Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a) (P) có đỉnh I(-1; -2)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-\dfrac{b}{2a}=-1\\-\dfrac{\Delta}{4a}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=2a\\\dfrac{b^2-4ac}{4a}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=2.2\\b^2-4.2.c=8.2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=4\\b^2-8c=16\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow4^2-8c=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow c=0\)
=> y = 2x2 + 4x
b) (P) có trục đối xứng x = 1 và cắt trục tung tại M(0; 4)
\(M\in\left(P\right)\Rightarrow4=2.0^2+b.0+c\)
\(\Leftrightarrow c=4\)
Trục đối xứng: \(x=-\dfrac{b}{2a}=1\)
<=> -b = 2a
<=> -b = 2.2
<=> b = -4
=> y = 2x2 - 4x + 4
c) Đi qua 2 điểm A(1; 6), B(-1; 0)
\(A\in\left(P\right)\Rightarrow6=2.1^2+b.1+c\)
\(\Leftrightarrow b+c=4\) (1)
\(B\in\left(P\right)\Rightarrow0=2.\left(-1\right)^2+b\left(-1\right)+c\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-b+c=-2\) (2)
Từ (1) và (2) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b+c=4\\-b+c=-2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=3\\c=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=> y = 2x2 + 3x + 1


ĐKXĐ: \(x>3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+2\sqrt{x-3}\sqrt{x+3}=\dfrac{4\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-3}\right)^2=\dfrac{4\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+3}+\sqrt{x-3}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x+3}}{x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{x+3}-\sqrt{x-3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{x+3}}{x-3}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x-9=x+3-\sqrt{x^2-9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x^2-9}=12-2x\) (\(x\le6\))
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-9=144-48x+4x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3x^2-48x+153=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=8-\sqrt{13}\)

Câu 2:
\(TH1:m+2=0. \Leftrightarrow m=-2.\)
Thay \(m=-2\) vào BPT ta có:
\(0x+\left(-2\right)^2-3>0.\\ \Leftrightarrow4-3>0.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1>0\) (Luôn đúng).
Vậy \(m=-2\) thì BPT có nghiệm.
\(TH2:m+2\ne0.\Leftrightarrow m\ne-2.\)
Khi đó BPT có nghiệm \(x>\dfrac{3-m^2}{m+2}.\)
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm với mọi giá trị thực của m.

\(|2x^2-3x+4|-|2x-x^2-1|=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow|2x^2-3x+4|=|2x-x^2-1|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^2-3x+4=2x-x^2-1\\2x^2-3x+4=-2x+x^2+1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^2-3x+4-2x+x^2+1=0\\2x^2-3x+4+2x-x^2-1=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x^2-5x+5=0\\x^2-x+3=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3\left(x^2-\frac{5}{3}x+\frac{25}{9}-\frac{25}{9}+\frac{5}{3}\right)=0\\x^2-2.x.\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{4}-\frac{1}{4}+3=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3\left(x-\frac{5}{3}^2\right)-\frac{10}{3}=0\\\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{11}{4}>0\left(Loai\right)\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x\sqrt{3}-\frac{5\sqrt{3}}{3}\right)^2-\left(\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x\sqrt{3}-\frac{5\sqrt{3}}{3}-\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}\right)\left(x\sqrt{3}-\frac{5\sqrt{3}}{3}+\frac{\sqrt{30}}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x\sqrt{3}-\frac{\sqrt{30}+5\sqrt{3}}{3}\right)\left(x\sqrt{3}+\frac{\sqrt{30}-5\sqrt{3}}{3}\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x\sqrt{3}-\frac{\sqrt{30}+5\sqrt{3}}{3}=0\\x\sqrt{3}+\frac{\sqrt{30}-5\sqrt{3}}{3}=0\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5+\sqrt{10}}{3}\\x=\frac{5-\sqrt{10}}{3}\end{cases}}\)
Vậy ...
\(\left|2x^2-3x+4\right|-\left|2x-x^2-1\right|=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x^2-3x+4\right|=\left|2x-x^2-1\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}2x^2-3x+4=2x-x^2-1\\2x^2-3x+4=x^2-2x+1\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}3x^2-5x+5=0\\x^2-x+3=0\end{cases}}\)
\(TH1:3x^2-5x+5=0\)
Ta có: \(\Delta=5^2-4.3.5=-35< 0\)(vô nghiệm)
\(TH2:x^2-x+3=0\)
Ta có: \(\Delta=1^2-4.1.3=-11< 0\)(vô nghiệm)
Vậy pt vô nghiệm

11 c)
\(a^2+2\ge2\sqrt{a^2+1}\Leftrightarrow a^2+1-2\sqrt{a^2+1}+1\ge0\Leftrightarrow\left(\sqrt{a^2+1}-1\right)^2\ge0\) (luôn đúng)
12 a) Có a+b+c=1\(\Rightarrow\) (1-a)(1-b)(1-c)= (b+c)(a+c)(a+b) (*)
áp dụng BĐT cô-si: \(\left(b+c\right)\left(a+c\right)\left(a+b\right)\ge2\sqrt{bc}2\sqrt{ac}2\sqrt{ab}=8\sqrt{\left(abc\right)2}=8abc\) ( luôn đúng với mọi a,b,c ko âm )
b) áp dụng BĐT cô-si: \(c\left(a+b\right)\le\dfrac{\left(a+b+c\right)^2}{4}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Tương tự: \(a\left(b+c\right)\le\dfrac{1}{4};b\left(c+a\right)\le\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow abc\left(a+b\right)\left(b+c\right)\left(c+a\right)\le\dfrac{1}{4}\dfrac{1}{4}\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{1}{64}\)

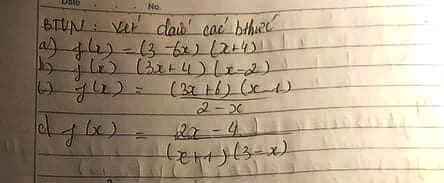






Câu 1
A ∪ B = 1; 3; 5; 7; 8; 9}
Câu 2:
A \ B = {0; 1}