Trộn 300ml dd h2so4 2M với 200ml dd h2so4 1M. Tính nồng độ mol dd h2so4 trog phản ứng trên
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Ta có: \(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}=0,2.1=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{H_2SO_4}=0,3.0,5=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
PT: \(Ba\left(OH\right)_2+H_2SO_4\rightarrow BaSO_{4\downarrow}+2H_2O\)
Xét tỉ lệ: \(\dfrac{0,2}{1}>\dfrac{0,15}{1}\), ta được Ba(OH)2 dư.
Theo PT: \(n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2\left(pư\right)}=n_{H_2SO_4}=0,15\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow n_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2\left(dư\right)}=0,05\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow C_{M_{Ba\left(OH\right)_2}}=\dfrac{0,05}{0,2+0,3}=0,1M\)
Bạn tham khảo nhé!
n Ba(OH)2 = 0,2.1 = 0,2(mol)
n H2SO4 = 0,3.0,5 = 0,15(mol)
$Ba(OH)_2 + H_2SO_4 \to BaSO_4 + 2H_2O$
Ta thấy :
n Ba(OH)2 = 0,2 > n H2SO4 = 0,15 nên Ba(OH)2 dư
n Ba(OH)2 pư = n H2SO4 = 0,15(mol)
n Ba(OH)2 dư = 0,2 - 0,15 = 0,05(mol)
V dd sau pư = 0,2 + 0,3 = 0,5(lít)
CM Ba(OH)2 dư = 0,05/0,5 = 0,1M

300ml NaOH 0,1 M
=> n OH- = 0,1 * 0,3 = 0,03 mol
300ml Ba(OH)2 0,025 M
=> n OH- = 2 * 0,025 * 0,3 = 0,015 mol
vậy n OH- = 0,03 + 0,015 = 0,045 mol
200ml dd H2SO4 có nồng độ x M
=> n H+ = 2 * 0,2 * x = 0,4x mol
sau phản ứng thu được 500ml dd có pH=2
pH=2 => [H+] dư = 10^-2 = 0,01 M
=> n H+ dư = 0,01 * 0,5 = 0,005 mol
H+ + OH- ---> H2O
0,045 <---0,045
ta có: 0,4x = 0,045 + 0,005 (số mol đề bài = số mol pu + số mol dư)
=> x = 0,125 M
--------------------------------------...
n SO4 2- = 0,2x = 0,2 * 0,125 = 0,025 mol
n Ba 2+ = 0,025 * 0,3 = 0,0075 mol
Ba 2+ + SO4 2- ---> BaSO4
0,0075 --> 0,0075
m BaSO4 = 0,0075 * 233 = 1,7475 g

\(n_{H_2SO_4\left(2M\right)}=0,15.2=0,3\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{H_2SO_4\left(3M\right)}=0,15.3=0,45\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{H_2SO_4\left(B\right)}=0,3+0,45=0,75\left(mol\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow C_{M_{ddB}}=\dfrac{0,75}{0,2}=3,75M\)
\(n_{H_2SO_4\left(tổng\right)}=0,15.2+0,05.3=0,45\left(mol\right)\\ V_{ddH_2SO_4\left(tổng\right)}=150+50=200\left(ml\right)=0,2\left(l\right)\\ C_{MddH_2SO_4\left(sau\right)}=C_{MddB}=\dfrac{0,45}{0,2}=2,25\left(M\right)\)

Số mol H2SO4 nồng độ 2M là:
\(n_{H_2SO_4}=C_M.V\)\(=2.0,3=0,6\) (mol)
Số mol H2SO4 nồng độ 1M là:
\(n_{H_2SO_4=}C_M.V=1.0,2=0,2\) (mol)
Nồng độ \(C_M\) của dd tạo thành là:
\(C_M=\dfrac{n}{V}=\dfrac{0,6+0,2}{0,3+0,2}=1,6M\)

\(n_{H_2SO_4}=0,3.1=0,3\left(mol\right)\)
PTHH: 2NaOH + H2SO4 --> Na2SO4 + 2H2O
_______0,6<------0,3----------->0,3
=> V = \(\dfrac{0,6}{1}=0,6\left(l\right)\)
b) \(C_{M\left(Na_2SO_4\right)}=\dfrac{0,3}{0,6+0,3}=0,333M\)
\(n_{H_2SO_4}=1.0,3=0,3(mol)\\ 2NaOH+H_2SO_4\to Na_2SO_4+2H_2O\\ \Rightarrow n_{NaOH}=0,6(mol)\\ a,V_{dd_{NaOH}}=\dfrac{0,6}{1}=0,6(l)\\ b,n_{Na_2SO_4}=0,3(mol)\\ \Rightarrow C_{M_{Na_2SO_4}}=\dfrac{0,3}{0,6+0,3}=0,33M\)
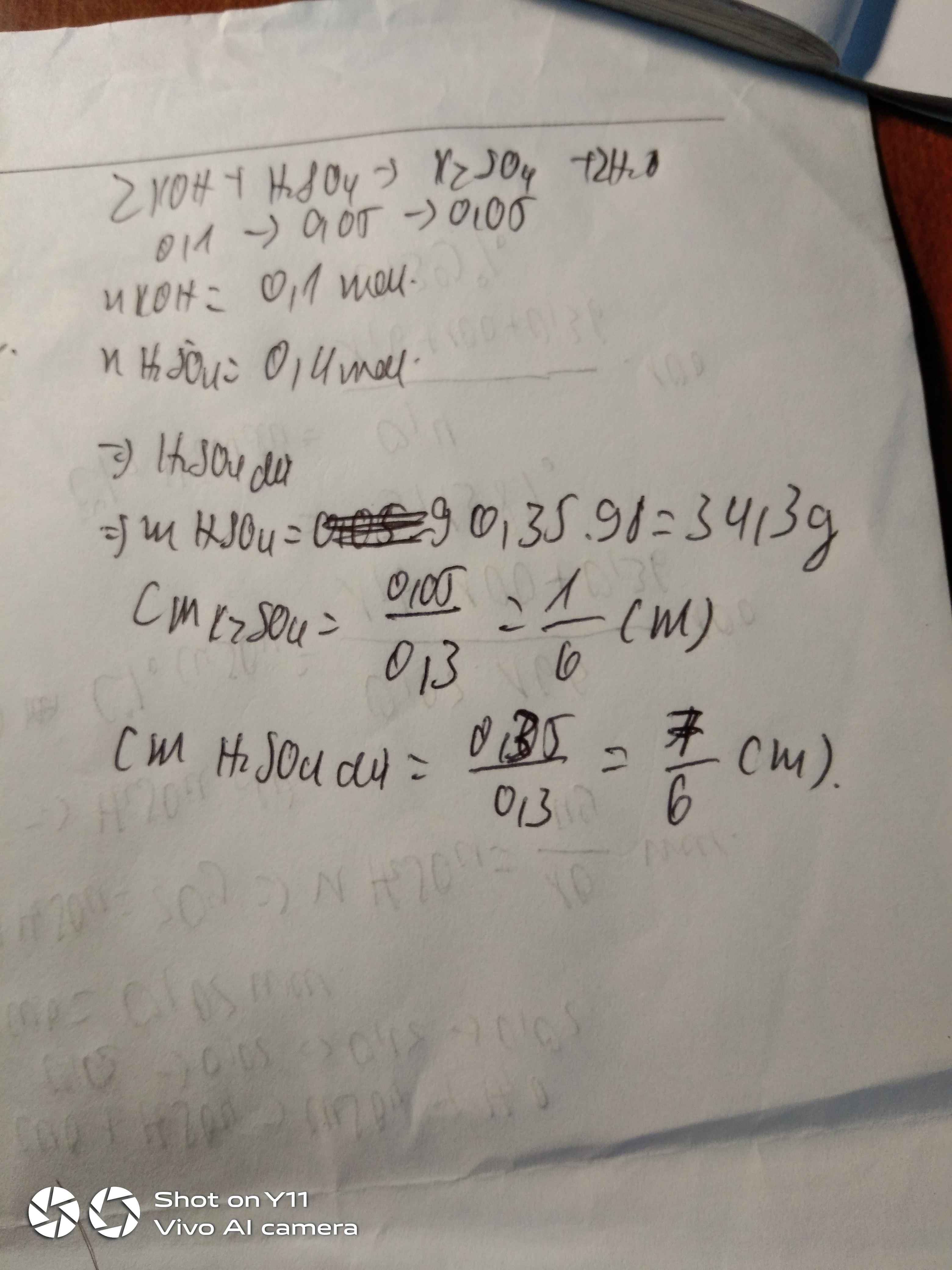
áp dụng quy tắc đường chéo
0,3l dd H2SO4 2M-----------------x-1 (M)
------------------------- x(M)
0,2l dd H2SO4 1M------------------2-x (M)
trong đó x là nồng độ mol của dd H2SO4 THU ĐƯỢC
=> \(\dfrac{0,3}{0,2}=\dfrac{3}{2}=\dfrac{x-1}{2-x}\)
giải PT=> x=1,6 (M)
+) Ta có: \(V_{ddH_2SO_4\left(1\right)}=300\left(ml\right)=0,3\left(l\right)\\ V_{ddH_2SO_4\left(2\right)}=200\left(ml\right)=0,2\left(l\right)\)
=> \(n_{H_2SO_4\left(1\right)}=0,3.2=0,6\left(mol\right)\\ n_{H_2SO_4\left(2\right)}=0,2.1=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
=> Nồng độ mol của dung dịch H2SO4 sau trộn:
\(C_{MddH_2SO_4\left(mới\right)}=\dfrac{0,6+0,2}{0,3+0,2}=1,6\left(M\right)\)