Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 5:
\(x^2+2mx+2m-6=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=\left(2m\right)^2-4\left(2m-6\right)\)
\(=4m^2-8m+24\)
\(=4m^2-8m+4+20\)
\(=\left(2m-2\right)^2+20>=20>0\forall m\)
=>Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt
Theo Vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{b}{a}=\dfrac{-2m}{1}=-2m\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{2m-6}{1}=2m-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=2x_1x_2+20\)
=>\(\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2-2x_1x_2=20\)
=>\(\left(-2m\right)^2-4\left(2m-6\right)=20\)
=>\(4m^2-8m+24-20=0\)
=>\(4m^2-8m+4=0\)
=>\(\left(2m-2\right)^2=0\)
=>2m-2=0
=>2m=2
=>m=1(nhận)
Câu 4:
a: \(2x^2-2x-m=0\)
\(\text{Δ}=\left(-2\right)^2-4\cdot2\cdot\left(-m\right)\)
\(=4+8m\)
Để phương trình có hai nghiệm phân biệt thì 8m+4>0
=>8m>-4
=>\(m>-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b: Theo Vi-et, ta có:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{-b}{a}=\dfrac{-\left(-2\right)}{2}=\dfrac{2}{2}=1\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{c}{a}=\dfrac{-m}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1-x_1x_2\right)^2+4\cdot\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)=16\)
=>\(\left(1+\dfrac{m}{2}\right)^2+4\cdot\left[\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\right]=16\)
=>\(\left(\dfrac{m+2}{2}\right)^2+4\left[1^2-2\cdot\dfrac{-m}{2}\right]=16\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{4}\left(m^2+4m+4\right)+4\left(1+m\right)=16\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{4}m^2+m+1+4+4m-16=0\)
=>\(\dfrac{1}{4}m^2+5m-11=0\)
=>\(m^2+20m-44=0\)
=>(m+22)(m-2)=0
=>\(\left[{}\begin{matrix}m+22=0\\m-2=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=-22\left(loại\right)\\m=2\left(nhận\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
5.
\(\Delta'=1+2m\)
a.
Phương trình có 2 nghiệm pb khi:
\(1+2m>0\Rightarrow m>-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
b.
Khi pt có 2 nghiệm, theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=1\\x_1x_2=-\dfrac{m}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(1-x_1x_2\right)^2+4\left(x_1^2+x_2^2\right)=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1-x_1x_2\right)^2+4\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-8x_1x_2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(1+\dfrac{m}{2}\right)^2+4.1^2+4m=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{m^2}{4}+5m-11=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=2\\m=-22< -\dfrac{1}{2}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
5.
\(\Delta'=m^2-\left(2m-6\right)=\left(m-1\right)^2+5>0;\forall m\)
Pt luôn có 2 nghiệm pb
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2m\\x_1x_2=2m-6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=2x_1x_2+20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2=4x_1x_2+20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2=4\left(2m-6\right)+20\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2m+1=0\Rightarrow m=1\)

a: BC=BH+CH
=4+9
=13(cm)
Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có AH là đường cao
nên \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}AH^2=HB\cdot HC\\AB^2=BH\cdot BC\\AC^2=CH\cdot BC\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}AH=\sqrt{4\cdot9}=6\left(cm\right)\\AB=\sqrt{4\cdot13}=2\sqrt{13}\left(cm\right)\\AC=\sqrt{9\cdot13}=3\sqrt{13}\left(cm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
b: AM=AC/2=1,5*căn 13(cm)
Xét ΔAMB vuông tại M có
\(\tan AMB=\dfrac{AB}{AM}=\dfrac{2\sqrt{13}}{1.5\sqrt{13}}=\dfrac{4}{3}\)
=>\(\widehat{AMB}\simeq53^0\)
=>\(\widehat{BMC}=180^0-53^0=127^0\)
c: Xét tứ giác AKHB có \(\widehat{AKB}=\widehat{AHB}=90^0\)
nên AKHB là tứ giác nội tiếp
=>\(\widehat{BKH}=\widehat{BAH}\)
mà \(\widehat{BAH}=\widehat{C}\)
nên \(\widehat{BKH}=\widehat{C}\)

5.
\(\Delta=m^2-4\left(m-1\right)=\left(m-2\right)^2\)
Pt có 2 nghiệm pb khi \(\left(m-2\right)^2>0\Rightarrow m\ne2\)
Khi đó theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=m\\x_1x_2=m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_2^2=x_1+x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=x_1+x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-2\left(m-1\right)=m\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2-3m+2=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\m=2\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
1.
\(\Delta=9+4m>0\Rightarrow m>-\dfrac{9}{4}\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-3\\x_1x_2=-m\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(5x_1+5x_2=1-\left(x_1x_2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(x_1+x_2\right)=1-\left(x_1x_2\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5.\left(-3\right)=1-\left(-m\right)^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2=16\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4\\m=-4< -\dfrac{9}{4}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
2.
\(\Delta=\left(2m+1\right)^2-4\left(m^2+1\right)=4m-3>0\Rightarrow m>\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m+1\\x_1x_2=m^2+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left(x_1+1\right)^2+\left(x_2+1\right)^2=13\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+2x_1+1+x_2^2+2x_2+1=13\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1^2+x_2^2+2\left(x_1+x_2\right)=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2+2\left(x_1+x_2\right)=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2m+1\right)^2-2\left(m^2+1\right)+2\left(2m+1\right)=11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m^2+8m-10=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\m=-5< \dfrac{3}{4}\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

`a(a+6)+10>0`
`<=>a^2+6a+10>0`
`<=>a^2+6a+9+1>0`
`<=>(a+3)^2+1>0` luôn đúng

a: ΔAMN vuông tại A
mà AI là đường trung tuyến
nên AI=IM=IN=MN/2
=>I là tâm đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔAMN
b: Xét (O) có
ΔBAC nội tiếp
BC là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBAC vuông tại A
Xét (O) có
ΔBEC nội tiếp
BC là đường kính
Do đó: ΔBEC vuông tại E

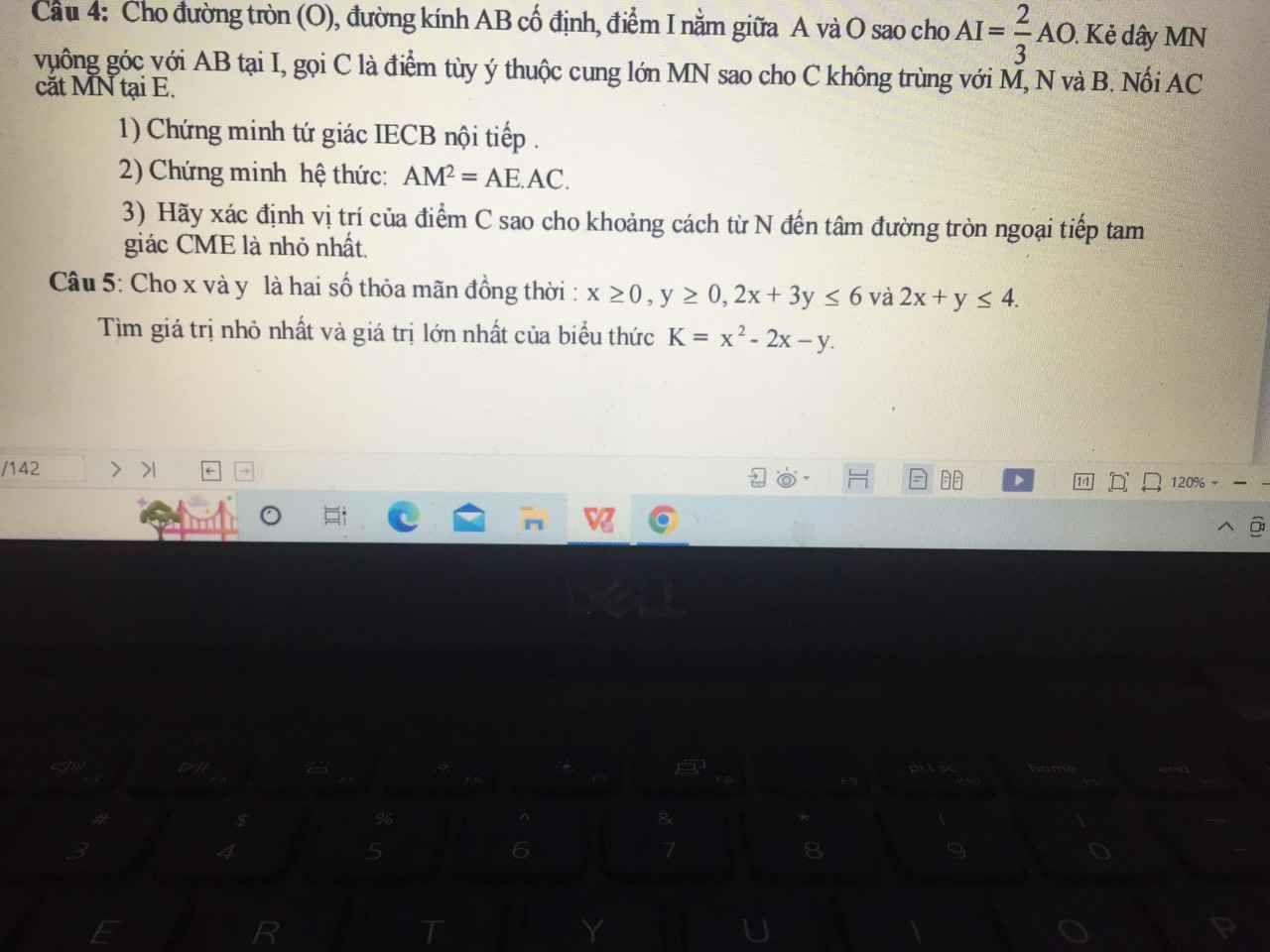
3: góc AMN=góic ACM
=>AM là tiếp tuyến của đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔECM
=>góc AMB=90 độ
=>Tâm o1 của đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔECM nằm trên BM
NO1 min khi NO1=d(N;BM)
=>NO1 vuông góc BM
Gọi O1 là chân đường vuông góc kẻ từ N xuống BM
=>O1 là tâm đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔECM có bán kính là O1M
=>d(N;tâm đường tròn ngoại tiếp ΔECM) nhỏ nhất khi C là giao của (O1;O1M) với (O) với O1 ;là hình chiếu vuông góc của N trên BM

Ta có:
\(\sqrt{3x^2+6x+12}+\sqrt{5x^4-10x^2+9}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(3x^2+6x+3\right)+9}+\sqrt{\left(5x^4-10x^2+5\right)+4}\)
\(=\sqrt{3\left(x+1\right)^2+9}+\sqrt{5\left(x^2-1\right)^2+4}\ge3+2=5\left(1\right)\)
Ta lại có:
\(-2x^2-4x+3=-2\left(x+1\right)^2+5\le5\left(2\right)\)
Từ (1) và (2) dấu = xảy ra khi \(x=-1\)
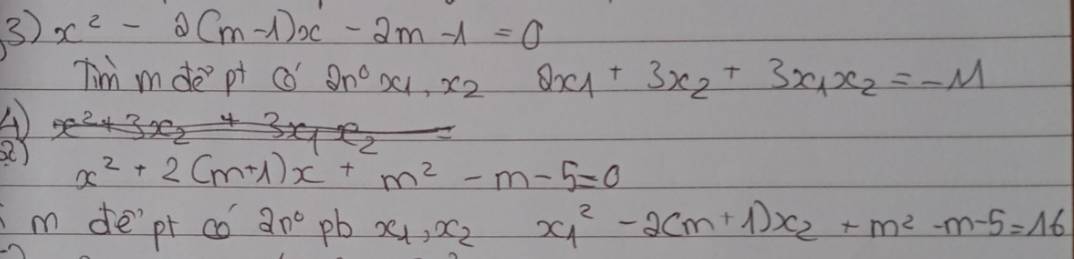
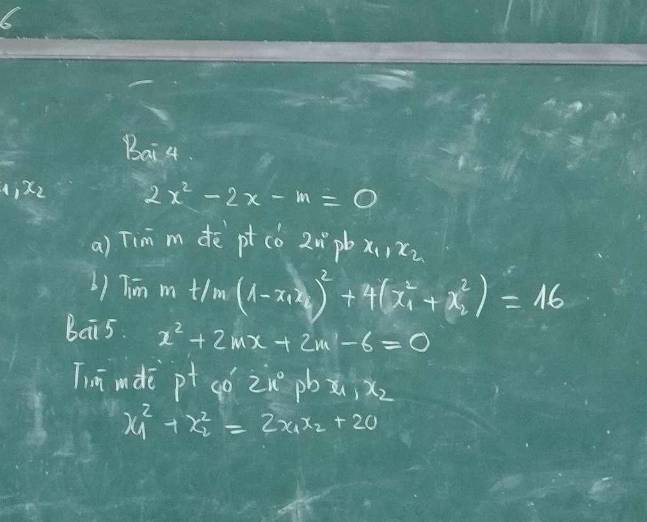
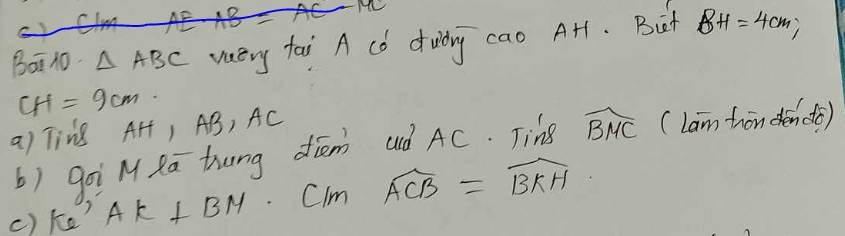
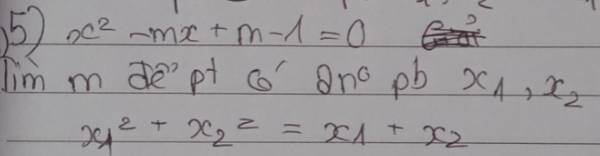
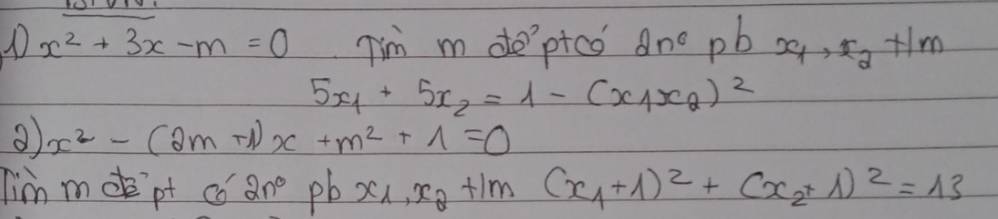
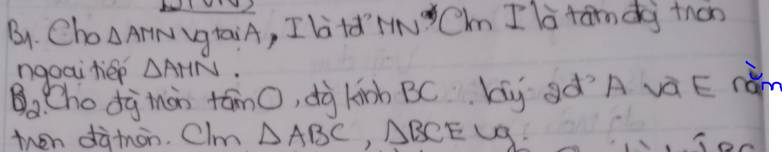
3.
\(\Delta'=\left(m-1\right)^2-\left(-2m-1\right)=m^2+2>0;\forall m\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Pt luôn có 2 nghiệm pb với mọi m
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\\x_1x_2=-2m-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(2x_1+3x_2+3x_1x_2=-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x_1+x_2\right)+x_2+3x_1x_2=-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m-1\right)+x_2+3\left(-2m-1\right)=-11\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_2=2m-4\)
Thế vào \(x_1+x_2=2\left(m-1\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x_1=2\left(m-1\right)-\left(2m-4\right)=2\)
Thế \(x_1=2;x_2=2m-4\) vào \(x_1x_2=-2m-1\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(2m-4\right)=-2m-1\)
\(\Rightarrow m=\dfrac{7}{6}\)
4.
\(\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(m^2-m-5\right)=3m+6>0\Rightarrow m>-2\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-2\left(m+1\right)\\x_1x_2=m^2-m-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
Do \(x_1\) là nghiệm của pt nên:
\(x_1^2+2\left(m+1\right)x_1+m^2-m-5=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x_1^2=-2\left(m+1\right)x_1-m^2+m+5\)
Từ đó ta được:
\(x_1^2-2\left(m+1\right)x_2+m^2-m-5=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(m+1\right)x_1-m^2+m-5-2\left(m+1\right)x_2+m^2-m-5=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-2\left(m+1\right)\left(x_1+x_2\right)=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(m+1\right)^2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)^2=4\)
\(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m+1=2\\m+1=-2\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=1\\m=-3< -2\left(loại\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)