Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



ĐKXĐ:\(x\ne\pm\dfrac{1}{2}\)
\(\dfrac{1+8x}{4+8x}-\dfrac{4x}{12x-6}+\dfrac{32x^2}{3\left(4-16x^2\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1+8x}{4\left(2x+1\right)}-\dfrac{4x}{6\left(2x-1\right)}+\dfrac{32x^2}{-6\cdot\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{6\cdot\left(1+8x\right)\left(2x-1\right)}{24\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}-\dfrac{4\cdot4x\left(2x+1\right)}{24\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}-\dfrac{32x^2\cdot4}{24\left(2x-1\right)\left(2x+1\right)}=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow96x^2-36x-6-36x^2-16x-144x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-84x^2-52x-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta=688\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{52-\sqrt{688}}{-168}=\dfrac{-13+\sqrt{43}}{42}\\x_2=\dfrac{52+\sqrt{688}}{-168}=\dfrac{-13-\sqrt{43}}{43}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy pt có 2 nghiệm phân biệt............

Ta có : \(\frac{12x^2+12x+11}{4x^2+4x+3}=\frac{5y^2-10y+9}{y^2-2y+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{3\left(4x^2+4x+3\right)+2}{4x^2+4x+3}=\frac{5\left(y^2-2y+2\right)-1}{y^2-2y+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow3+\frac{2}{4x^2+4x+3}=5-\frac{1}{y^2-2y+2}\)
Do \(\frac{2}{4x^2+4x+3}=\frac{2}{\left(2x+1\right)^2+2}\le\frac{2}{2}=1\) \(\Rightarrow3+\frac{2}{4x^2+4x+3}\le4\left(1\right)\)
\(\frac{1}{y^2-2y+2}=\frac{1}{\left(y-1\right)^2+1}\le\frac{1}{1}=1\) \(\Rightarrow5-\frac{1}{y^2-2y+2}\ge5-1=4\left(2\right)\)
Từ ( 1 ) ; ( 2 ) \(\Rightarrow VT=VP=4\)
Dấu " = " xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x+1=0\\y-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-\frac{1}{2}\\y=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ....

\(x^2-6x+y^2+10y=24\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-6x+9+y^2+10x+25=58\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2+\left(y+5\right)^2=58\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2\le58\Leftrightarrow\left(x-3\right)^2\in\left\{0;1;4;9;16;25;36;49\right\}\)
Dễ nhận thấy chỉ có tổng của 49 và: 9; 9 và 49 thỏa mãn (vì các số trên là số chính phương
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\hept{\begin{cases}\left(x-3\right)^2=49\Leftrightarrow x-3=7\Leftrightarrow x=10\\\left(y+5\right)^2=9\Leftrightarrow y+5=3\Leftrightarrow y=-2\end{cases}}\\\end{cases}}\)<=> (x-3)^2+(y+5)^2=49+9=9+49
+) (x-3)^2+(y+5)^2=49+9
=> x-3=7=>x=10 và: y+5=3=>y=-2
+) (x-3)^2+(y+5)^2=9+49
=> (x-3)=3=>x=6 và y+5=7=>y=2
Vậy có 2 cặp (x,y)={(6;2);(10;-2)}
thỏa mãn điều kiện

Điều kiện xác định: x ≠ ±3; x ≠ -7/2.
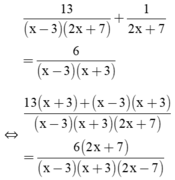
⇒ 13(x + 3) + (x – 3)(x + 3) = 6(2x + 7)
⇔ 13x + 39 + x2 – 9 = 12x + 42
⇔ x2 + x – 12 = 0
⇔ x2 +4x – 3x – 12 = 0
⇔ x(x + 4) – 3(x + 4) = 0
⇔ (x – 3)(x + 4) = 0
⇔ x – 3 = 0 hoặc x + 4 = 0
x – 3 = 0 ⇔ x = 3 (không thỏa mãn đkxđ)
x + 4 = 0 ⇔ x = -4 (thỏa mãn đkxđ).
Vậy phương trình có tập nghiệm S = {-4}.
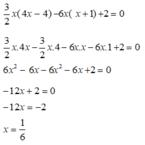
\(\Leftrightarrow x^4-4x^3+12x^2-32x+32=\left(y-5\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2\left(x^2+8\right)=\left(y-5\right)^2\)
- Với \(x=2\Rightarrow y=5\)
- Với \(x\ne2\Rightarrow x-2\) là ước của \(y-5\)
Đặt \(y-5=n\left(x-2\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2\left(x^2+8\right)=n^2\left(x-2\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+8=n^2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(n-x\right)\left(n+x\right)=8\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1;n=-3\Rightarrow y=8\\x=-1;n=-3\Rightarrow y=14\\x=1;n=3\Rightarrow y=2\\x=-1;n=3\Rightarrow y=-4\end{matrix}\right.\)