Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

c: M>=0
=>x^2/(-x+6)>=0
=>-x+6>0
=>-x>-6
=>x<6
=>x<6 và \(x\notin\left\{0;3\right\}\)

\(\left(\frac{9}{x.x^2-9.x}+\frac{1}{x+_{ }3}\right):\left(\frac{x-3}{x.3+x^2}-\frac{x}{3.x+9}\right)\) đk (x\(\ne\)o; công trừ 3)
<=>\(9+\frac{x.\left(x-3\right)}{x.\left(x^2-9\right)}\):\(\frac{3.\left(x-3\right)-x^2}{3x.\left(x+3\right)}\)
<=>\(-\frac{3}{x-3}=\frac{3}{3-x}\)
Bạn ơi mk k hiểu sao lại ra bước 2 ... bạn giải chi tiết giùm mk nha
dù sao cx cảm ơn bạn đã giúp mk


\(\Leftrightarrow6x-3-4x+20< =4x-1+24\)
=>2x+17-4x-23<=0
=>-2x-6<=0
=>-2x<=6
hay x>=-3
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{6x-3-4x+20-4x+1-24}{12}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2x-6< 0\\-2x-6\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>-3\\x\ne-3\end{matrix}\right.\)

a ) \(\dfrac{\left(x-3\right)^2}{3}-\dfrac{\left(2x-1\right)^2}{12}\le x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x-3\right)^2-\left(2x-1\right)^2\le12x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x^2-6x+9\right)-\left(4x^2-4x+1\right)-12x\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2-24x+36-4x^2+4x-1-12x\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-36x\le-35\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{35}{36}\)
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm \(x\ge\dfrac{35}{36}\).
b ) \(2+\dfrac{3\left(x+1\right)}{3}< 3-\dfrac{x-1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2+x+1< 3-\dfrac{x-1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+3< 3-\dfrac{x-1}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4\left(x+3\right)< 12-x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x+12+x< 13\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x< 13-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x< 1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< \dfrac{1}{5}\)
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm \(x< \dfrac{1}{5}\)

bài này bạn lấy các phân số nhân thêm với 1 rồi bỏ nhân tử chung ra ngoài
\(\frac{5}{x}\)+ \(\frac{4}{x+1}\)= \(\frac{3}{x+2}\)+ \(\frac{2}{x+3}\)
ĐKXĐ: x\(\ne\)0,-1,-2,-3
(=) \(\frac{5}{x}\)\(+1\)+\(\frac{4}{x+1}\)\(+1\)=\(\frac{3}{x+2}\)\(+1\)+\(\frac{2}{x+3}\)\(+1\)
(=) \(\frac{5}{x}\)\(+\)\(\frac{x}{x}\)\(+\)\(\frac{4}{x+1}\)\(+\)\(\frac{x+1}{x+1}\)=\(\frac{3}{x+2}\)\(+\)\(\frac{x+2}{x+2}\)\(+\)\(\frac{2}{x+3}\)\(+\)\(\frac{x+3}{x+3}\)
(=) \(\frac{5+x}{x}\)\(+\)\(\frac{5+x}{x+1}\)=\(\frac{5+x}{x+2}\)\(+\)\(\frac{5+x}{x+3}\)
(=) \(\frac{5+x}{x}\)\(+\)\(\frac{5+x}{x+1}\)\(-\)\(\frac{5+x}{x+2}\)\(-\)\(\frac{5+x}{x+3}\)\(=0\)
(=) \(\left(5+x\right)\)\(\left(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x+1}-\frac{1}{x+2}-\frac{1}{x+3}\right)\)\(=0\)
(=) \(\orbr{\begin{cases}5+x=0\\\left(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x+1}-\frac{1}{x+2}-\frac{1}{x+3}\right)\end{cases}}=0\)(Loại vì \(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x+1}-\frac{1}{x+2}-\frac{1}{x+3}\)> \(0\))
(=) \(x=-5\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x = -5
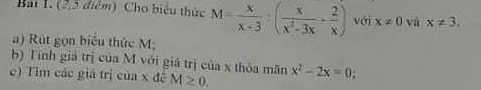 giúp mình câu c với ạ (câu a đáp án là
giúp mình câu c với ạ (câu a đáp án là
x\(\le\)11
=>3(x-1)-2(x-2)<=6/4(x-3)
=>3x-3-2x+4<=3/2x-9/2
=>-1/2x<=-9/2-1=-11/2
=>x>=11