
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 3:
\(a,ĐK:2\le x\le1+\sqrt{5}\\ PT\Leftrightarrow4+2x-x^2=x^2-4x+4\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2-6x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=3\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\\ b,ĐK:1\le x\le5\\ PT\Leftrightarrow25-x^2=x^2-2x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2-2x-24=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x+3\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-3\left(ktm\right)\\x=4\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=4\\ c,PT\Leftrightarrow3x^2-9x+1=x^2-4x+4\\ \Leftrightarrow2x^2-5x-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\left(tm\right)\\x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=3\)


a) ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le-1\\x\ge2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\sqrt{x^2-x-2}-\sqrt{x-2}=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-x-2}=\sqrt{x-2}\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-x-2=x-2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow x\left(x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\left(ktm\right)\\x=2\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(a,ĐK:x\ge2\\ PT\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-2=x-2\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-2x=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(tm\right)\\x=0\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x=2\\ b,ĐK:\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le-1\\x\ge1\end{matrix}\right.\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-1}=x^2-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-1=\left(x^2-1\right)^2\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2-1-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x-\sqrt{2}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{2}\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\left(tm\right)\\x=-1\left(tm\right)\\x=\sqrt{2}\left(tm\right)\\x=-\sqrt{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(c,ĐK:\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\le-2\\x\ge1\end{matrix}\right.\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-x}=-\sqrt{x^2+x-2}\\ \Leftrightarrow x^2-x=x^2+x-2\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x=1\left(tm\right)\)

a) Xét (O) có
\(\widehat{BAD}\) là góc nội tiếp chắn \(\stackrel\frown{BD}\)
\(\widehat{CAD}\) là góc nội tiếp chắn \(\stackrel\frown{CD}\)
mà \(\widehat{BAD}=\widehat{CAD}\)(AD là tia phân giác của \(\widehat{BAC}\))
nên \(\stackrel\frown{BD}=\stackrel\frown{CD}\)
hay BD=CD
Ta có: OB=OC(=R)
nên O nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(Tính chất đường trung trực của một đoạn thẳng)(1)
Ta có: BD=CD(cmt)
nên D nằm trên đường trung trực của BC(Tính chất đường trung trực của một đoạn thẳng)(2)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra OD là đường trung trực của BC
hay OD\(\perp\)BC(đpcm)

\(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{20}-6}{\sqrt{14-6\sqrt{5}}}-\dfrac{\sqrt{20}-\sqrt{28}}{\sqrt{12-2\sqrt{35}}}=\dfrac{-2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)}{\sqrt{\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)^2}}+\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{5}\right)}{\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{5}\right)^2}}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2\left(3-\sqrt{5}\right)}{3-\sqrt{5}}+\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{5}\right)}{\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{5}}=-2+2=0\)
\(B=\sqrt{\dfrac{\left(9-4\sqrt{3}\right)\left(6-\sqrt{3}\right)}{\left(6-\sqrt{3}\right)\left(6+\sqrt{3}\right)}}-\sqrt{\dfrac{\left(3+4\sqrt{3}\right)\left(5\sqrt{3}+6\right)}{\left(5\sqrt{3}-6\right)\left(5\sqrt{3}+6\right)}}\)
\(=\sqrt{\dfrac{66-33\sqrt{3}}{33}}-\sqrt{\dfrac{78+39\sqrt{3}}{39}}=\sqrt{2-\sqrt{3}}-\sqrt{2+\sqrt{3}}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\sqrt{4-2\sqrt{3}}-\sqrt{4+2\sqrt{3}}\right)=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}-1\right)^2}-\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{3}+1\right)^2}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\left(\sqrt{3}-1-\sqrt{3}-1\right)=-\sqrt{2}\)
a) Ta có: \(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{10}-3\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{7-3\sqrt{5}}}-\dfrac{\sqrt{10}-\sqrt{14}}{\sqrt{6-\sqrt{35}}}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{5}-6}{3-\sqrt{5}}-\dfrac{2\sqrt{5}-2\sqrt{7}}{\sqrt{7}-\sqrt{5}}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(2\sqrt{5}-6\right)\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)}{4}-\dfrac{\left(2\sqrt{5}-2\sqrt{7}\right)\left(\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{5}\right)}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{5}-3\right)\left(3+\sqrt{5}\right)-\left(2\sqrt{5}-2\sqrt{7}\right)\left(\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{5}\right)}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{5-9-2\left(5-7\right)}{2}\)
\(=\dfrac{-4-2\cdot\left(-2\right)}{2}\)
\(=0\)

a: Xét tứ giác EOBM có
\(\widehat{OBM}+\widehat{OEM}=180^0\)
Do đó: EOBM là tứ giác nội tiếp


a: góc AQE=góc AKE=90 độ
=>AQKE nội tiếp
=>góc KQE=góc KAE=góc BCE
b: góc EAC=góc EBC
góc EBC=góc DKE
=>góc EBC=góc DKE
=>góc EAN=góc EKN
=>AKEN nội tiếp
=>góc ANE+góc AKE=180 độ
=>góc ANE=90 độ
DNCE có góc ENC=góc EDC=90 độ
nên DNEC nội tiếp
+>góc E1=góc C1
mà góc C1=góc A1=góc E2
nên góc E1=góc E2
=>ΔQKE đồng dạng với ΔDNE
=>EN*QK=ND*EQ



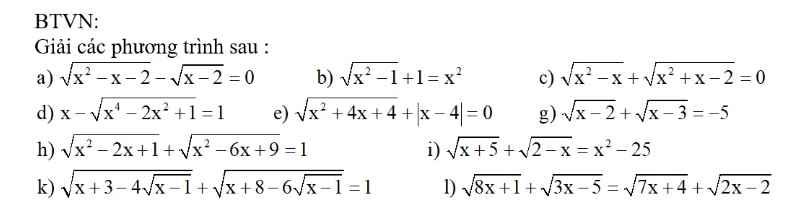





a: Xét (O) có
EM là tiếp tuyến
EN là tiếp tuyến
Do đó: EM=EN
hay E nằm trên đường trung trực của MN(1)
Ta có: OM=ON
nên O nằm trên đường trung trực của MN(2)
Từ (1) và (2) suy ra OE là đường trung trực của MN