
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Lời giải:
$x+2y=4$
$3x+3y=1$
$\Rightarrow 3(x+2y)-(3x+3y)=4.3-1$
$\Leftrightarrow 3y=11$
$\Leftrightarrow y=\frac{11}{3}$
$x=4-2y=4-2.\frac{11}{3}=\frac{-10}{3}$
Vậy......

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=3\\x+2y=5\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2=3\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\y=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+y=3\\x+2y=5\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=2\\x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)

Lời giải:
Đặt $\sqrt[3]{2x+1}=a; \sqrt[3]{x}=b$ thì ta có:
$a+b=1$ và $a^3-2b^3=1$
$\Rightarrow a^3-2b^3=(a+b)^3$
$\Leftrightarrow a^3-2b^3=a^3+3a^2b+3ab^2+b^3$
$\Leftrightarrow 3a^2b+3ab^2+3b^3=0$
$\Leftrightarrow b(a^2+ab+b^2)=0$
$\Leftrightarrow b=0$ hoặc $a^2+ab+b^2=0$
Nếu $b=0\Leftrightarrow \sqrt[3]{x}=0\Leftrightarrow x=0$ (thử lại thấy tm)
Nếu $a^2+ab+b^2=0$
$\Leftrightarrow (a+\frac{b}{2})^2+\frac{3}{4}b^2=0$
$\Rightarrow a+\frac{b}{2}=b=0$
$\Rightarrow a=b=0$
$\Leftrightarrow \sqrt[3]{2x+1}=\sqrt[3]{x}=0$
$\Leftrightarrow x=\frac{-1}{2}=0$ (vô lý)
Vậy $x=0$

a.\(\hept{\begin{cases}3x-2y=1\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}6x-4y=2\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}8x=5\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\2\cdot\frac{5}{8}+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\4y=\frac{7}{4}\end{cases}}\)
<=>\(\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\y=\frac{7}{16}\end{cases}}\)
a) \(\hept{\begin{cases}3x-2y=1\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}6x-4y=2\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}8x=5\\2x+4y=3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\\frac{5}{4}+4y=3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\4y=\frac{7}{4}\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=\frac{5}{8}\\y=\frac{7}{16}\end{cases}}\)
vậy hpt có nghiệm duy nhất \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(\frac{5}{8};\frac{7}{16}\right)\)
b) \(\hept{\begin{cases}4x-3y=1\\-x+2y=1\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}8x-6y=2\\-3x+6y=3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}5x=5\\-3x+6y=3\end{cases}}\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\-3+6y=3\end{cases}}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=1\\y=1\end{cases}}\)
vậy hpt có nghiệm duy nhất \(\left(x;y\right)=\left(1;1\right)\)

câu 2 thì mk có pt nhưng mk ko bt giải
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\dfrac{1}{x}-\dfrac{1}{y}=\dfrac{1}{10}\\x-y=15\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2y\\4x-3y=-25\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=2y\\8y-3y=-25\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=-10\\y=-5\end{matrix}\right.\)

\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}\sqrt{2}x+2\sqrt{3}y=5\\3\sqrt{2}x-\sqrt{3}y=4,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\sqrt{2}=5-2\sqrt{3}y\\3\sqrt{2}\cdot x-y\cdot\sqrt{3}=4,5\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}3\left(5-2\sqrt{3}y\right)-y\sqrt{3}=4,5\\x\sqrt{2}=5-2\sqrt{3}\cdot y\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}15-7\sqrt{3}y=4,5\\x\sqrt{2}=5-2\sqrt{3}\cdot y\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}y=\dfrac{10.5}{7\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\\x\sqrt{2}=5-2\sqrt{3}\cdot\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{2}\\y=\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)

 p
p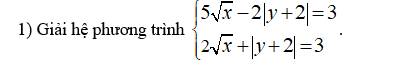

Đặt $|x-1|=a,\sqrt{y+2}=b(x\in \Bbb R, y\ge -2)$
$\Rightarrow \begin{cases}2a-b=4\\a+3b=9\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow \begin{cases}2a=b+4\\a+3b=9\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow \begin{cases}a=\dfrac{b+4}{2}\\a+3b=9\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}a=\dfrac{b+4}{2}\\\dfrac{b+4}{2}+3b=9\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}a=\dfrac{b+4}{2}\\b+4+6b=18\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}a=\dfrac{b+4}{2}\\7b=14\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}a=\dfrac{b+4}{2}\\b=2\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}a=3\\b=2(TM)\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}|x-1|=3\\\sqrt{y+2}=2\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}\left[\begin{array}{1}x-1=3\\x-1=-3\end{array}\right.\\y+2=4\end{cases}\\\Leftrightarrow\begin{cases}\left[\begin{array}{1}x=4\\x=-2\end{array}\right.\\y=2(TM)\end{cases}$
Vậy $(x,y)=\{(4;2);(-2;2)\}$