
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Xét ΔABC vuông tại A có AH là đường cao ứng với cạnh huyền BC
nên \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}AB^2=BH\cdot BC\\AC^2=CH\cdot BC\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}AB=4\sqrt{41}\left(cm\right)\\AC=5\sqrt{41}\left(cm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

Lời giải:
Vì $(d)$ đi qua điểm $M(2,3)$ nên:
$y_M=ax_M+b\Leftrightarrow 3=2a+b(1)$
Vì $(d)$ cắt trục tung tại điểm có tung độ 2, tức là $(d)$ cắt trục tung tại điểm $(0,2)$
$\Rightarrow 2=a.0+b(2)$
Từ $(1); (2)\Rightarrow b=2; a=\frac{1}{2}$

Lời giải:
$y=ax+b$ đi qua điểm $A(2;-1)$ khi: $y_A=ax_A+b$
$\Leftrightarrow -1=2a+b(1)$
Gọi $I$ là giao điểm của $y=ax+b$ và $y=2x-4$. Vì $I\in Oy$ nên $x_I=0$
$I\in (y=2x-4)$ nên $y_I=2x_I-4=2.0-4=-4$
Vậy $I$ có tọa độ $(0;-4)$
$I\in (y=ax+b)$ nên: $y_I=ax_I+b$
$\Leftrightarrow -4=a.0+b\Rightarrow b=-4(2)$
Từ $(1); (2)\Rightarrow b=-4; a=\frac{3}{2}$

a, xét \(\Delta ABC\left(\widehat{BAC}=90^o\right)\) có \(AM\) là đường cao
\(BC^2=AB^2+AC^2\left(pytago\right)\Leftrightarrow BC=\sqrt{12^2+16^2}=20\left(cm\right)\)
\(sinABC=\dfrac{AC}{BC}=\dfrac{16}{20}\Rightarrow\widehat{ABC}\approx53^o8'\)
\(sinACB=\dfrac{AB}{BC}=\dfrac{12}{20}\Rightarrow\widehat{ACB}\approx32^o52'\)
\(AB^2=BM.BC\Rightarrow BM=\dfrac{AB^2}{BC}=\dfrac{12^2}{20}=7,2\left(cm\right)\)
b, Xét \(\Delta ABM\left(\widehat{AMB}=90^o\right)\) có \(AE\perp AB\)
\(AB^2=BM^2+AM^2\left(pytago\right)\Leftrightarrow AM=\sqrt{20^2-7,2^2}=\dfrac{16\sqrt{34}}{5}\left(cm\right)\)
\(AM^2=AE.AB\) (hệ thức lượng trong tam giác vuông)\(\left(1\right)\)
c, Xét \(\Delta AMC\left(\widehat{AMC}=90^o\right)\)
\(AC^2=AM^2+MC^2\left(pytago\right)\Leftrightarrow AM^2=AC^2-MC^2\left(2\right)\)
\(\left(1\right)\left(2\right)\Rightarrow AE.AB=AC^2-MC^2\left(đpcm\right)\)

1) \(\sqrt{2x-5}=7\)
\(\left(\sqrt{2x-5}\right)^2=7^2\)
\(2x-5=49\)
\(2x=54\)
\(x=27\)
2) \(3+\sqrt{x-2}=4\)
\(\sqrt{x-2}=1\)
\(\left(\sqrt{x-2}\right)^2=1^2\)
\(x-2=1\)
\(x=3\)
1) \(\sqrt{2x-5}=7\left(đk:x\ge\dfrac{5}{2}\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-5=49\Leftrightarrow2x=54\Leftrightarrow x=27\left(tm\right)\)
2) \(3+\sqrt{x-2}=4\left(đk:x\ge2\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x-2}=1\Leftrightarrow x-2=1\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
3) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-1\right)^2}=1\Leftrightarrow\left|x-1\right|=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-1=1\\x-1=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\\x=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
4) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(x-2\right)^2}=1\Leftrightarrow\left|x-2\right|=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=1\\x-2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=3\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
5) \(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{\left(2x-1\right)^2}=\sqrt{\left(x+4\right)^2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|2x-1\right|=\left|x+4\right|\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}2x-1=x+4\\2x-1=-x-4\end{matrix}\right.\)\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\\x=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
6) \(ĐK:x\ge-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\sqrt{x+2}-3\sqrt{x+2}-\sqrt{x+2}=\sqrt{x+7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{x+2}=\sqrt{x+7}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2=x+7\Leftrightarrow2=7\left(VLý\right)\)
Vậy \(S=\varnothing\)
7) \(ĐK:x\ge-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\sqrt{2x+1}+3\sqrt{x+1}=4\sqrt{x+1}+4\sqrt{2x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\sqrt{2x+1}=\sqrt{x+1}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+1=x+1\Leftrightarrow x=0\left(tm\right)\)

a: Xét (O) có
ΔABC nội tiếp
AB là đường kính
Do đó: ΔACB vuông tại C
=>CB\(\perp\)CA tại C
=>CB\(\perp\)AF tại C
Xét tứ giác BHCF có \(\widehat{BHF}=\widehat{BCF}=90^0\)
nên BHCF là tứ giác nội tiếp
=>B,H,C,F cùng thuộc một đường tròn

Ta có \(P=\sum\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{2a^2+5ab+2b^2}}\le\sum\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{9ab}}=\dfrac{1}{3}\sum\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{ab}}\le\dfrac{1}{6}\sum\left(\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{b}\right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(\dfrac{1}{a}+\dfrac{1}{b}+\dfrac{1}{c}\right)=\dfrac{2}{3}\).
Dấu "=" xảy ra khi và chỉ khi \(a=b=c=\dfrac{3}{2}\)

\(3x^2-2\left(m-3\right)x-2m+3=0\)
\(\Delta'=\left(m-3\right)^2-\left(-2m+3\right)=m^2-4m+6=\left(m-2\right)^2+2>0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) PT luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-et ta có: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2\left(m-3\right)\\x_1x_2=-2m+3\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó ta có:
\(P=x_1^2+x_2^2=\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2\\ =4\left(m-3\right)^2-2\left(-2m+3\right)=4m^2-20m+30\)
\(=\left(4m^2-20m+25\right)+5=\left(2m-5\right)^2+5\ge5\)
Dấu = xảy ra \(\Leftrightarrow2m-5=0\Leftrightarrow m=\dfrac{5}{2}\)
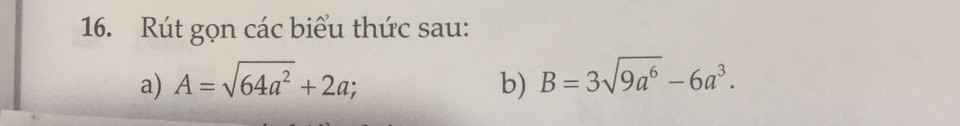

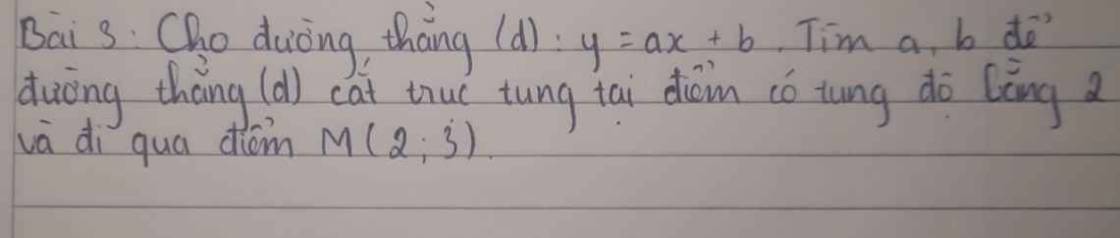





a: \(A=\sqrt{64a^2}+2a=8a+2a=10a\)
b: \(B=3\sqrt{9a^6}-6a^3=3\cdot3a^3-6a^3=3a^3\)
a) \(A=\sqrt{64a^2}+2a=8\left|a\right|+2a\)
b) \(B=3\sqrt{9a^6}-6a^3=9\left|a^3\right|-6a^3\)