
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3x-1\right)^2+4\left(x^2+3x-1\right)-2\left(x^2+3x-1\right)-8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2+3x-1\right)\left(x^2+3x-1+4\right)-2\left(x^2+3x-1+4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+3x-3=0\)
\(\Delta=3^2-4\cdot1\cdot\left(-3\right)=9+12=21>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-3-\sqrt{21}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{-3+\sqrt{21}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+6\left(x^2-3x\right)+8=3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-3x\right)^2+5\left(x^2-3x\right)+\left(x^2-3x\right)+5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-3x+1=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-3\right)^2-4\cdot1\cdot1=5>0\)
Do đó: Phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{5}}{2}\\x_2=\dfrac{3+\sqrt{5}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(5\sqrt{2x^3+16}=2\left(x^2+8\right)\left(x>-2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow20\sqrt{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=2\left(x^2+8\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2+8\right)-20\sqrt{\left(x+2\right)\left(x^2-2x+4\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+8-10\sqrt{x+2}\sqrt{x^2-2x+4}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+4+2x+4-10\sqrt{x+2}\sqrt{x^2-2x+4}=0\)
Đặt a = \(\sqrt{x^2-2x+4}\left(a>0\right)\)
b = \(\sqrt{x+2}\left(b\ge0\right)\)
=> pt có dạng:
\(a^2-10ab+b^2=0\)
bạn phân tích rồi làm tiếp nhá

ĐKXĐ : \(1\le x\le3\)
\(x-\sqrt{x-1}-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)-\sqrt{x-1}-2=0\)
Đặt \(t=\sqrt{x-1},t\ge0\), suy ra pt trên trở thành \(t^2-t-2=0\Leftrightarrow\left(t-2\right)\left(t+1\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}t=2\left(\text{nhận}\right)\\t=-1\left(\text{loại}\right)\end{cases}}\)
Với t = 2 suy ra x = 5

\(x^2+6x-3=4x\sqrt{2x-1}\left(1\right)\) ĐK: \(x\ge\frac{1}{2}\)
Đặt \(\sqrt{2x-1}=a\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow6x-3=3a^2\)
=> (1) <=> x^2 +3a^2 = 4ax
<=> x^2 -4ax +3a^2 =0
<=> x^2 -ax - 3ax + 3a^2 =0
<=> x(x-a) -3a(x-a) =0
<=> (x-a) ( x-3a ) =0
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=a\\x=3a\end{cases}}\)
TH1: x=a
\(\Rightarrow x=\sqrt{2x-1}\)\(\left(x\ge0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=2x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2=0\)
<=> x=1 (tm)
TH2: x= 3a
\(\Rightarrow x=3\sqrt{2x-1}\left(x\ge0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2=18x-9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-18x+9=0\)
\(\Delta=288\)
=> pt có 2 nghiệm pb \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{18+12\sqrt{2}}{2}=9+6\sqrt{2}\left(tm\right)\\x=\frac{18-12\sqrt{2}}{2}=9-6\sqrt{2}\left(tm\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy ...

Đặt m = x - 1 .Điều kiện : m ≥ 0, x ≥ 1
Ta có : x - x - 1 -3 = 0 ⇔ (x -1) - x - 1 -2 =0
⇔ m 2 -m - 2 =0
Phương trình m 2 -m - 2 = 0 có hệ số a = 1, b = -1 , c = -2 nên có dạng
a – b + c = 0
Suy ra : m 1 = -1 (loại) , m 2 = -(-2)/1 = 2
Với m =2 ta có: x - 1 =2 ⇒ x -1 =4 ⇔ x =5
Giá trị của x thỏa mãn điều kiện bài toán
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 1 nghiệm : x=5


Đặt m = x/(x+1) .Điều kiện : x ≠ -1
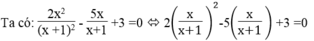
⇔ 2 m 2 -5m +3 =0
Phương trình 2m2 -5m +3 = 0 có hệ số a = 2, b = -5 , c = 3 nên có dạng
a +b + c = 0
suy ra : m 1 = 1 , m 2 =3/2
Với m 1 =1 ta có: x/(x+1) =1 ⇔ x =x+1 ⇔ 0x =1 (vô nghiệm)
Với m = 3/2 ta có: x/(x+1) = 3/2 ⇔ 2x =3(x +1)
⇔ 2x =3x +3 ⇔ x =-3
Giá trị của x thỏa mãn điều kiện bài toán
Vậy phương trình đã cho có 1 nghiệm : x=-3
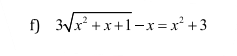
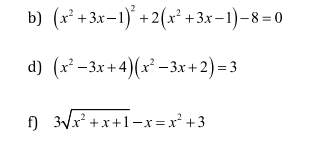

Đặt \(\sqrt{x^2+x+1}=a\)
Pt trở thành \(3a=a^2+2\)
=>(a-1)(a-2)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+x+1=1\\x^2+x+1=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x^2+x=0\\\left(x+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2=\dfrac{13}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{0;-1;\dfrac{\sqrt{13}-1}{2};\dfrac{-\sqrt{13}-1}{2}\right\}\)