-\dfrac{1}{4}\right)\)và nghịch biến trên \(\left(-\dfrac{1}{4};+\infty\right)\).
- Nếu m = 1,hàm số trở thành y = -x + 4 luôn nghịch biến trên \(\left(-\infty;+\infty\right)\).Vậy m=1 là một giá trị nguyên thỏa mãn.
- Nếu m \(\ne\pm1\),ta có y'=3(m2-1)x2+2(m-1)x-1.
Để hàm số nghịch biến trên khoảng\(\left(-\infty;+\infty\right)\Leftrightarrow\)y'\(\le\)0,\(\forall x\in\)R
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m^2-1< 0\\\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2+3\left(m^2-1\right)\le0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1< m< 1\\\left(m-1\right)\left(4m+2\right)\le0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-1< m< 1\\-\dfrac{1}{2}\le m\le1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow}-\dfrac{1}{2}\le m< 1}\)
Suy ra có 1 nguyên m=0 thỏa mãn yêu cầu bài toán trong trường hợp này.
Vậy có tất cả hai giá trị nguyên m=0,m=1 thỏa mãn bài toán.

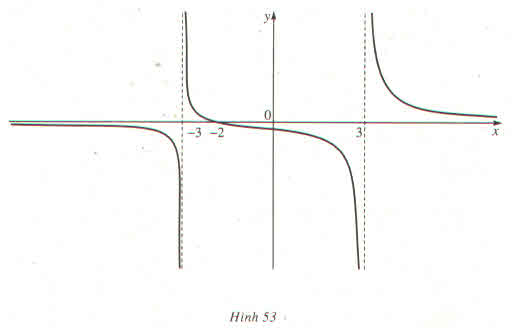
Quan sát đồ thị ta thấy x → -∞ thì f(x) → 0; khi x → 3- thì f(x) → -∞;
khi x → -3+ thì f(x) x → +∞.
b) f(x) =
=
= 0.
f(x) =
=
= -∞ vì
=
> 0 và
= -∞.
f(x) =
=
.
= +∞
vì
=
=
> 0 và
= +∞.

\(y'=x^2-2\left(m-1\right)x+3\left(m-1\right)\)
Hàm đồng biến trên khoảng đã cho khi với mọi \(x>1\) ta luôn có:
\(g\left(x\right)=x^2-2\left(m-1\right)x+3\left(m-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\min\limits_{x>1}g\left(x\right)\ge0\)
Do \(a=1>0;-\dfrac{b}{2a}=m-1\)
TH1: \(m-1\ge1\Rightarrow m\ge2\)
\(\Rightarrow g\left(x\right)_{min}=f\left(m-1\right)=\left(m-1\right)^2-2\left(m-1\right)^2+3\left(m-1\right)\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(m-1\right)\left(4-m\right)\ge0\Rightarrow1\le m\le4\Rightarrow2\le m\le4\)
TH2: \(m-1< 1\Rightarrow m< 2\Rightarrow g\left(x\right)_{min}=g\left(1\right)=m\ge0\)
Vậy \(0\le m\le4\)
help