
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


b: \(B=\dfrac{2x-8+x+20}{\left(x+4\right)\left(x-4\right)}=\dfrac{3x+12}{\left(x+4\right)\left(x-4\right)}=\dfrac{3}{x-4}\)

\(A=\left(\dfrac{-\left(x+2\right)}{x-2}-\dfrac{4x^2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}+\dfrac{x-2}{x+2}\right)\cdot\dfrac{x^2\left(2-x\right)}{4x\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-x^2-4x-4-4x^2+x^2-4x+4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-x\left(x-2\right)}{4\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{-4x^2-8x}{x+2}\cdot\dfrac{-x}{4\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{-4x\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)}\cdot\dfrac{-x}{4\left(x-3\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2}{x-3}\)

Lời giải:
a)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\neq 0; x\neq - 1\)
\(M=\frac{(x+2)(x+1)+2.3x-3.3x(x+1)}{3x(x+1)}:\frac{2-4x}{x+1}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}\)
\(=\frac{-8x^2+2}{3x(x+1)}.\frac{x+1}{2-4x}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}=\frac{2(1-4x^2)}{3x(2-4x)}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}\)
\(=\frac{2(1-2x)(1+2x)}{6x(1-2x)}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}=\frac{1+2x}{3x}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}=\frac{x^2-x}{3x}=\frac{x-1}{3}\)
b)
Khi $x=2006\Rightarrow M=\frac{2006-1}{3}=\frac{2005}{3}$
c)
\(M< 0\Leftrightarrow \frac{x-1}{3}< 0\Leftrightarrow x-1< 0\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ suy ra $x< 1; x\neq 0; x\neq -1$
d)
Để \(\frac{1}{M}=\frac{3}{x-1}\in\mathbb{Z}\) thì \(3\vdots x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\in\left\{\pm 1;\pm 3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2;-2;4\right\}\)
Kết hợp đkxđ suy ra $x\in\left\{-2;2;4\right\}$
Lời giải:
a)
ĐKXĐ: \(x\neq 0; x\neq - 1\)
\(M=\frac{(x+2)(x+1)+2.3x-3.3x(x+1)}{3x(x+1)}:\frac{2-4x}{x+1}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}\)
\(=\frac{-8x^2+2}{3x(x+1)}.\frac{x+1}{2-4x}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}=\frac{2(1-4x^2)}{3x(2-4x)}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}\)
\(=\frac{2(1-2x)(1+2x)}{6x(1-2x)}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}=\frac{1+2x}{3x}-\frac{3x-x^2+1}{3x}=\frac{x^2-x}{3x}=\frac{x-1}{3}\)
b)
Khi $x=2006\Rightarrow M=\frac{2006-1}{3}=\frac{2005}{3}$
c)
\(M< 0\Leftrightarrow \frac{x-1}{3}< 0\Leftrightarrow x-1< 0\Leftrightarrow x< 1\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ suy ra $x< 1; x\neq 0; x\neq -1$
d)
Để \(\frac{1}{M}=\frac{3}{x-1}\in\mathbb{Z}\) thì \(3\vdots x-1\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\in\left\{\pm 1;\pm 3\right\}\)
\(\Rightarrow x\in\left\{0;2;-2;4\right\}\)
Kết hợp đkxđ suy ra $x\in\left\{-2;2;4\right\}$

\(a,P=\dfrac{2x^2+2x+2+2x-1+x^2+6x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\\ P=\dfrac{3x^2+10x+3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)

\(P=\dfrac{x-5}{x-4}:\dfrac{x-5}{2x}=\dfrac{2x}{x-4}\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(\dfrac{2x}{x-4}\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(\dfrac{2\left(x-4\right)+8}{x-4}\in Z\)
\(\Rightarrow\)\(2+\dfrac{8}{x-4}\in Z\Rightarrow\)\(\dfrac{8}{x-4}\in Z\Rightarrow x-4\inƯ\left(8\right)=\left\{...\right\}\)
Bạn làm tiếp nhé!

a: ĐKXĐ: x<>1
Sửa đề: \(C=\dfrac{5x+1}{x^3-1}+\dfrac{2x-1}{x^2+x+1}+\dfrac{2}{x-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{5x+1+\left(2x-1\right)\left(x-1\right)+2x^2+2x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x^2+7x+3+2x^2-2x-x+1}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4x^2+4x+4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}=\dfrac{4}{x-1}\)
b: |x|=4
=>x=4 hoặc x=-4
Khi x=4 thì \(C=\dfrac{4}{4-1}=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
Khi x=-4 thì \(C=\dfrac{4}{-4-1}=\dfrac{4}{-5}=\dfrac{-4}{5}\)
c: C>0
=>4/x-1>0
=>x-1>0
=>x>1
d: C nguyên
=>x-1 thuộc {1;-1;2;-2;4;-4}
=>x thuộc {2;0;3;-1;5;-3}
Trong xu thế hội nhập hiện nay, hợp tác quốc tế là vấn đề quan trọng và tất yếu của mỗi quốc gia, dân tộc trên thế giới. Trong những năm gần đây, Việt Nam đã và đang trở thành một trong những điển hình về hợp tác quốc tế
a, từ nhận định trên em hãy cho biết hợp tác là gì? cơ sở và nguyên tắc của đang và nhà nước ta?
b, nêu 1 số thành quả hợp tác giữa các nước ta và các nước trên thế giới? từ đó em hãy cho biết hộc sinh hiên nay cần phải làm gì để rèn luyện tinh thần hợp tác

a, Để B xác định
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-2\ne0\\x+2\ne0\\4-x^2\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ne2\\x\ne-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(b,B=\dfrac{3}{x-2}+\dfrac{-2}{x+2}-\dfrac{x-14}{4-x^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{-2\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\dfrac{x-14}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3x+6-2x+4+x-14}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2x-4}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{2}{x+2}\)
c, Đẻ B có giá trị nguyên
\(\Leftrightarrow2⋮x+2\Leftrightarrow x+2\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
Ta có bẳng sau:
| \(x+2\) | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 |
| 2 | -1 | -3 | 0 | -4 |
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-1;-3;0;-4\right\}\) thì B có giá trị nguyên

Bổ sung phần c và d luôn:
c, C = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5(x2 - 1) = 2(2x2 + 3)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5x2 - 5 = 4x2 + 6
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = 11
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 - 11 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) (x - \(\sqrt{11}\))(x + \(\sqrt{11}\)) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{11}=0\\x+\sqrt{11}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\\x=-\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
d, Ta có: \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{5}{2}}{2\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) - \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\)
C nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) 5 \(⋮\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) \(\in\) Ư(5)
Xét các TH:
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-1}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-11}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{11}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-5}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{5}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-7}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{7}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
Vậy không có giá trị nào của x \(\in\) Z thỏa mãn C \(\in\) Z
Chúc bn học tốt! (Ko bt đề sai hay ko nữa :v)

a) đk: x khác 0;1
\(A=\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x}+\dfrac{1}{x-1}+\dfrac{2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\right)\)
= \(\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\left[\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)+x+2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\right]\)
= \(\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}:\dfrac{x^2-1+x+2-x^2}{x\left(x-1\right)}\)
= \(\dfrac{x\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}.\dfrac{x\left(x-1\right)}{x+1}=\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}\)
b) Để \(\left|2x-5\right|=3\)
<=> \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-5=3< =>2x=8< =>x=4\left(c\right)\\2x-5=-3< =>2x=2< =>x=1\left(l\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Thay x = 4 vào A, ta có:
\(A=\dfrac{4^2}{4-1}=\dfrac{16}{3}\)
c) Để A = 4
<=> \(\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}=4\)
<=> \(\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}-4=0< =>\dfrac{x^2-4x+4}{x-1}=0\)
<=> \(\left(x-2\right)^2=0\)
<=> x = 2 (T/m)
d) Để A < 2
<=> \(\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}< 2< =>\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}-2< 0< =>\dfrac{x^2-2x+2}{x-1}< 0\)
<=> \(\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2+1}{x-1}< 0\)
Mà \(\left(x-1\right)^2+1>0\)
<=> x - 1 < 0 <=> x < 1
KHĐK: x < 1 ( x khác 0)
e) Để A thuộc Z
<=> \(\dfrac{x^2}{x-1}\in Z\)
<=> \(x^2⋮x-1\)
<=> \(x^2-x\left(x-1\right)-\left(x-1\right)⋮x-1\)
<=> \(1⋮x-1\)
Ta có bảng:
| x-1 | 1 | -1 |
| x | 2 | 0 |
| T/m | T/m |
KL: Để A thuộc Z <=> \(x\in\left\{2;0\right\}\)
f) Để A thuộc N <=> \(x\in\left\{2;0\right\}\)
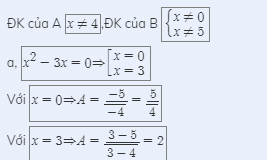

Để A nguyên thì x^2 chia hết cho x+1
=>x^2-1+1 chia hết cho x+1
=>\(x+1\in\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{0;-2\right\}\)