Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

LEARN THIS! not much, not many, a lot of. a little, a few
a. We use not much or a little + uncountable noun for a small quantity of something.
(Ta dùng not much hoặc a little + danh từ không đếm được cho một lượng nhỏ của một thứ gì đó.
b. We use not many or a few + plural noun for a small number of something.
(Ta dùng not many hoặc a few + danh từ số nhiều cho số lượng nhỏ của một thứ gì đó.)
c. We use much + uncountable noun for a large quantity of something.
(Ta dùng much + danh từ không đếm được cho một lượng lớn của một thứ gì đó.)
d We use many + plural noun for a large number of something.
(Ta dùng many + danh từ số nhiều cho một số lượng lớn của một thứ gì đó.)
e. We use a lot of + uncountable or plural noun for a large quantity or number of something.
(Ta dùng a lot of + danh từ không đếm được hoặc danh từ số nhiều cho một lượng lớn hoặc một số lượng của một thứ gì đó.)
f. We use how much …? + uncountable noun or how many …? + plural noun for questions about quantity or number.
(Ta dùng how much…? + danh từ không đếm được hoặc how many…? + danh từ đếm được cho câu hỏi về lượng hoặc số lượng.)

1. present simple
2. present continuous
3. present continuous
4. present simple
5. present simple
6. present continuous

co-creator (đồng sáng lập), ex-student (cựu sinh viên), overestimate (đánh giá quá cao), postgraduate (sau đại học), semiprofessional (bán chuyện nghiệp), undervalue (coi thường), oversleep (ngủ nướng).

a. the toughest
b. the biggest
c. the most powerful; the most difficult
d. the worst
e. one of the biggest tsunamis
f. the most powerful (earthquake ever) in Japan; the (fifth) most powerful in the world
a: the toughest
b: the biggest
c: the most powerful, the most difficult
d: the worst
e: one of the biggest tsunamis
f:. the most powerful (earthquake ever) in Japan; the (fifth) most powerful in the world

acceptable - unacceptable (chấp nhận – không chấp nhận)
dependent – independent (phụ thuộc – độc lập)
fair – unfair (công bằng – không công bằng)
honest - dishonest (thật thà – dối trá)
legal – illegal (hợp pháp – bất hợp pháp)
likely - unlikely (giống – không giống)
surprising - unsurprising (bất ngờ - không bất ngờ)
visible – invisible (có thể nhìn thấy – tàng hình)

a. We use the second conditional to describe an unreal or imaginary situation and its result.
(Chúng ta dùng câu điều kiện loại 2 để mô tả những sự kiện không có thật hoặc tưởng tượng ra và kết quả của chúng.)
If shops didn't exist (imaginary situation), we would buy (result) everything online.
(Nếu các cửa hàng không tồn tại (tình huống tưởng tượng), chúng ta sẽ mua (kết quả) mọi thứ trên mạng.)
We use the (1) past simple in the if clause and we use (2) would + (3) infinite in the main clause.
(Chúng ta sử dụng thì quá khứ đơn trong mệnh đề if và dùng would + nguyên mẫu không to trong mệnh đề chính.)
b. We can put the main clause first. In this case, we don't need the comma.
(Ta có thể để mệnh đề chính lên trước. Trong trường hợp này, ta không cần dấu phẩy.)
I'd buy you a present if I had enough money.
(Tôi sẽ mua cho cậu một món quà nếu tôi có đủ tiền.)
c. We use could to mean would + be able to. It is also the past simple of can.
(Ta dùng could với nghĩa là would + be able to. Nó cũng là thể quá khứ đơn của can.)
If I won the lottery, I could stop work.
(Nếu tôi thắng xổ số, tôi có thể nghỉ việc.)
If she could speak English, she'd get a job in the USA.
(Nếu cô ấy có thể nói tiếng Anh, cô ấy có thể có việc ở Mỹ.)
The world would be much better if money didn’t exist.
If money didn’t exist, how would you buy things?
If you needed something, you would make it.
If you couldn’t make it, you would swap with somebody else.
So if I wanted a new mobile phone, how would I get it?
If money didn’t exist, life wouldn’t be better for poor people.
If nobody had any money, everybody would be equal.

Rule a:
+ Harris Aslam is an ambitious young man who left school at the age of thirteen to work in his family's grocery business.
(Harris Aslam là một chàng trai trẻ đầy tham vọng, bỏ học năm 13 tuổi để làm việc trong công việc kinh doanh tạp hóa của gia đình.)
+ Now, at the age of eighteen, he owns three shops in Kirkcaldy, Scotland, the town where he was born and broupht up.
(Bây giờ, ở tuổi mười tám, anh sở hữu ba cửa hàng ở Kirkcaldy, Scotland, thị trấn nơi anh sinh ra và lớn lên.)
+ The job he is now applying for is CEO of Nisa Retail, a grocery business whose annual sales are about £1.6 billion!
(Công việc hiện anh đang ứng tuyển là Giám đốc điều hành của Nisa Retail, một công ty kinh doanh tạp hóa có doanh thu hàng năm khoảng 1,6 tỷ bảng Anh!)

LEARN THIS! Past perfect (Thì quá khứ hoàn thành)
a. We form the past perfect with (1) had or (2) hadn’t and the past participle.
(Chúng ta tạo thì quá khứ hoàn thành với had hoặc hadn’t với động từ ở thể quá khứ phân từ.)
b. We use the past perfect when we are already talking about past events and we want to talk about an even earlier event.
(Chúng ta dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành khi ai đó đang nói về những sự kiện xảy ra trong quá khứ và chúng ta muốn nói đến những sự kiện trước đó nữa.)
When I got to the classroom, the lesson had started.
(Khi mình đến lớp thì bài học đã bắt đầu.)
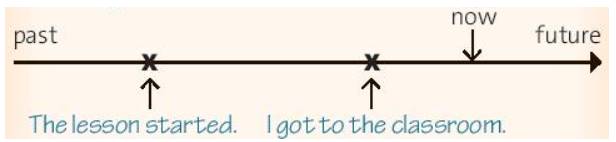
c. We often use the past perfect with after, before or when.
(Chúng ta thường dùng thì quá khứ hoàn thành với after, before hoặc when.)
Before I got to the bus station, the bus had already left.
(Trước khi mình đến trạm xe buýt, thì xe buýt đã đi mất.)
After I’d called Maggie, I watched a film on TV.
(Sau khi mình gọi cho Maggie, mình xem một bộ phim trên TV.)
had thrown … away; had risen; had increased; had spilled; had kept; had sold; had thrown; had … forgotten; hadn’t saved
some: some important differences; some hobbies
any: any countries or continents; any coal or oil; any food; any special missions
LEARN THIS! some and any
We use some and any with uncountable and plural countable nouns. (Chúng ta dùng some và any với những danh từ không đếm được và danh từ đếm được ở dạng số nhiều.)
a. We use some in affirmative sentences. (Ta dùng some cho câu khẳng định.)
b. We use any in negatives sentences and questions. (Ta dùng any cho câu phủ định và câu nghi vấn.)