Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

giả sử : \(\frac{mx+m}{\left(m+1\right)x-m+2}>0\)\(,\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{m.0+m}{\left(m+1\right).0-m+2}>0\) \(\Rightarrow\frac{m}{2-m}>0\)
\(\Rightarrow0\)\(<\)\(m<\)\(2\)
ngược lại \(0<\)\(m<2\) thì:
\(mx+m>0,\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\left(m+1\right)x\ge0>m-2,\)\(\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(m+1\right)x-m+2>0,\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{mx+m}{\left(m+1\right)x-m+2}>0,\text{∀}x\in\left[0;2\right]\)
vậy: \(0\)\(<\)\(m<\)\(2\) là kết quả cần tìm

với \(m=0\) : PT \(\left(1\right)\Leftrightarrow\) \(-2x+1=0\) \(\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{1}{2}\in\left(0;1\right)\)
với \(m\ne0\) : PT \(\left(1\right)\) có đúng 1 nghiệm \(\in\left(0;1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f\left(0\right).f\left(1\right)<0\)
( để ý: \(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-m=\)\(m^2+m+1>0,\text{∀}x\in R\))
\(\Leftrightarrow m-2\left(m+1\right)+1<0\) \(\Leftrightarrow m>-1\)
vậy \(m>-2\) là kết quả cần tìm
với m=0m=0 : PT (1)⇔(1)⇔ −2x+1=0−2x+1=0 ⇔x=12∈(0;1)⇔x=12∈(0;1)
với m≠0m≠0 : PT (1)(1) có đúng 1 nghiệm ∈(0;1)∈(0;1)
⇔f(0).f(1)<0⇔f(0).f(1)<0
( để ý: Δ′=(m+1)2−m=Δ′=(m+1)2−m=m2+m+1>0,∀x∈Rm2+m+1>0,∀x∈R)
⇔m−2(m+1)+1<0⇔m−2(m+1)+1<0 ⇔m>−1⇔m>−1
vậy m>−2m>−2 là kết quả cần tìm

Đáp án A
Phương pháp: Chia cả 2 vế cho 3x, đặt  , tìm điều kiện của t.
, tìm điều kiện của t.
Đưa về bất phương trình dạng ![]()
Cách giải :
![]()

Ta có 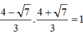
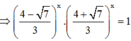
Đặt 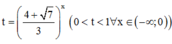 , khi đó phương trình trở thành
, khi đó phương trình trở thành
![]()
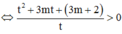
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Ta có: 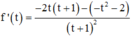
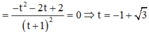
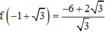
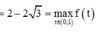
Vậy 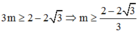

Câu 1 :
Đk: \(x\ge1\)
\(\sqrt{x-1}+\sqrt{2x-1}=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1+2\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)\left(2x-1\right)}+2x-1=25\\ \Leftrightarrow2\sqrt{2x^2-3x+1}=27-3x\\ \)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}27-3x\ge0\\4\left(2x^2-3x+1\right)=9x^2-162x+729\end{cases}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x\le9\\x^2-150x+725=0\end{cases}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}x\le9\\x=145hoặcx=5\end{cases}\)
với x= 5 thoản mãn điều kiện, x=145 loại
Vậy \(S=\left\{5\right\}\)

a) \(4x-7>0\Leftrightarrow4x>7\)\(\Leftrightarrow x>\frac{7}{4}\)
b) \(-5x+8>0\Leftrightarrow5x<8\Leftrightarrow x<\frac{8}{5}\)
c)\(9x-10\le0\Leftrightarrow9x\le10\)\(\Leftrightarrow x\le\frac{10}{9}\)
d) \(\left(x+1\right)^2+4\le x^2+3x+10\)\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x+1+4\le x^2+3x+10\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x\ge-5\Leftrightarrow x\ge-1\)
a,
4x - 7 > 0
↔ 4x > 7
↔ x > \(\dfrac{7}{4}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S = { x / x>\(\dfrac{7}{4}\) }
b,
-5x + 8 > 0
↔ 8 > 5x
↔ \(\dfrac{8}{5}\) > x
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S = { x / \(\dfrac{8}{5}\) > x }
c,
9x - 10 ≤ 0
↔ 9x ≤ 10
↔ x ≤ \(\dfrac{10}{9}\)
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S = { x / x ≤ \(\dfrac{10}{9}\) }
d,
( x - 1 )\(^2\) + 4 ≤ x\(^2\) + 3x + 10
↔ x\(^2\) - 2x +1 +4 ≤ x\(^2\) + 3x + 10
↔ 1 + 4 - 10 ≤ x \(^2\) - x\(^2\) + 3x + 2x
↔ -5 ≤ 5x
↔ -1 ≤ x
Vậy tập nghiệm của bất phương trình là S = { x / -1 ≤ x}

a) ĐK: \(x\ge0,x\ne1,x\ne\frac{1}{4}\)
\(A=1+\left(\frac{2x+\sqrt{x}-1}{1-x}-\frac{2x\sqrt{x}-\sqrt{x}+x}{1-x\sqrt{x}}\right)\frac{x-\sqrt{x}}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(A=1+\left[\frac{\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)}-\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\right]\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(A=1+\left[\frac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{1-\sqrt{x}}-\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(2\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(1-\sqrt{x}\right)\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\right]\frac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{2\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(A=1-\sqrt{x}+\frac{x\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}\)
\(A=\frac{x+1}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}\)
Để \(A=\frac{6-\sqrt{6}}{5}\Rightarrow\frac{x+1}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}=\frac{6-\sqrt{6}}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow5x+5=\left(6-\sqrt{6}\right)x+\left(6-\sqrt{6}\right)\sqrt{x}+6-\sqrt{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(1-\sqrt{6}\right)x+\left(6-\sqrt{6}\right)\sqrt{x}+1-\sqrt{6}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x-\sqrt{6}.\sqrt{x}+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}\sqrt{x}=\frac{\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{6}}{2}\\\sqrt{x}=\frac{-\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{6}}{2}\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=2+\sqrt{3}\\x=2-\sqrt{3}\end{cases}}\left(tmđk\right)\)
b) Xét \(A-\frac{2}{3}=\frac{x+1}{x+\sqrt{x}+1}-\frac{2}{3}=\frac{3x+3-2x-2\sqrt{x}-2}{3\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x-2\sqrt{x}+1}{3\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}=\frac{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{3\left(x+\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
Do \(x\ge0,x\ne1,x\ne\frac{1}{4}\Rightarrow\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2>0\)
Lại có \(x+\sqrt{x}+1=\left(\sqrt{x}+\frac{1}{2}\right)+\frac{3}{4}>0\)
Nên \(A-\frac{2}{3}>0\Rightarrow A>\frac{2}{3}\).
Khi đó bất phương trình trở thành
Suy ra hàm số f(x) đồng biến trên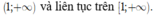
Do đó yêu cầu bài toán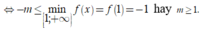
Chọn B.