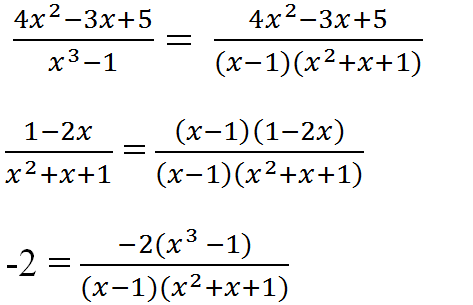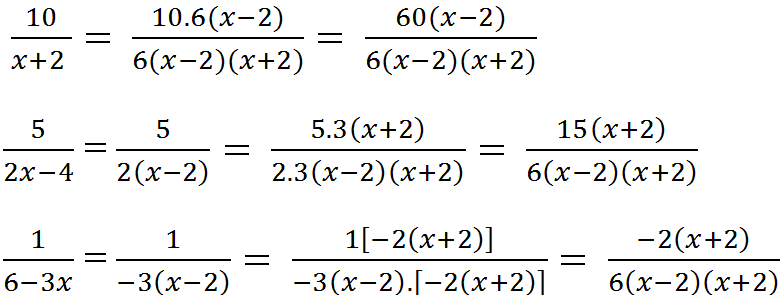Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: MTC=80
b:
ĐKXĐ: x<>0; y<>0
MTC=12xy
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\cdot y\cdot z\ne0\)
MTC=12xyz

a) Tìm MTC: x3 – 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Nên MTC = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Nhân tử phụ:
(x3 – 1) : (x3 – 1) = 1
(x – 1)(x2 + x + 1) : (x2 + x + 1) = x – 1
(x – 1)(x2+ x + 1) : 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Qui đồng:
b) Tìm MTC: x + 2
2x – 4 = 2(x – 2)
6 – 3x = 3(2 – x)
MTC = 6(x – 2)(x + 2)
Nhân tử phụ:
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : (x + 2) = 6(x – 2)
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : 2(x – 2) = 3(x + 2)
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : -3(x – 2) = -2(x + 2)
Qui đồng:

\(a,\dfrac{16+x}{x^2-2x}+\dfrac{18}{2x-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{16+x}{x^2-2x}-\dfrac{18}{x^2-2x}\)
\(=\dfrac{16+x-18}{x^2-2x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x}\)
\(b,\dfrac{2y}{2x^2-xy}+\dfrac{4x}{xy-2x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2y}{2x^2-xy}-\dfrac{4x}{2x^2-xy}\)
\(=\dfrac{2y-4x}{2x^2-xy}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(y-2x\right)}{x\left(2x-y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2\left(2x-y\right)}{x\left(2x-y\right)}\)
\(=-\dfrac{2}{x}\)
\(c,\dfrac{4-x^2}{x-3}+\dfrac{2x-2x^2}{3-x}+\dfrac{5-4x}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{4-x^2}{x-3}-\dfrac{2x^2-2x}{x-3}+\dfrac{5-4x}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{4-x^2-2x^2+2x+5-4x}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{-3x^2-2x+9}{x-3}\)
\(a,\dfrac{16+x}{x^2-2x}+\dfrac{18}{2x-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{16+x}{x^2-2x}-\dfrac{18}{x^2-2x}\)
\(=\dfrac{16+x-18}{x^2-2x}\)
\(=\dfrac{x-2}{x\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{1}{x}\)
\(b,\dfrac{2y}{2x^2-xy}+\dfrac{4x}{xy-2x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2y}{2x^2-xy}-\dfrac{4x}{2x^2-xy}\)
\(=\dfrac{2y-4x}{2x^2-xy}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(y-2x\right)}{x\left(2x-y\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-2\left(2x-y\right)}{x\left(2x-y\right)}\)
\(=-\dfrac{2}{x}\)
\(c,\dfrac{4-x^2}{x-3}+\dfrac{2x-2x^2}{3-x}+\dfrac{5-4x}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{4-x^2}{x-3}-\dfrac{2x^2-2x}{x-3}+\dfrac{5-4x}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{4-x^2-2x^2+2x+5-4x}{x-3}\)
\(=\dfrac{-3x^2-2x+9}{x-3}\)

a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;3\right\}\)
MTC=150(x-2)(x-3)
b: ĐKXĐ: x<>-3
MTC=2(x+3)^2
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
MTC=x^2-1

a, Do mẫu thức \(20\ne0\) với mọi x, suy ra phân thức trên xác định với mọi \(x\in R\)
b, Để phân thức \(\dfrac{8}{x+2004}\) xác định \(\Rightarrow x+2004\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne2004\)
c, Để phân thức \(\dfrac{4x}{3x-7}\) xác định\(\Rightarrow3x-7\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne\dfrac{7}{3}\)
d, Để phân thức \(\dfrac{x^2}{x+z}\) xác định\(\Rightarrow x+z\ne0\Rightarrow x\ne z\)