
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.



a: \(\overrightarrow{AB}=\left(-3;-2\right)\)
\(\overrightarrow{AC}=\left(1;-4\right)\)
Vì \(\overrightarrow{AB}< >\overrightarrow{AC}\) nên A,B,C ko thẳng hàng
hay A,B,C lập thành 1 tam giác
b: Gọi M là trung điểm của BC
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_M=\dfrac{2-\left(-2\right)}{2}=2\\y_M=\dfrac{-1-1}{2}=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy: M(2;-1)
A(1;3)
\(AM=\sqrt{\left(2-1\right)^2+\left(-1-3\right)^2}=\sqrt{17}\)

Bài 4:
Theo định lý sin ta có:
\(\dfrac{AC}{sinB}=\dfrac{BC}{sinA}\)
\(\Rightarrow BC=a=\dfrac{b\cdot sinA}{sinB}=\dfrac{2\cdot sin60^o}{sin45^o}=\sqrt{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{C}=180^o-60^o-45^o=75^o\)
\(\dfrac{AC}{sinB}=\dfrac{AB}{sinC}\)
\(\Rightarrow AB=c=\dfrac{b\cdot sinC}{sinB}=\dfrac{2\cdot sin75^o}{sin45^o}=1+\sqrt{3}\)
Diện tích tam giác ABC là:
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot AC\cdot AB\cdot sinA=\dfrac{1}{2}\cdot2\cdot\left(1+\sqrt{3}\right)\cdot sin75^o=\dfrac{\sqrt{6}+2\sqrt{2}}{2}\) (đvdt)
Bán kình hình tròn tam giác ABC khi đó là:
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{abc}{4R}\)
\(\Rightarrow R=\dfrac{abc}{4S_{ABC}}=\dfrac{2\cdot\left(1+\sqrt{3}\right)\cdot\sqrt{6}}{4\cdot\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{6}+2\sqrt{2}}{2}\right)}=3-\sqrt{3}\)
Bài 3:
a) Xét tam giác ABC theo định lý côsin ta có:
\(cosC=\dfrac{a^2+b^2-c^2}{2ab}=\dfrac{8^2+10^2-13^2}{2\cdot8\cdot10}=-0,03125\)
\(\Rightarrow\widehat{C}=cos^{-1}-0,03125\approx91^o>90^o\)
Nên tam giác ABC có góc C là góc tù
c) Theo hệ thức Heron ta có diện tích tam giác ABC là:
\(S_{ABC}=\sqrt{p\cdot\left(p-a\right)\cdot\left(p-b\right)\cdot\left(p-c\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow S_{ABC}=\sqrt{\dfrac{8+10+13}{2}\cdot\left(\dfrac{8+10+13}{2}-8\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{8+10+13}{2}-10\right)\cdot\left(\dfrac{8+10+13}{2}-13\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow S_{ABC}\approx40\) (đvdt)
b) Bán kính đường tròn ngoại tiếp tam giác ABC là:
\(S_{ABC}=\dfrac{abc}{4R}\)
\(\Rightarrow R=\dfrac{abc}{4S_{ABC}}=\dfrac{8\cdot10\cdot13}{4\cdot40}=6,5\)

`2)`
`@` Xét `3x+6 >= 0<=>x >= -2`
`=>A=[-2;+oo)`
`@` Xét `|x-2| < 3`
`<=>-3 < x-2 < 3`
`<=>-1 < x < 5=>B=(-1;5)`
Có: `A nn B=(-1;5)`
`A uu B=[-2;+oo)`
`R \\ B=(-oo;-1]uu[5;+oo)`
_______
`3)`
`@` Xét `x+3 >= 2x+7<=>x <= -4=>A=(-oo;-4]`
`@` Xét `4x+5 > 0<=>x > -5/4=>B=(-5/4;+oo)`
`@` Xét `|x+4| < 2<=>-2 < x+4 < 2<=>-6 < x < -2 =>C=(-6;-2)`
Có: `A nn B nn C=\emptyset`
`A \\ B nn C=(-6;-4]`
`C \\ A nn B=\emptyset`.













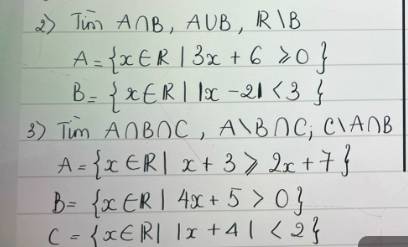
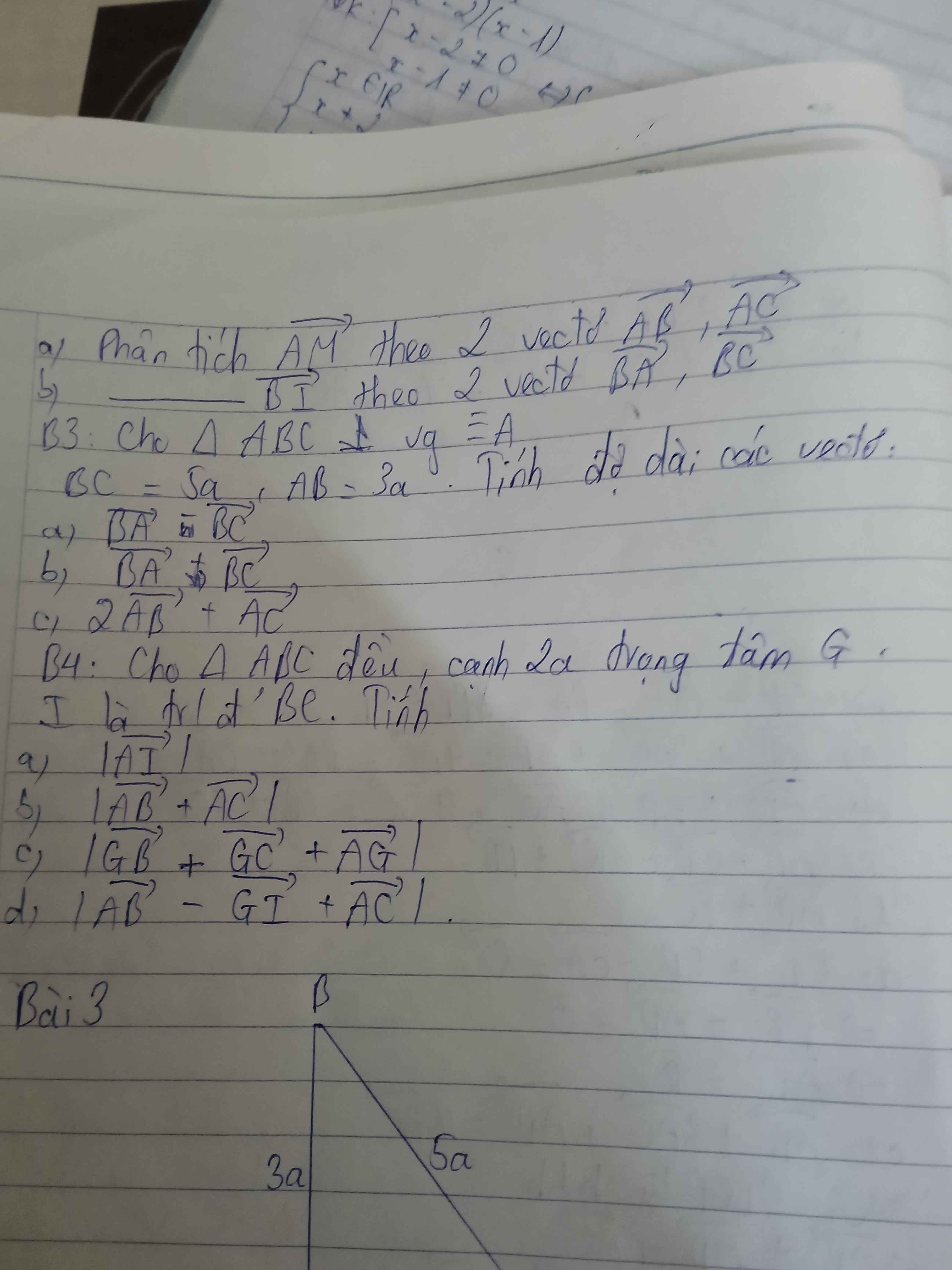



Câu 6:
a: Gọi M là trung điểm của BC
\(AM=2a\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=a\sqrt{3}\)
\(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}+\overrightarrow{AC}\right|=2\cdot AM=2a\sqrt{3}\)
b:
\(AG=GB=GC=\dfrac{2}{3}\cdot a\sqrt{3}=\dfrac{2a\sqrt{3}}{3}\)
\(\left(\overrightarrow{AB}-\overrightarrow{GC}\right)^2=AB^2+GC^2-2\cdot\overrightarrow{AB}\cdot\overrightarrow{GC}\)
\(=4a^2+\dfrac{4}{9}\cdot3\cdot a^2-2\cdot\overrightarrow{GC}\left(\overrightarrow{GB}-\overrightarrow{GA}\right)\)
\(=AB^2+GC^2-2\cdot\overrightarrow{GC}\cdot\left(\overrightarrow{GB}-\overrightarrow{GA}\right)\)
\(=\dfrac{16}{3}a^2-2\cdot\overrightarrow{GC}\cdot\overrightarrow{GB}+2\cdot\overrightarrow{GC}\cdot\overrightarrow{GA}\)
\(=\dfrac{16}{3}a^2-2\cdot GC\cdot GB\cdot cos120+2\cdot GC\cdot GA\cdot cos120\)
=16/3a^2
=>\(\left|\overrightarrow{AB}-\overrightarrow{GC}\right|=\dfrac{4a}{\sqrt{3}}\)