Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(ĐK:x\ne0;x\ne1\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{1}{x}+2\right)\left(2+\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-x-2\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}=-2\\\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}=x\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x+1=x^2-x\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x^2-2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\\x=1+\sqrt{2}\\x=1-\sqrt{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(ĐK:x\ne-1\\ PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{1}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}=\dfrac{1}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow4x-4=x+1\\ \Leftrightarrow3x=5\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{3}\left(tm\right)\)

Thay \(x=\dfrac{3}{4}y\) vào phương trình dưới, ta có:
\(\dfrac{1}{2}\left(\dfrac{3}{4}y+3\right)\left(y-2\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{3}{4}y^2=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{8}y^2-\dfrac{3}{4}y+\dfrac{3}{2}y-3-\dfrac{3}{8}y^2=9\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{4}y=12\\ \Leftrightarrow y=18\Rightarrow x=12\)
Vậy hệ phương trình có nghiệm \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(12;18\right)\)

a) + 2 = x(1 - x)
⇔ x2 – 9 + 6 = 3x – 3x2
⇔ 4x2 – 3x – 3 = 0; ∆ = 57
x1 = , x2 =
b) + 3 =
. Điều kiện x ≠ 2, x ≠ 5.
(x + 2)(2 – x) + 3(x – 5)(2 – x) = 6(x – 5)
⇔ 4 – x2 – 3x2 + 21x – 30 = 6x – 30 ⇔ 4x2 – 15x – 4 = 0
∆ = 225 + 64 = 289, √∆ = 17
x1 = , x2 = 4
c) =
. Điều kiện: x ≠ -1; x ≠ -2
Phương trình tương đương: 4(x + 2) = -x2 – x + 2
⇔ 4x + 8 = 2 – x2 – x
⇔ x2 + 5x + 6 = 0
Giải ra ta được: x1 = -2 không thỏa mãn điều kiện của ẩn nên phương trình chỉ có một nghiệm x = -3.
a) + 2 = x(1 - x)
⇔ x2 – 9 + 6 = 3x – 3x2
⇔ 4x2 – 3x – 3 = 0; ∆ = 57
x1 = , x2 =
b) + 3 =
. Điều kiện x ≠ 2, x ≠ 5.
(x + 2)(2 – x) + 3(x – 5)(2 – x) = 6(x – 5)
⇔ 4 – x2 – 3x2 + 21x – 30 = 6x – 30 ⇔ 4x2 – 15x – 4 = 0
∆ = 225 + 64 = 289, √∆ = 17
x1 = , x2 = 4
c) =
. Điều kiện: x ≠ -1; x ≠ -2
Phương trình tương đương: 4(x + 2) = -x2 – x + 2
⇔ 4x + 8 = 2 – x2 – x
⇔ x2 + 5x + 6 = 0
Giải ra ta được: x1 = -2 không thỏa mãn điều kiện của ẩn nên phương trình chỉ có một nghiệm x = -3.
nhớ like nha

1:
\(=\left(\dfrac{1}{x-2\sqrt{x}}+\dfrac{2}{3\sqrt{x}-6}\right):\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}+3}{3\sqrt{x}}\)
\(=\dfrac{3+2\sqrt{x}}{3\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{3\sqrt{x}}{2\sqrt{x}+3}=\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x}-2}\)

=>3|x-1|+2/y-1=8 và 3|x-1|=9/y-1=-3
=>11/y-1=11 và |x-1|-3/y-1=-1
=>y-1=1 và |x-1|=2
=>y=2 và (x-1=2 hoặc x-1=-2)
=>y=2 và (x=3 hoặc x=-1)

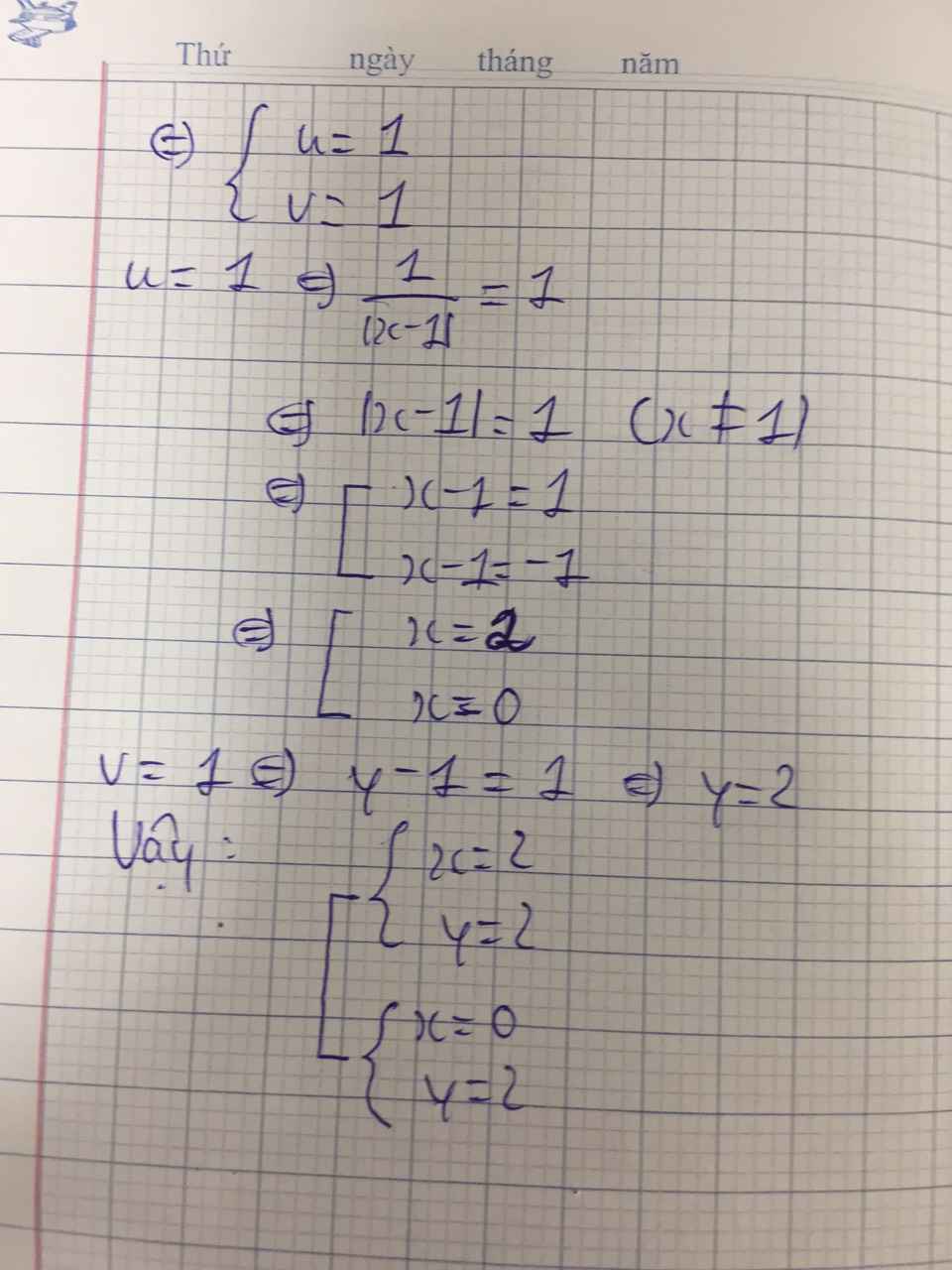
Ta có : \(\dfrac{1}{x\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{1}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x+3\right)}=\dfrac{3}{10}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{x+1}+\dfrac{1}{x+1}-\dfrac{1}{x+2}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}=\dfrac{3}{10}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{x+3}=\dfrac{3}{10}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10\left(x+3\right)-10x=3x\left(x+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-3x^2-9x+30=0\)
\(\Delta=\left(-9\right)^2+4.3.30=81+360=441>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{9+\sqrt{441}}{-6}=-5\\x_2=\dfrac{9-\sqrt{441}}{-6}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(S=\left\{-5;2\right\}\)