Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Sắp xếp các hạng tử của mỗi đa thức theo lũy thừa tăng của biến.
Thu gọn: P(x) = 3x2 - 5 + x4 - 3x3 - x6 - 2x2 - x3
= x2 - 5 + x4 - 4x3 - x6
Sắp xếp: P(x) = -5 + x2 - 4x3 + x4 - x6
Thu gọn: Q(x) = x3 + 2x5 - x4 + x2 - 2x3 + x - 1= -x3 +2x5 - x4 + x2 + x - 1
Sắp xếp: Q(x) = -1 + x + x2 - x3 - x4 + 2x5
b) Ta có:
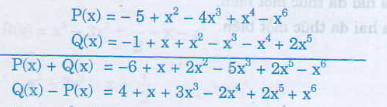 .
.
a) Sắp xếp các hạng tử của mỗi đa thức theo lũy thừa tăng của biến.
Thu gọn: P(x) = 3x2 - 5 + x4 - 3x3 - x6 - 2x2 - x3
= x2 - 5 + x4 - 4x3 - x6
Sắp xếp: P(x) = -5 + x2 - 4x3 + x4 - x6
Thu gọn: Q(x) = x3 + 2x5 - x4 + x2 - 2x3 + x - 1= -x3 +2x5 - x4 + x2 + x - 1
Sắp xếp: Q(x) = -1 + x + x2 - x3 - x4 + 2x5
b) Ta có:
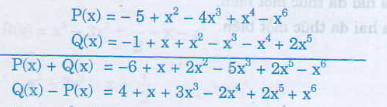

\(P\left(x\right)=5x^2+3x-4-2x^3+4x^2-6\)
\(P\left(x\right)=\left(5x^2+4x^2\right)+3x+\left(-4-6\right)-2x^3\)
\(P\left(x\right)=9x^2+3x-10-2x^3\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=2x^4-x+3x^2-2x^3+\frac{1}{4}-x^5\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=2x^4-x+3x^2-2x^3+\frac{1}{4}-x^5\)
Sắp giảm :
\(P\left(x\right)=-2x^3+9x^2+3x-10\)
\(Q\left(x\right)=-x^5+2x^4-2x^3+3x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}\)
\(A\left(x\right)=P\left(x\right)+Q\left(x\right)\)
\(A\left(x\right)\)= \(\left[\left(-2x^3+9x^2+3x-10\right)-\left(-x^5+2x^4-2x^3+3x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}\right)\right]\)
\(A\left(x\right)=\)\(-2x^3+9x^2+3x-10+x^5-2x^4+2x^3-3x^2+x-\frac{1}{4}\)
\(A\left(x\right)=\)\(\left(-2x^3+2x^3\right)+\left(9x^2-3x^2\right)+\left(3x-x\right)+\left(-10-\frac{1}{4}\right)+x^5-2x^4\)
\(A\left(x\right)=6x^2+2x-2,75+x^5-2x^4\)

a) \(P\left(x\right)=2+5x^2-3x^2+4x^2-2x-x^3+6x^5\)
\(P=6x^5-x^3+\left(5x^2-3x^2+4x^2\right)-2x+2\)
\(P=6x^5-x^2+6x^2-2x+2\)
b) Hệ số khác 0 của đa thức P(x): 6; -1; 6; -2; 2

a)P(x)=\(x^5-3x^2+7x^4-9x^3+x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}x\)
=\(x^5+7x^4-9x^3-2x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}x\)
Q(x)=\(5x^4-x^5+x^2-2x^3+3x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
=\(-x^5+5x^4-2x^3+4x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
b) P(x)=\(x^5+7x^4-9x^3-2x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}x\)
+ Q(x)=\(-x^5+5x^4-2x^3+4x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
__________________________________
P(x)+Q(x)= \(12x^4-11x^3+2x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}x-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
P(x)=\(x^5+7x^4-9x^3-2x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}x\)
- Q(x)=\(-x^5+5x^4-2x^3+4x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
_________________________________________
P(x)-Q(x)=\(2x^5+2x^4-7x^3-6x^2-\dfrac{1}{4}x-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
c)Thay x=0 vào đa thức P(x), ta có:
P(x)=\(0^5+7\cdot0^4-9\cdot0^3-2\cdot0^2-\dfrac{1}{4}\cdot0\)
=0+0-0-0-0
=0
Vậy x=0 là nghiệm của đa thức P(x).
Thay x=0 vào đa thức Q(x), ta có:
Q(x)=\(-0^5+5\cdot0^4-2\cdot0^3+4\cdot0^2-\dfrac{1}{4}\)
=0+0-0+0-\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
=0-\(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
=\(\dfrac{-1}{4}\)
Vậy x=0 không phải là nghiệm của đa thức Q(x).
a) Sắp xếp theo lũy thừa giảm dần
P(x)=x5−3x2+7x4−9x3+x2−14xP(x)=x5−3x2+7x4−9x3+x2−14x
=x5+7x4−9x3−2x2−14x=x5+7x4−9x3−2x2−14x
Q(x)=5x4−x5+x2−2x3+3x2−14Q(x)=5x4−x5+x2−2x3+3x2−14
=−x5+5x4−2x3+4x2−14=−x5+5x4−2x3+4x2−14
b) P(x) + Q(x) = (x5+7x4−9x3−2x2−1

a) x7-x4+2x3-3x4-x2+x7-x+5-x3
= 5-x-x2+(2x3-x3)-(x4+3x4)+(x7+x7)
= 5-x-x2+x3-4x4+2x7
Hệ số cao nhất là 2. Hệ số tự do là 5
b) 2x2-3x4-3x2-4x5-\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)x-x2+1
= 1-\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)x+(2x2-3x2-x2)-3x4-4x5
= 1-\(\dfrac{1}{2}\)x-2x2-3x4-4x5
Hệ số cao nhất là -4. Hệ số tự do là 1

1) \(A\left(x\right)=-5x^3+3x^4+\frac{5}{7}-8x^2-10x\)
\(A\left(x\right)=3x^4-5x^3-8x^2-10x+\frac{5}{7}\)
\(B\left(x\right)=-2x^4-\frac{2}{7}+7x^2+8x^3+6x\)
\(B\left(x\right)=-2x^4+8x^3+7x^2+6x-\frac{2}{7}\)
2) \(A\left(x\right)=3x^4-5x^3-8x^2-10x+\frac{5}{7}\)
+
\(B\left(x\right)=-2x^4+8x^3+7x^2+6x-\frac{2}{7}\)
\(A\left(x\right)+B\left(x\right)=x^4+3x^3-x^2-4x+\frac{3}{7}\)
\(A\left(x\right)=3x^4-5x^3-8x^2-10x+\frac{5}{7}\)
-
\(B\left(x\right)=-2x^4+8x^3+7x^2+6x-\frac{2}{7}\)
\(A\left(x\right)-B\left(x\right)=5x^4-13x^3-15x^2-16x+1\)

\(M\left(x\right)=P\left(x\right)+Q\left(x\right)=2,5x^6-4+2,5x^5-6x^3+2x^2\)-5x+\(3x-2,5x^6-x^2+5-2,5x^5+6x^3\)
=\(\left(2,5x^6-2,5x^6\right)\)+\(\left(2,5x^5-2,5x^5\right)\)\(\left(-6x^3+6x^3\right)\)+\(\left(2x^2-x^2\right)\)+\(\left(-5x+3x\right)\)+(-4+5)
= \(x^2-2x+1\)
P(x) = 3x2 – 5 + x4 – 3x3 – x6 – 2x2 – x3
= – x6 + x4 + (– 3x3 – x3) + (3x2 – 2x2) – 5
= – x6 + x4 – 4x3 + x2 – 5.
= – 5+ x2 – 4x3 + x4 – x6
Và Q(x) = x3 + 2x5 – x4 + x2 – 2x3 + x –1
= 2x5 – x4 + (x3 – 2x3) + x2 + x –1
= 2x5 – x4 – x3 + x2 + x –1.
= –1+ x + x2 – x3 – x4 + 2x5