
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(\text{#ID07 - DNfil}\)
`A = -(x + 1)^2 + 5`
Ta có: `(x + 1)^2 \ge 0` `AA` `x`
`=> -(x + 1)^2 \le 0` `AA` `x`
`=> -(x + 1)^2 + 5 \le 5` `AA` `x`
Vậy, GTLN của A là `5` khi `(x + 1)^2 = 0 => x + 1 = 0 => x = -1`
________
2.
`2x - 0,7 = 1,3`
`=> 2x = 1,3 + 0,7`
`=> 2x = 2`
`=> x = 1`
Vậy, `x = 1`
__
`x - \sqrt{25} = (2/5 - 6/5)`
`=> x - \sqrt{25} = -3/5`
`=> x = -3/5 + \sqrt{25}`
`=> x = -3/5 + 5`
`=> x = 22/5`
Vậy, `x = 22/5`
__
`3/4 + 1/4 \div x = 2/5`
`=> 1/4 \div x = 2/5 - 3/4`
`=> 1/4 \div x = -7/20`
`=> x = 1/4 \div (-7/20)`
`=> x = -5/7`
Vậy, `x = -5/7.`

2. -x2 + x - 33 = -x2 + x - 1/4 - 131/4 = -( x2 - x + 1/4 ) - 131/4 = -( x - 1/2 )2 - 131/4
-( x - 1/2 )2 ≤ 0 ∀ x => -( x - 1/2 )2 - 131/4 ≤ -131/4 < 0 ∀ x ( đpcm )
3. x2 + 4x + 33 = x2 + 4x + 4 + 29 = ( x + 2 )2 + 29
( x + 2 )2 ≥ 0 ∀ x => ( x + 2 )2 + 29 ≥ 29 > 0 ∀ x ( đpcm )
4. x2 + 8x = x2 + 8x + 16 - 16 = ( x + 4 )2 - 16
( x + 4 )2 ≥ 0 ∀ x => ( x + 4 )2 - 16 ≥ -16 ∀ x
Đẳng thức xảy ra <=> x + 4 = 0 => x = -4
Vậy GTNN của biểu thức = -16, đạt được khi x = -4

Lời giải:
a.
$|2x-5|=12-3x$
Nếu $x\geq \frac{5}{2}$ thì $2x-5=12-3x$
$\Leftrightarrow x=3,4$ (thỏa mãn)
Nếu $x< \frac{5}{2}$ thì: $5-2x=12-3x$
$\Leftrightarrow x=7$ (loại)
Vậy......
b.
$4x=|x+1|+|x+2|+|x+3|\geq 0$
$\Rightarrow x\geq 0$
Do đó: $|x+1|+|x+2|+|x+3|=(x+1)+(x+2)+(x+3)=3x+6$
Vậy: $3x+6=4x$
$\Leftrightarrow x=6$ (thỏa mãn)
c.
$|x^2+|x+2||=x^2+3$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2+|x+2|=x^2+3$
$\Leftrightarrow |x+2|=3$
$\Leftrightarrow x+2=3$ hoặc $x+2=-3$
$\Leftrightarrow x=1$ hoặc $x=-5$
d.
$|x^2-3|=6$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2-3=6$ hoặc $x^2-3=-6$
$\Leftrightarrow x^2=9$ (chọn) hoặc $x^2=-3< 0$ (loại)
$\Leftrightarrow x=\pm 3$

10:
Vì n là số lẻ nên n=2k-1
Số số hạng là (2k-1-1):2+1=k(số)
Tổng là (2k-1+1)*k/2=2k*k/2=k^2 là số chính phương
11:
n^3-n^2+2n+7 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^3+n-n^2-1+n+8 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n+8 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^2-64 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^2+1-65 chia hết cho n^2+1
=>n^2+1 thuộc {1;5;13;65}
=>\(n\in\left\{0;2;-2;2\sqrt{3};-2\sqrt{3};8;-8\right\}\)

Lời giải:
1.
$4x+9=0$
$4x=-9$
$x=\frac{-9}{4}$
2.
$-5x+6=0$
$-5x=-6$
$x=\frac{6}{5}$
3.
$x^2-1=0$
$x^2=1=1^2=(-1)^2$
$x=\pm 1$
4.
$x^2-9=0$
$x^2=9=3^2=(-3)^2$
$x=\pm 3$
5.
$x^2-x=0$
$x(x-1)=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x-1=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x=1$
6.
$x^2-2x=0$
$x(x-2)=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x-2=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x=2$
7.
$x^2-3x=0$
$x(x-3)=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x-3=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x=3$
8.
$3x^2-4x=0$
$x(3x-4)=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $3x-4=0$
$x=0$ hoặc $x=\frac{4}{3}$

Theo c) \(f\left(\frac{5}{7}\right)=f\left(\frac{2}{7}+\frac{3}{7}\right)=f\left(\frac{2}{7}\right)+f\left(\frac{3}{7}\right)\)
\(f\left(\frac{2}{7}\right)=f\left(\frac{1}{7}+\frac{1}{7}\right)=f\left(\frac{1}{7}\right)+f\left(\frac{1}{7}\right)=2.f\left(\frac{1}{7}\right)\)
\(f\left(\frac{3}{7}\right)=f\left(\frac{1}{7}+\frac{2}{7}\right)=f\left(\frac{1}{7}\right)+f\left(\frac{2}{7}\right)=f\left(\frac{1}{7}\right)+2f\left(\frac{1}{7}\right)=3.f\left(\frac{1}{7}\right)\)
\(\implies\)\(f\left(\frac{5}{7}\right)=5.f\left(\frac{1}{7}\right)\) (1)
Theo b) \(f\left(\frac{1}{7}\right)=\frac{1}{7^2}.f\left(7\right)\) (2)
Theo c) \(f\left(7\right)=f\left(3+4\right)=f\left(3\right)+f\left(4\right)\)
\(=2.f\left(3\right)+f\left(1\right)\)
\(=6.f\left(1\right)+f\left(1\right)\)
\(=7.f\left(1\right)\)
Theo a)\(f\left(1\right)=1\)\(\implies\)\(f\left(7\right)=7\) (3)
Từ (1);(2);(3)
\(\implies\) \(f\left(\frac{5}{7}\right)=\frac{5}{7}\)
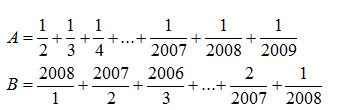
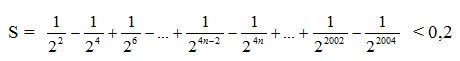
ko biết đâu
\(x^2-\frac{7}{6}x+\frac{1}{3}=0\)
=> \(\left[x^2-2\cdot x\cdot\frac{7}{12}+\left(\frac{7}{12}\right)^2\right]-\frac{1}{144}=0\)
=> \(\left(x-\frac{7}{12}\right)^2-\frac{1}{144}=0\)
=> \(\left(x-\frac{7}{12}\right)^2-\left(\frac{1}{12}\right)^2=0\)
=> \(\left(x-\frac{7}{12}+\frac{1}{12}\right)\left(x-\frac{7}{12}-\frac{1}{12}\right)=0\)
=> \(\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)\left(x-\frac{2}{3}\right)=0\)
=> x = 1/2 hoặc x = 2/3