Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) P xác định \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x+5\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-5\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy P xác định \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-5\end{cases}}\)
b) \(P=\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x\left(x+2\right)}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^2\left(x+2\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)2}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
Có: \(P=0\)
\(\Rightarrow P=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=0\Leftrightarrow x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)=0\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x-5=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x^2-x\right)+\left(5x-5\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\left(x-1\right)+5\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x-1=0\\x+5=0\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)
Vậy \(P=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=-5\end{cases}}\)

a: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{2;3\right\}\)
MTC=150(x-2)(x-3)
b: ĐKXĐ: x<>-3
MTC=2(x+3)^2
c: ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
MTC=x^2-1

a) P xác định \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}2x+10\ne0\\x\ne0\\2x\left(x+5\right)\ne0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow x\ne\left\{-5;0\right\}}\)
b) \(P=\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^2\left(x+2\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{2\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{5\left(10-x\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^3+5x^2-x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x^2\left(x+5\right)-x\left(x+5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{\left(x+5\right)\left(x^2-x\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(P=\frac{x\left(x-1\right)}{2x}\)
\(P=\frac{x-1}{2}\)
c) Để P = 0 thì \(x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\)( thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ )
Để P = 1/4 thì \(\frac{x-1}{2}=\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x-1\right)=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-4=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x=6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{3}{2}\)( thỏa mãn ĐKXĐ )
d) Để P > 0 thì \(\frac{x-1}{2}>0\)
Mà 2 > 0, do đó để P > 0 thì \(x-1>0\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
Để P < 0 thì \(\frac{x-1}{2}< 0\)
Mà 2 > 0, do đó để P < 0 thì \(x-1< 0\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)

a) Tìm MTC: x3 – 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Nên MTC = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Nhân tử phụ:
(x3 – 1) : (x3 – 1) = 1
(x – 1)(x2 + x + 1) : (x2 + x + 1) = x – 1
(x – 1)(x2+ x + 1) : 1 = (x – 1)(x2 + x + 1)
Qui đồng:
b) Tìm MTC: x + 2
2x – 4 = 2(x – 2)
6 – 3x = 3(2 – x)
MTC = 6(x – 2)(x + 2)
Nhân tử phụ:
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : (x + 2) = 6(x – 2)
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : 2(x – 2) = 3(x + 2)
6(x – 2)(x + 2) : -3(x – 2) = -2(x + 2)
Qui đồng:

a) \(B=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(B=\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
( ĐKXĐ : \(x\ne0,x\ne-5\) )
\(B=\dfrac{\left(x^2+2x\right).x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x-5\right).2\left(x+5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(B=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2+10x-10x-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(B=\dfrac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(B=\dfrac{x^3-x^2+5x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(B=\dfrac{x^2\left(x-1\right)+5x\left(x-1\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(B=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)
Câu b và c dễ vì đã có kết quả rút gọn rồi :)

\(\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{5x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
a ) ĐKXĐ : \(x\ne0,x\ne-5\)
b ) Rút gọn trước cái đã
\(\dfrac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\dfrac{5x-5}{x}+\dfrac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+10x^2+50x-10x-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+12x^2+35x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x+7\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x+7}{2x}\)
Khi \(A=1\), thì :
\(\dfrac{x+7}{2x}=1\Leftrightarrow x=7\)
Khi A = 3, thì :
\(\dfrac{x+7}{2x}=3\Leftrightarrow x=-1.\)
Bài 2 :
a ) ĐKXĐ : x\(\ne-3;2\)
b ) \(\dfrac{x-2}{x+3}-\dfrac{5}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{1}{2-x}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)-5-\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2-x-12}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}\)
c ) Khi \(A=-\dfrac{3}{4}\), thì :
\(\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}=-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x-16=-3x+6\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{22}{7}\)
d ) Ta có :
\(A=\dfrac{x-4}{x-2}=\dfrac{x-2-2}{x-2}=1-\dfrac{2}{x-2}\)
Để A nguyên thi \(x-2\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
Thay vào rồi tìm ra nếu x có trong đkxđ thì loại .
e ) \(x^2-9=0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay từng x vào A là tìm ra

a: ĐKXĐ: x<>0; x<>-5
b: \(P=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+2\left(x^2-25\right)+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^3+2x^2+50-5x+2x^2-50}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\dfrac{x-1}{2}\)
Để P=0 thì x-1=0
=>x=1
c: Để P=-1/4 thì x-1/2=-1/4
=>x-1=-1/2
=>x=1/2
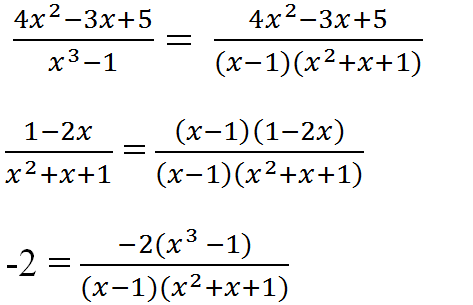
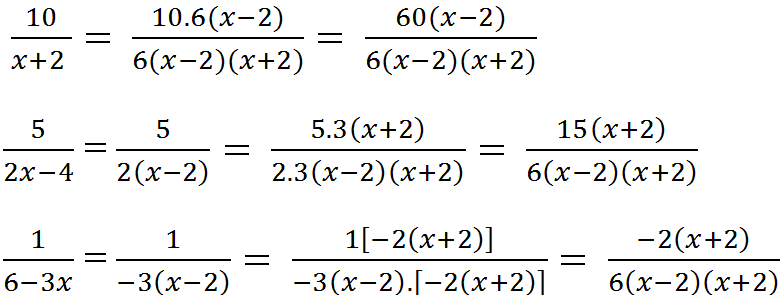

a) ĐK: \(x-5\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne5\)
b)
ĐK: \(\left(\dfrac{1}{2}x+4\right)\ne0\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{1}{2}x\ne-4\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ne-8\)
c)ĐK:
\(-2x-10\ne0\\ \Leftrightarrow-2x\ne10\\ \Leftrightarrow x\ne-5\)
a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne5\)
b) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-8\)
c) ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne-5\)