Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Xí câu BĐT:
ta cần chứng minh \(\dfrac{a^2}{b^2c}+\dfrac{b^2}{c^2a}+\dfrac{c^2}{a^2b}\ge\dfrac{ab+bc+ca}{abc}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{a^3}{b}+\dfrac{b^3}{c}+\dfrac{c^3}{a}\ge ab+bc+ca\)
Áp dụng BĐT cauchy:
\(\dfrac{a^3}{b}+ab\ge2\sqrt{\dfrac{a^3}{b}.ab}=2a^2\)
tương tự ta có:\(\dfrac{b^3}{c}+bc\ge2b^2;\dfrac{c^3}{a}+ac\ge2c^2\)
cả 2 vế các BĐT đều dương,cộng vế với vế ta có:
\(\dfrac{a^3}{b}+\dfrac{b^3}{c}+\dfrac{c^3}{a}+ab+bc+ca\ge2a^2+2b^2+2c^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{a^3}{b}+\dfrac{b^3}{c}+\dfrac{c^3}{a}\ge2\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)-\left(ab+bc+ca\right)\)
mà a2+b2+c2\(\ge ab+bc+ca\) ( chứng minh đầy đủ nhá)
do đó \(S=\dfrac{a^3}{b}+\dfrac{b^3}{c}+\dfrac{c^3}{a}\ge2\left(ab+bc+ca\right)-ab+bc+ca=ab+bc+ca\)
suy ra BĐT ban đầu đúng
dấu = xảy ra khi và chỉ khi a=b=c.
P/s: cách khác :Áp dụng BĐT cauchy-schwarz:
\(\dfrac{a^3}{b}+\dfrac{b^3}{c}+\dfrac{c^3}{a}=\dfrac{a^4}{ab}+\dfrac{b^4}{bc}+\dfrac{c^4}{ca}\ge\dfrac{\left(a^2+b^2+c^2\right)^2}{ab+bc+ca}\)
\(S\ge\dfrac{\left(ab+bc+ca\right)^2}{ab+bc+ca}=ab+bc+ca\)
Câu hệ này =))
b, Từ hệ đã cho ta thấy x,y > 0
Trừ vế cho vế pt (1) và (2) của hệ ta được:
\(x^4-y^4=4y-4x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)=4\left(y-x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)+4\left(x-y\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y\right)\left[\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)+4\right]=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-y=0\) ( Vì \(\left(x+y\right)\left(x^2+y^2\right)+4>0\) với x,y > 0)
\(\Leftrightarrow x=y\)
Với x = y thay vào pt đầu của hệ ta được:
\(x^4-4x+3=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^3+x^2+x-3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x^2+2x+3\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=0\) ( Vì \(x^2+2x+3>0\) )
\(\Leftrightarrow x=1\)
Với x=1 suy ra y=1
Vậy hệ đã cho có nghiệm duy nhất (x;y) = (1;1)

Bài 2:
a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2-x+y-3x-3y=5\\3x-3y+5x+5y=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-4x-2y=3 và 8x+2y=-2
=>x=1/4; y=-2
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{5}{y-1}=1\\\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{y-1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y-1=5\\\dfrac{1}{x-2}=1-\dfrac{1}{5}=\dfrac{4}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>y=6 và x-2=5/4
=>x=13/4; y=6
c: =>x+y=24 và 3x+y=78
=>-2x=-54 và x+y=24
=>x=27; y=-3
d: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\sqrt{x-1}-6\sqrt{y+2}=4\\2\sqrt{x-1}+5\sqrt{y+2}=15\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-11\sqrt{y+2}=-11\\\sqrt{x-1}=2+3\cdot1=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>y+2=1 và x-1=25
=>x=26; y=-1

Ta có:
\(Q=\dfrac{2002}{a}+\dfrac{2017}{b}+2996a-5501b\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2002}{a}+8008a\right)+\left(\dfrac{2017}{b}+2017b\right)-\left(5012a+7518b\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{2002}{a}+8008a\right)+\left(\dfrac{2017}{b}+2017b\right)-2506\left(2a+3b\right)\)
Áp dụng BĐT Cauchy cho hai số không âm ta có:
\(\dfrac{2002}{a}+8008a\ge2\sqrt{\dfrac{2002}{a}.8008a}=2.4004=8008\) (1)
\(\dfrac{2017}{b}+2017b\ge2\sqrt{\dfrac{2017}{b}.2017b}=2.2017=4034\) (2)
Có \(2a+3b\le4\Rightarrow-\left(2a+3b\right)\ge-4\Rightarrow-2506\left(2a+3b\right)\ge-10024\)(3)
Từ (1), (2) và (3) \(\Rightarrow Q\ge8008+4034-10024=2018\)
Dấu '=' xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2002}{a}=8008a\\\dfrac{2017}{b}=2017b\\2a+3b=4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{1}{2}\\b=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy,...
![]()

3a)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x-2}+\dfrac{1}{2y-1}=2\\\dfrac{2}{x-2}-\dfrac{3}{2y-1}=1\end{matrix}\right.\) (ĐK: x≠2;y≠\(\dfrac{1}{2}\))
Đặt \(\dfrac{1}{x-2}=a;\dfrac{1}{2y-1}=b\) (ĐK: a>0; b>0)
Hệ phương trình đã cho trở thành
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=2\\2a-3b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2-b\\2\left(2-b\right)-3b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2-b\\4-2b-3b=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=2-b\\b=\dfrac{3}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{7}{5}\left(TM\text{Đ}K\right)\\b=\dfrac{3}{5}\left(TM\text{Đ}K\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) Khi đó \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x-2}=\dfrac{7}{5}\\\dfrac{1}{2y-1}=\dfrac{3}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7\left(x-2\right)=5\\3\left(2y-1\right)=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7x-14=5\\6y-3=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{19}{7}\left(TM\text{Đ}K\right)\\y=\dfrac{4}{3}\left(TM\text{Đ}K\right)\end{matrix}\right.\) Vậy hệ phương trình đã cho có nghiệm duy nhất (x;y)=\(\left(\dfrac{19}{7};\dfrac{4}{3}\right)\)
b) Bạn làm tương tự như câu a kết quả là (x;y)=\(\left(\dfrac{12}{5};\dfrac{-14}{5}\right)\)
c)\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\sqrt{x-1}+2\sqrt{y}=13\\2\sqrt{x-1}-\sqrt{y}=4\end{matrix}\right.\)(ĐK: x≥1;y≥0)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\sqrt{x-1}+2\sqrt{y}=13\\\sqrt{y}=2\sqrt{x-1}-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\sqrt{x-1}+4\sqrt{x-1}=13\\\sqrt{y}=2\sqrt{x-1}-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}7\sqrt{x-1}=13\\\sqrt{y}=2\sqrt{x-1}-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}49\left(x-1\right)=169\\\sqrt{y}=2\sqrt{x-1}-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}49x-49=169\\\sqrt{y}=2\sqrt{x-1}-4\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{218}{49}\\y=\dfrac{4}{49}\end{matrix}\right.\left(TM\text{Đ}K\right)\)
Bài 4:
Theo đề, ta có hệ:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\left(3a-2\right)-2\left(2b+1\right)=30\\3\left(a+2\right)+2\left(3b-1\right)=-20\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>9a-6-4b-2=30 và 3a+6+6b-2=-20
=>9a-4b=38 và 3a+6b=-20+2-6=-24
=>a=2; b=-5

\(P=\dfrac{4}{2\sqrt{a+3}}+\dfrac{2}{2\sqrt{b+3}}\ge\dfrac{4}{\dfrac{a+3+4}{2}}+\dfrac{2}{\dfrac{b+3+4}{2}}\)
\(\Rightarrow P\ge\dfrac{16}{2a+14}+\dfrac{4}{b+7}\ge\dfrac{\left(4+2\right)^2}{2a+b+21}\ge\dfrac{36}{3+21}=\dfrac{3}{2}\)
\(\Rightarrow P_{min}=\dfrac{3}{2}\) khi \(a=b=1\)

a: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\left(x+2\right)\left(y+3\right)-xy=100\\xy-\left(x-2\right)\left(y-2\right)=64\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>xy+3x+2y+6-xy=100 và xy-xy+2x+2y-4=64
=>3x+2y=94 và 2x+2y=68
=>x=26 và x+y=34
=>x=26 và y=8
b: \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{3x+3+2}{x+1}-\dfrac{2}{y+4}=4\\\dfrac{2x+2-2}{x+1}-\dfrac{5y+20-11}{y+4}=9\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{2}{x+1}-\dfrac{2}{y+4}=4-3=1\\\dfrac{-2}{x+1}+\dfrac{11}{y+4}=9+5-2=12\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>x+1=18/35; y+4=9/13
=>x=-17/35; y=-43/18

Giải hệ sau :
Câu a :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=-1\\2x+y=1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=-1\\-x=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=-1\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-3\\x=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy ...........................
Câu b :
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}=a\\\dfrac{1}{y}=b\end{matrix}\right.\) . Ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a+b=\dfrac{1}{5}\\3a+4b=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3a+3b=\dfrac{3}{5}\\3a+4b=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-b=-\dfrac{7}{5}\\3a+4b=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}b=\dfrac{7}{5}\\a=-\dfrac{6}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}=\dfrac{7}{5}\\\dfrac{1}{y}=-\dfrac{6}{5}\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{7}\\y=-\dfrac{5}{6}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy..................
\(a,\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=4\\x+5y=3\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-y=4\\2x+10y=6\end{matrix}\right.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}11y=2\\2x+10y=6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{2}{11}\\2x+10.\dfrac{2}{11}=6\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{2}{11}\\2x=\dfrac{46}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{2}{11}\\x=\dfrac{23}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(a.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=12\\\dfrac{1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{y}=-3\end{matrix}\right.\) (1)
ĐK xác định : x≠0 ; y≠0
Đặt ẩn phụ : a = \(\dfrac{1}{x}\) ; b = \(\dfrac{1}{y}\)
Thay vào (1) ta được :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}4a+b=12\\a+b=-3\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3a=15\\a+b=-3\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=5\\b=-8\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{1}{5}\\y=-\dfrac{1}{8}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S = {(\(\dfrac{1}{5};-\dfrac{1}{8}\))}
\(b.\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5\dfrac{1}{x}+2\dfrac{1}{y}=6\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=3\end{matrix}\right.\) (2)
ĐK xác định : x≠0 ; y≠0
Đặt ẩn phụ : a = 1/x ; b = 1/y
Thay vào (2) ta được : \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5a+2b=6\\2a-b=3\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}5a+2b=6\\4a-2b=6\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}9a=12\\2a-b=3\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=\dfrac{4}{3}\\b=-\dfrac{1}{3}\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{3}{4}\\y=-3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S = {(\(\dfrac{3}{4};-3\) )}
c) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\dfrac{1}{x}-6\dfrac{1}{y}=2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.\)
ĐK xác định : x≠0 ; y ≠0
Áp dụng quy tác cộng đại số ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\dfrac{1}{x}-6\dfrac{1}{y}=2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\dfrac{1}{x}-6\dfrac{1}{y}=2\\3\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=15\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=-13\\\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{3}{13}\\x=\dfrac{3}{28}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S = {(\(\dfrac{3}{28};\dfrac{3}{13}\))}
d) \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-4\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
ĐK xác định : x≠0 ; y≠0
áp dụng quy tắc cộng đại số ta có :
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-4\dfrac{1}{y}=5\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2\dfrac{1}{x}-8\dfrac{1}{y}=10\\2\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=1\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-5\dfrac{1}{y}=9\\\dfrac{1}{x}-4\dfrac{1}{y}=5\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=-\dfrac{5}{9}\\x=-\dfrac{5}{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S = {(\(-\dfrac{5}{11};-\dfrac{5}{9}\))}
e) ĐK xác định x≠0 ; y≠0
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=4\\6\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=2\end{matrix}\right.< =>\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=4\\18\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=6\end{matrix}\right.\) <=> \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-17\dfrac{1}{x}=-2\\\dfrac{1}{x}-3\dfrac{1}{y}=4\end{matrix}\right.\) <=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{17}{2}\\y=-\dfrac{17}{22}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy S={(\(\dfrac{17}{2};-\dfrac{17}{22}\))}

Bài này mình làm lâu rồi á bann sửa dấu `2a+3b<=4` thành `2a+3b=4` nhé!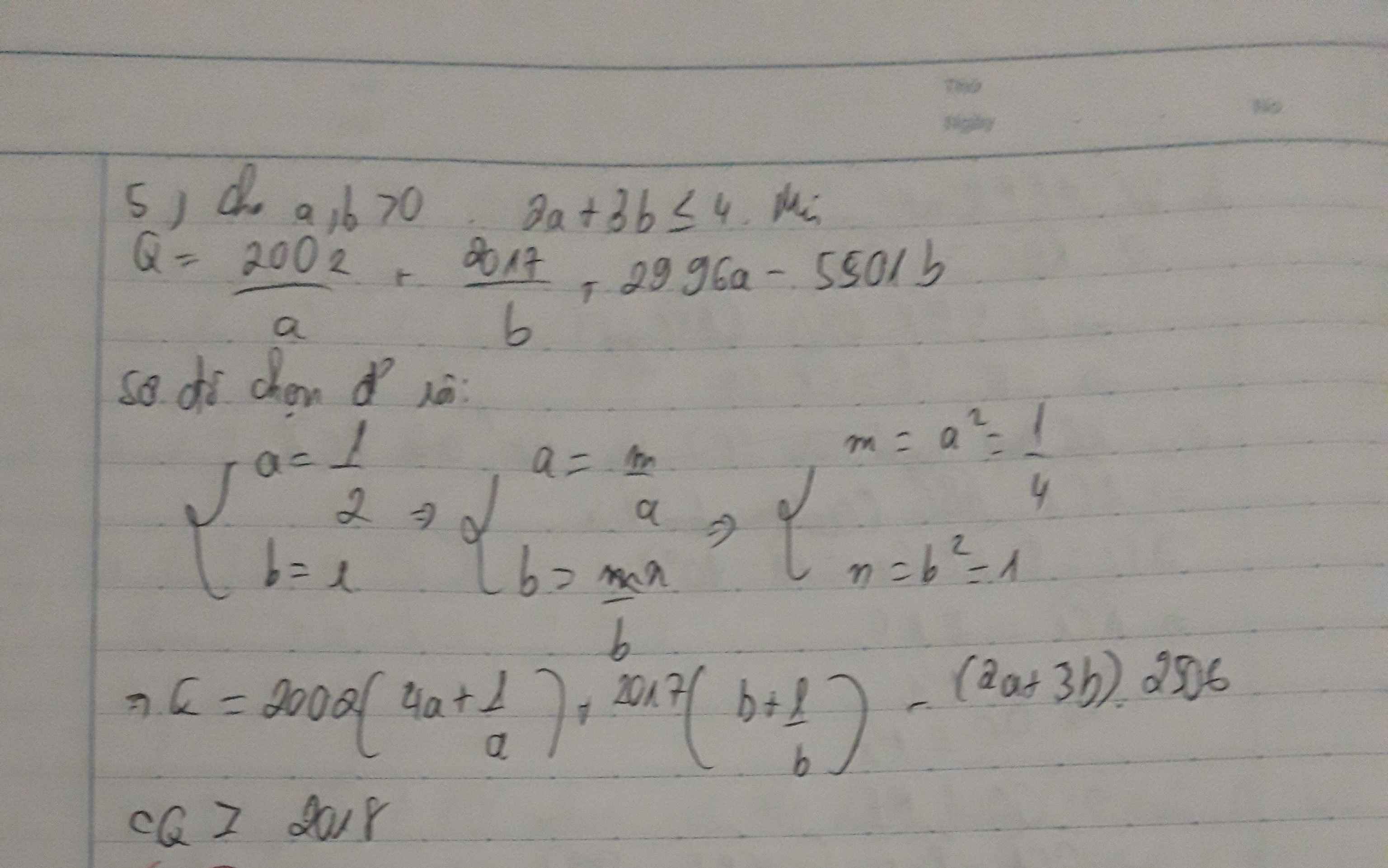
Bài này mình làm lâu rồi á bann sửa dấu 2a+3b≤42a+3b≤4 thành 2a+3b=42a+3b=4 nhé!
Là 2a+3b≤42a+3b≤4 ⇒ 2a+3b=42a+3b=4
hay 2a+3b=42a+3b=4 ⇒ 2a+3b≤42a+3b≤4