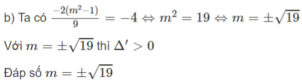Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Phương trình có hai nghiệm
![]()
B = 2 ( x 1 2 + x 2 2 ) + 16 − 3 x 1 x 2
= 2 ( x 1 + x 2 ) 2 − 4 x 1 x 2 + 16 − 3 x 1 x 2 = 2 ( 2 m + 2 ) 2 − 4 ( m 2 + 2 ) + 16 − 3 ( m 2 + 2 ) = 4 m 2 + 16 m + 16 − 3 ( m 2 + 2 ) = 2 m + 4 − 3 ( m 2 + 2 ) = − 3 m 2 + 2 m − 2
Xét hàm số y = − 3 m 2 + 2 m − 2 với m ≥ 1 2
Bảng biến thiên
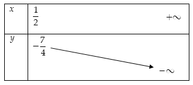
Suy ra giá trị m a x m ≥ 1 2 y = − 7 4 khi m = 1 2
Vậy giá trị lớn nhất của biểu thức B là - 7 4 khi m = 1 2
Đáp án cần chọn là: B

a.
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm trái dấu khi và chỉ khi:
\(ac< 0\Leftrightarrow1.\left(2m+1\right)< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m< -\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b.
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm nằm cùng phía trục Oy \(\Leftrightarrow\) phương trình có 2 nghiệm cùng dấu
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(2m+1\right)>0\\x_1x_2=2m+1>0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\ne0\\m>-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\Delta=\left(m+1\right)^2-4\left(m^2-2m+2\right)=-3m^2+10m-7\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow1\le m\le\dfrac{7}{3}\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m+1\\x_1x_2=m^2-2m+2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(P=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\)
\(=\left(m+1\right)^2-2\left(m^2-2m+2\right)\)
\(=-m^2+6m-3\)
\(=\left(-m^2+6m-\dfrac{77}{9}\right)+\dfrac{50}{9}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{11}{3}-m\right)\left(m-\dfrac{7}{3}\right)+\dfrac{50}{9}\le\dfrac{50}{9}\)
\(P_{max}=\dfrac{50}{9}\) khi \(m=\dfrac{7}{3}\)

PT x 2 − 2 m + 1 x + m 2 − 1 = 0 ( 1 ) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt x 1 , x 2
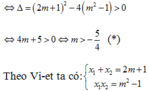
Theo Vi-et ta có: x 1 + x 2 = 2 m + 1 x 1 x 2 = m 2 − 1
Ta có: x 1 2 + x 2 2 + 8 x 1 x 2 = x 1 + x 2 2 + 6 x 1 x 2 = 2 m + 1 2 + 6 m 2 − 1
= 10 m 2 + 2 5 m + 1 25 − 27 5 = 10 m + 1 5 2 − 27 5
⇒ x 1 2 + x 2 2 + 8 x 1 x 2 ≥ − 27 5
Dấu ‘=’ xảy ra khi m = − 1 5 (thỏa mãn (*))
Vậy x 1 2 + x 2 2 + 8 x 1 x 2 đạt giá trị nhỏ nhất khi m = − 1 5
Đáp án cần chọn là: C

3:
x^2-2x+1-m^2<=0
=>(x-1)^2-m^2<=0
=>(x-1)^2<=m^2
=>-m<=x-1<=m
=>-m+1<=x<=m+1
mà x thuộc [-1;2]
nên -m+1>=-1 và m+1<=2
=>-m>=-2 và m<=1
=>m<=2 và m<=1
=>m<=1

\(a,x^2-\left(2m-3\right)x+m^2=0-vô-ngo\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta< 0\Leftrightarrow[-\left(2m-3\right)]^2-4m^2< 0\Leftrightarrow m>\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(b,\left(m-1\right)x^2-2mx+m-2=0\)
\(m-1=0\Leftrightarrow m=1\Rightarrow-2x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=-0,5\left(ktm\right)\)
\(m-1\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne1\Rightarrow\Delta'< 0\Leftrightarrow\left(-m\right)^2-\left(m-2\right)\left(m-1\right)< 0\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{2}{3}\)
\(c,\left(2-m\right)x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+4-m=0\)
\(2-m=0\Leftrightarrow m=2\Rightarrow-6x+2=0\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(ktm\right)\)
\(2-m\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne2\Rightarrow\Delta'< 0\Leftrightarrow[-\left(m+1\right)]^2-\left(4-m\right)\left(2-m\right)< 0\Leftrightarrow m< \dfrac{7}{8}\)

Điều kiện: \(m+2\ne0\Leftrightarrow m\ne-2\)
Ta có: \(\left(m+2\right)^2-2\left(m-1\right)x+3-m=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\Delta=4\left(m-1\right)^2-4\left(m+2\right)\left(3-m\right)\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm thì \(\Delta\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow4\left(m^2-2m+1\right)-4\left(3m-m^2+6-2m\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m^2-2m+1\right)\ge\left(m-m^2+6\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2-3m-5\ge0\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m\le-1\\m\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Áp dụng định lí Vi-et ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_1=\dfrac{2\left(m-1\right)}{m+2}\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{3-m}{m+2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_2^2=x_1+x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=x_1+x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{2\left(m-1\right)}{m+2}\right)^2-2\dfrac{3-m}{m+2}=\dfrac{2\left(m-1\right)}{m+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4\left(m^2-2m+1\right)}{m^2+4m+4}=\dfrac{2m-2+6-2m}{m+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4m^2-8m+4}{m^2+4m+4}=\dfrac{4}{m+2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4m^2-8m+4\right)\left(m+2\right)=4m^2+16m+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4m^3-8m^2+4m+8m^2-16m+8\right)=4m^2+16m+16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(4m^3-4m^2-28m-8\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m\approx3,3\\m\approx-0,3\left(loai\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy m \(\in\left(3;4\right)\)
Câu A