Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

1:
a: 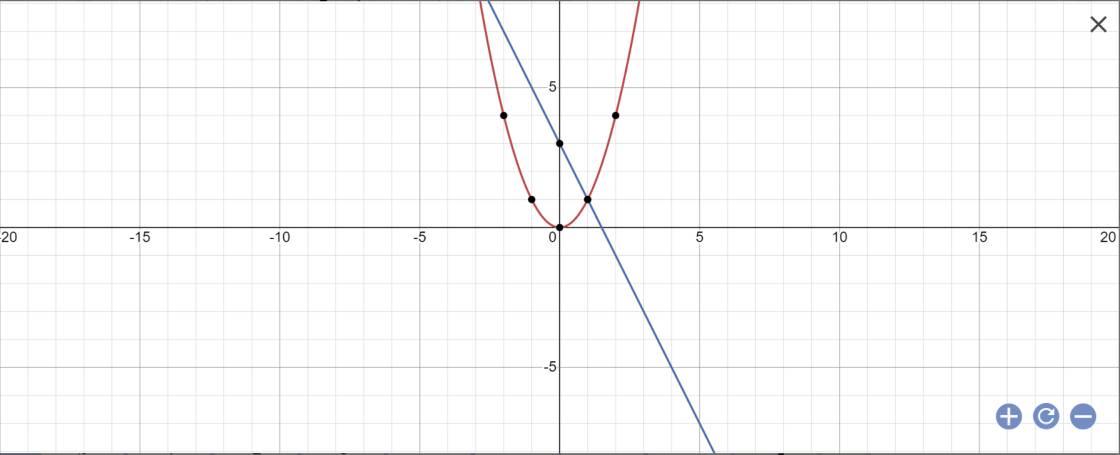
b: PTHĐGĐ là:
x^2+2x-3=0
=>(x+3)(x-1)=0
=>x=-3 hoặc x=1
=>y=9 hoặc y=1

PT hoành độ giao điểm: \(-2x+3=\dfrac{1}{2}x-3\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5}{2}x=6\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{12}{5}\Leftrightarrow y=-\dfrac{9}{5}\Leftrightarrow A\left(\dfrac{12}{5};-\dfrac{9}{5}\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(\dfrac{12}{5};-\dfrac{9}{5}\right)\) là giao điểm 2 đths

a: Khi m=3 thì (d): y=2x+3
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(x^2-2x-3=0\)
=>(x-3)(x+1)=0
=>x=3 hoặc x=-1
Khi x=3 thì y=9
Khi x=-1 thì y=1
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
\(x^2-2x-m=0\)
Δ=4+4m
Để (P) tiếp xúc với (d) thì 4m+4=0
hay m=-1

1:
a: 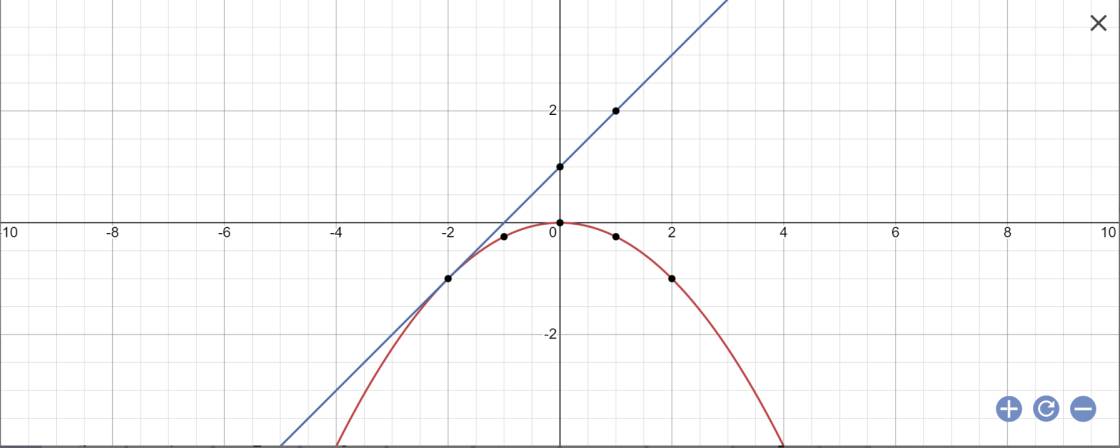
b: PTHĐGĐ là:
-1/4x^2-x-1=0
=>x^2+4x+4=0
=>(x+2)^2=0
=>x=-2
=>y=-1/4*(-2)^2=-1
2: 3x-y=5 và 2x+3y=18
=>9x-3y=15 và 2x+3y=18
=>11x=33 và 3x-y=5
=>x=3 và y=3*3-5=4

b. PTHDGD: \(\dfrac{5}{2}x-4=3x-1\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}x=-3\Leftrightarrow x=-6\Leftrightarrow y=-17\Leftrightarrow A\left(-6;-17\right)\)
Vậy \(A\left(-6;-17\right)\) là tọa độ giao điểm
c. Gọi \(\left(d_1\right):y=ax+b\left(a\ne0\right)\) là đt cần tìm
\(\left(d_1\right)//\left(d\right);A\left(-2;3\right)\in\left(d_1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{5}{2}\\b\ne-4\\-2a+b=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{5}{2}\\b=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy \(\left(d_1\right):y=\dfrac{5}{2}x+8\)
Chúc bạn học tốt!

2: Tọa độ giao điểm là:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-3=-3x+2\\y=2x-3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }-\dfrac{2}{3}x+1=\dfrac{3}{2}x-3\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{13}{6}x=4\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{24}{13}\Leftrightarrow y=-\dfrac{3}{13}\Leftrightarrow A\left(\dfrac{24}{13};-\dfrac{3}{13}\right)\\ \text{Vậy giao điểm 2 đths là }A\left(\dfrac{24}{13};-\dfrac{3}{13}\right)\)