
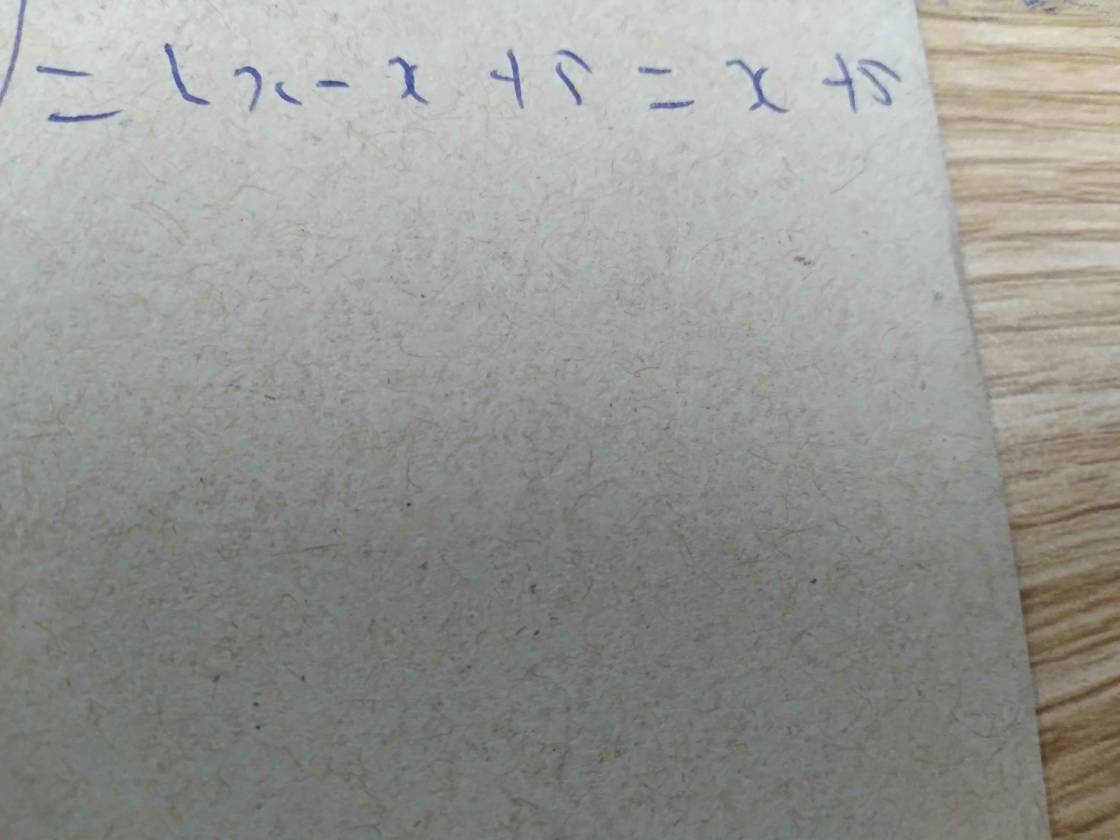
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

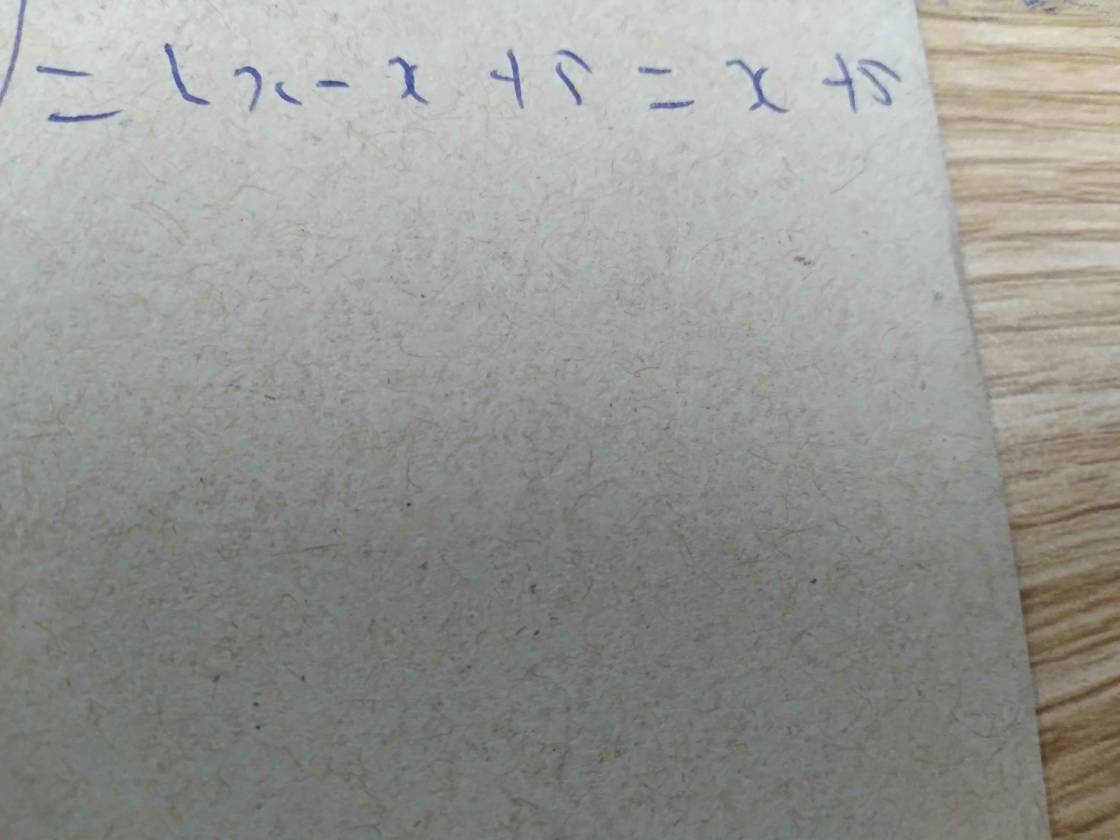

a, ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne1;x\ne-1\)
b, Với \(x\ne1;x\ne-1\)
\(B=\left[\dfrac{x+1}{2\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}-\dfrac{x+3}{2\left(x+1\right)}\right]\cdot\dfrac{4\left(x^2-1\right)}{5}\\ =\left[\dfrac{x^2+2x+1+6-x^2-2x+3}{2\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\right]\cdot\dfrac{4\left(x^2-1\right)}{5}\\ =\dfrac{5}{x^2-1}\cdot\dfrac{4\left(x^2-1\right)}{5}\\ =4\)
=> ĐPCM

a: \(A=\left(x+1\right)\left(x-2\right)-x\left(2x-3\right)+2x^2+4\)
\(=x^2-x-2-2x^2+3x+2x^2+4\)
\(=x^2+2x+2\)
\(a,A=x^2-x-2-2x^2+3x+4+2x^2=x^2+2x+2\\ c,A=\left(x^2+2x+1\right)+1=\left(x+1\right)^2+1\ge1>0\)

a có A = x^2+2x+5 =(x^2+2x+1)+4=(x+1)^2+4 \(\ge\)4
Dấu bằng xảy ra <=>x+1=0 <=>x=-1
\(A=x^2+2x+5=x^2+2.x+1+4=\left(x+1\right)^2+4\ge4\)
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi: \(x+1=0\Rightarrow x=-1\)
Vậy giá trị nhỏ nhất của A là 4 khi x= -1

ĐK: \(x\ne-\dfrac{2}{3};x\ne3\)
\(\dfrac{6x-1}{3x+2}=\dfrac{2x+5}{x-3}\Rightarrow\left(6x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=\left(2x+5\right)\left(3x+2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-19x+3=6x^2+19x+10\Leftrightarrow38x=-7\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{7}{38}\).
ĐKXĐ : x ≠ -2/3 ; x ≠ 3
\(\dfrac{6x-1}{3x+2}=\dfrac{2x+5}{x-3}\Rightarrow\left(6x-1\right)\left(x-3\right)=\left(3x+2\right)\left(2x+5\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6x^2-19x+3=6x^2+19x+10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-38x=7\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{7}{38}\)(tm)
Vậy ...

Lời giải:
a.
\(A=\left[\frac{(2+x)^2}{(2-x)(2+x)}+\frac{4x^2}{(2-x)(2+x)}-\frac{(2-x)^2}{(2-x)(2+x)}\right]:\frac{x(x-3)}{x^2(2-x)}\)
\(=\frac{(2+x)^2+4x^2-(2-x)^2}{(2-x)(2+x)}.\frac{x^2(2-x)}{x(x-3)}=\frac{4x(x+2)}{(2-x)(2+x)}.\frac{x^2(2-x)}{x(x-3)}=\frac{4x^2}{x-3}\)
b.
Khi $x=12$ thì $A=\frac{4.12^2}{12-3}=64$
c.
$A=1\Leftrightarrow \frac{4x^2}{x-3}=1$
$\Leftrightarrow 4x^2=x-3$
$\Leftrightarrow 4x^2-x+3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (2x-\frac{1}{4})^2=-\frac{47}{16}< 0$ (vô lý)
Vậy không tồn tại $x$
d. Để $A$ nguyên thì $\frac{4x^2}{x-3}$ nguyên
$\Leftrightarrow 4x^2\vdots x-3$
$\Leftrightarrow 4(x^2-9)+36\vdots x-3$
$\Leftrightarrow 36\vdots x-3$
$\Leftrightarrow x-3\in\left\{\pm 1;\pm 2;\pm 3;\pm 4;\pm 9; \pm 12; \pm 36\right\}$
Đến đây bạn có thể tự tìm $x$ được rồi, chú ý ĐKXĐ để loại ra những giá trị không thỏa mãn.
e.
$A>4\Leftrightarrow \frac{4x^2}{x-3}>4$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{x^2}{x-3}>1$
$\Leftrightarrow \frac{x^2-x+3}{x-3}>0$
$\Leftrightarrow x-3>0$ (do $x^2-x+3>0$ với mọi $x$ thuộc ĐKXĐ)
$\Leftrightarrow x>3$. Kết hợp với đkxđ suy ra $x>3$

a, ĐKXĐ: x≠±2
A=\(\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{2}{2-x}+\dfrac{1}{x+2}\right)\left(x-2+\dfrac{10-x^2}{x+2}\right)\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{x}{x^2-4}-\dfrac{2x+4}{x^2-4}+\dfrac{x-2}{x^2-4}\right)\left(\dfrac{x^2+2x}{x+2}-\dfrac{2x+4}{x+2}+\dfrac{10-x^2}{x+2}\right)\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{-6}{x^2-4}\right)\left(\dfrac{6}{x+2}\right)\)
A=\(\dfrac{-36}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)^2}\)
b, |x|=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
TH1z: x≥0 ⇔ x=\(\dfrac{1}{2}\) (TMĐKXĐ)
TH2: x<0 ⇔ x=\(\dfrac{-1}{2}\) (TMĐXĐ)
Thay \(\dfrac{1}{2}\), \(\dfrac{-1}{2}\) vào A ta có:
\(\dfrac{-36}{\left(\dfrac{1}{2}-2\right)\left(\dfrac{1}{2}+2\right)^2}\)=\(\dfrac{96}{25}\)
\(\dfrac{-36}{\left(\dfrac{-1}{2}-2\right)\left(\dfrac{-1}{2}+2\right)^2}\)=\(\dfrac{32}{5}\)
c, A<0 ⇔ \(\dfrac{-36}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)^2}\) ⇔ (x-2)(x+2)2 < 0
⇔ {x-2>0 ⇔ {x>2
[ [
{x+2<0 {x<2
⇔ {x-2<0 ⇔ {x<2
[ [
{x+2>0 {x>2
⇔ x<2
Vậy x<2 (trừ -2)

a, ĐKXĐ: x≠±3
A=\(\left(\dfrac{3-x}{x+3}.\dfrac{x^2+6x+9}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{3-x}{x+3}.\dfrac{\left(x+3\right)^2}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{3-x}{x-3}+\dfrac{x}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{9-x^2}{x^2-9}+\dfrac{x^2-3x}{x^2-9}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\left(\dfrac{-3}{x+3}\right):\dfrac{3x^2}{x+3}\)
A=\(\dfrac{-1}{x^2}\)
b, Thay x=\(-\dfrac{1}{2}\) (TMĐKXĐ) vào A ta có:
\(\dfrac{-1}{\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^2}\)=-4
c, A<0 ⇔ \(\dfrac{-1}{x^2}< 0\) ⇔ x2>0 (Đúng với mọi x)
Vậy để A<0 thì x đúng với mọi giá trị (trừ ±3)