Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Ta có: \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2-7x+41\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-2=0\)
hay x=2
Thay x=2 vào (2), ta được:
\(2^2-2m+m^2-5m+8=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-7m+12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-3\right)\left(m-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=3\\m=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: Có 2 giá trị nguyên của m thỏa mãn hai phương trình có nghiệm chung

câu a
Gọi x0 là nghiệm chung của PT(1) và (2)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x^2_0+\left(3m-1\right)x_0-3=0\left(\times3\right)\\6.x^2_0-\left(2m-1\right)x_0-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}6x^2_0+3\left(3m-1\right)x_0-9=0\left(1\right)\\6x^2_0-\left(2m-1\right)x_0-1=0\left(2\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) Lấy (1)-(2) ,ta được
PT\(\Leftrightarrow3\left(3m-1\right)-9+\left(2m-1\right)+1\)=0
\(\Leftrightarrow9m-3-9+2m-1+1=0\Leftrightarrow11m-12=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{12}{11}\)

a, Thay m vào pt ta được :
(3+1).x2-2(3+1).x+3-3=0
\(\Leftrightarrow\)4x2-8x=0
\(\Leftrightarrow4x\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\\\x-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy m=3 phương trình có 2 nghiệm là 0 và 2
b, Theo Vi et ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1.x_2=\dfrac{m-3}{m+1}\\x_1+x_2=\dfrac{2\left(m+1\right)}{m+1}\end{matrix}\right.\left(vớim\ne-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1.x_2=\dfrac{m-3}{m+1}\\x_1+x_2=2\end{matrix}\right.\) (1)
Ta có : (4x1+1)(4x2+1)=18
\(\Leftrightarrow16x_1.x_2+4x_1+4x_2+1=18\)
\(\Leftrightarrow16.x_1.x_2+4\left(x_1+x_2\right)=17\) (2)
Thay (1) vào (2) ta được :
16.\(\dfrac{m-3}{m+1}+4.2=17\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{16m-48}{m+1}=9\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9\left(m+1\right)=16m-48\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9m+9=16m-48\)
\(\Leftrightarrow7m=57\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{57}{7}\) (thỏa mãn m\(\ne-1\))
Vậy ..

b) phương trình có 2 nghiệm \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(m-1\right)\left(m+3\right)\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1-m^2-3m+m+3\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4m+4\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le1\)
Ta có: \(x_1^2+x_1x_2+x_2^2=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=1\)
Theo viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[-2\left(m-1\right)^2\right]-2\left(m+3\right)=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-8m+4-2m-6-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-10m-3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m_1=\dfrac{5+\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(ktm\right)\\m_2=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{5-\sqrt{37}}{4}\)

a:Sửa đề: x^2-(m+1)x+2m-8=0
Khi m=2 thì (1) sẽ là x^2-3x-4=0
=>(x-4)(x+1)=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=-1
b: Δ=(-m-1)^2-4(2m-8)
=m^2+2m+1-8m+32
=m^2-6m+33
=(m-3)^2+24>=24>0
=>(1) luôn có hai nghiệm pb
\(x_1^2+x_2^2+\left(x_1-2\right)\left(x_2-2\right)=11\)
=>(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2+x1x2-2(x1+x2)+4=11
=>(m+1)^2-(2m-8)-2(m+1)+4=11
=>m^2+2m+1-2m+8-2m-2+4=11
=>m^2-2m=0
=>m=0 hoặc m=2


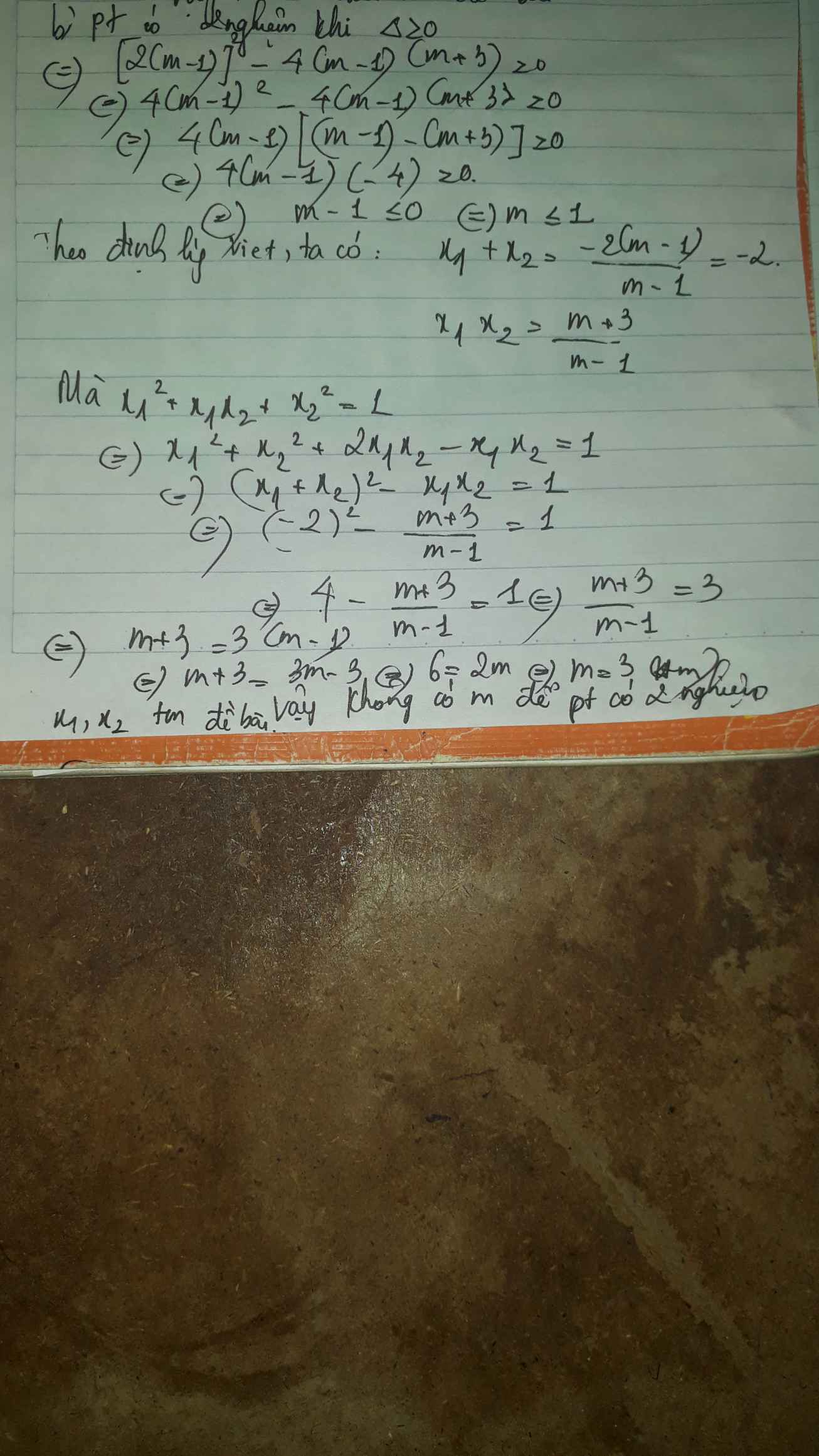
Nhiều thế, chắc phải đưa ra đáp thôi