Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: 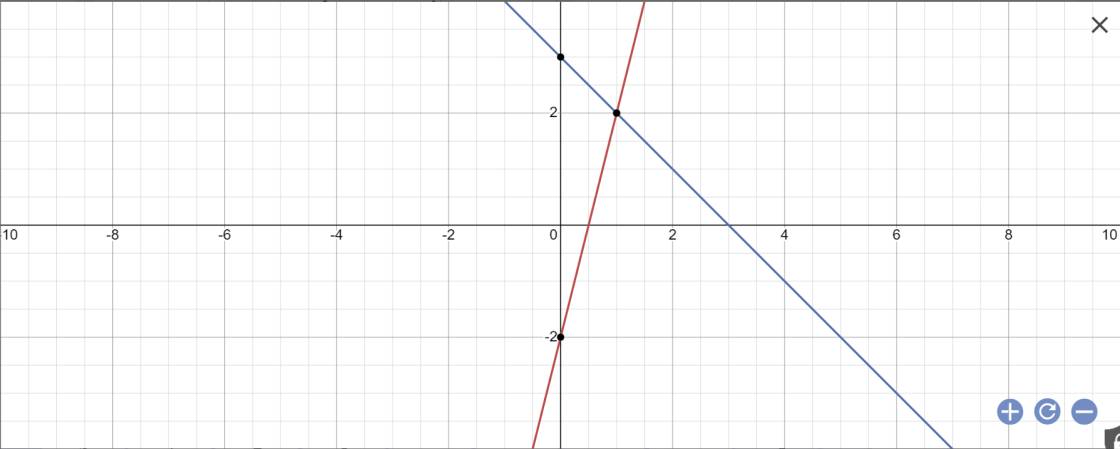
b: Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm là:
4x-2=-x+3
=>4x+x=3+2
=>5x=5
=>x=1
Thay x=1 vào y=-x+3, ta được:
\(y=-1+3=2\)
Vậy: M(1;2)
c: Gọi \(\alpha;\beta\) lần lượt là góc tạo bởi (d1),(d2) với trục Ox
(d1): y=4x-2
=>\(tan\alpha=4\)
=>\(\alpha=76^0\)
(d2): y=-x+3
=>\(tan\beta=-1\)
=>\(\beta=135^0\)
d: Thay y=6 vào (d1), ta được:
4x-2=6
=>4x=8
=>x=2
=>A(2;6)
Thay x=6/2=3 vào (d2), ta được:
\(y=-3+3=0\)
vậy: B(3;0)
Vì (d):y=ax+b đi qua A(2;6) và B(3;0) nên ta có hệ phương trình:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b=6\\3a+b=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2a+b-3a-b=6-0\\3a+b=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-a=6\\b=-3a\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-6\\b=-3\cdot\left(-6\right)=18\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: (d): y=-6x+18
e: A(2;6); B(3;0); M(1;2)
\(AM=\sqrt{\left(1-2\right)^2+\left(2-6\right)^2}=\sqrt{17}\)
\(BM=\sqrt{\left(1-3\right)^2+\left(2-0\right)^2}=2\sqrt{2}\)
\(AB=\sqrt{\left(3-2\right)^2+\left(0-6\right)^2}=\sqrt{37}\)
Chu vi tam giác AMB là:
\(C_{AMB}=\sqrt{17}+2\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{37}\)
Xét ΔAMB có
\(cosAMB=\dfrac{MA^2+MB^2-AB^2}{2\cdot MA\cdot MB}=\dfrac{17+8-37}{2\cdot2\sqrt{2}\cdot\sqrt{17}}=\dfrac{-3}{\sqrt{34}}\)
=>\(\widehat{AMB}\simeq121^0\) và \(sinAMB=\sqrt{1-\left(-\dfrac{3}{\sqrt{34}}\right)^2}=\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{34}}\)
Xét ΔAMB có
\(\dfrac{AB}{sinAMB}=\dfrac{AM}{sinABM}=\dfrac{BM}{sinBAM}\)
=>\(\dfrac{\sqrt{17}}{sinABM}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{2}}{sinBAM}=\sqrt{37}:\dfrac{5}{\sqrt{34}}\)
=>\(sinABM\simeq0,58;\widehat{BAM}\simeq0,4\)
=>\(\widehat{ABM}\simeq35^0;\widehat{BAM}\simeq24^0\)

\(b,\text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }2x+1=x-1\Leftrightarrow x=-2\Leftrightarrow y=-3\Leftrightarrow A\left(-2;-3\right)\\ c,\text{Gọi góc đó là }\alpha\\ \text{Vì }1>0\Leftrightarrow\alpha< 90^0\\ \text{Hệ số góc }\left(d_2\right):1\Leftrightarrow\tan\alpha=1\\ \Leftrightarrow\alpha=45^0\)

\(b,\text{PT hoành độ giao điểm: }-2x+5=x-1\Leftrightarrow x=2\Leftrightarrow y=1\Leftrightarrow A\left(2;1\right)\\ \text{Vậy }A\left(2;1\right)\text{ là giao điểm }\left(d_1\right)\text{ và }\left(d_2\right)\\ c,\text{Gọi }\left(d_3\right):y=ax+b\left(a\ne0\right)\text{ là đt cần tìm}\\ \left(d_3\right)\text{//}\left(d_1\right)\text{ và }M\left(-2;1\right)\in\left(d_3\right)\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-2\\b\ne5\\-2a+b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=-2\\b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(d_3\right):y=-2x-1\)
b) Lập phương trình hoành độ giao điểm ta có;
2x - 1 = -x+2
-> 2x + x =2+1
-> 3x = 3
-> x = 1
Thay x=1 vào hàm số y = 2x - 1 ta được y= 2-1 = 1
Vậy tọa độ giao điểm M ( 1;1)
c) Thao đn TSLG có :
tanABO = \(\frac{1}{0,5}\)= 2
-> ABO ( bạn thêm kí hiệu góc vào ) \(\approx\) 63độ 26phut
Gọi \(\alpha\)là góc tạo bởi hàm số y=2x-1 và trục 0x ta có \(\alpha\)= ABO ( bạn thêm kí hiệu góc vào ) ( đối đỉnh) = 63độ 26phut
a) Xét hàm số y=2x-1 ( x\(\in\)R)
Cho x=0 -> y=-1 -> A( 0;-1)
Cho y=0 -> x= 0.5 -> B ( 0.5 : 0)
Xét hàm số y= -x+2 ( x \(\in\)R)
Cho x=0 -> y=2 -> C (0;2)
Cho y =0-> x= 2 -> D( 2;0)
vẽ đồ thị