Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+4}-2}{x}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{x}{x\left(\sqrt{x+4}+2\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{1}{\sqrt{x+4}+2}=\dfrac{1}{4}\)
\(f\left(0\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}\left(mx^2+2m+\dfrac{1}{4}\right)=2m+\dfrac{1}{4}\)
Hàm liên tục tại x=0 khi: \(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^-}f\left(x\right)=f\left(0\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m+\dfrac{1}{4}=\dfrac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow m=0\)

TH1: \(m=3\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)=-5< 0\) với mọi x(ktm)
TH2: \(m>3\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) đồng biến trên R
\(\Rightarrow\min\limits_{\left[3;4\right]}f\left(x\right)=f\left(3\right)=3\left(m-3\right)-2m+1=m-8\)
\(m-8>0\Rightarrow m>8\)
TH3: \(m< 3\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)\) nghịch biến trên R
\(\Rightarrow\min\limits_{\left[3;4\right]}=f\left(4\right)=4\left(m-3\right)-2m+1=2m-11\)
\(2m-11>0\Rightarrow m>\dfrac{11}{2}\) (ktm điều kiện \(m< 3\))
Kết hợp lại ta được \(m>8\)

\(f\left(0\right)=2.0+m+1=m+1\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{\sqrt[3]{x+1}-1}{x}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}\dfrac{x+1-1}{x(\sqrt[3]{\left(x+1\right)^2}+\sqrt[3]{x+1}+1)}=\dfrac{1}{1+1+1}=\dfrac{1}{3}\)\(f\left(0\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}f\left(x\right)\Leftrightarrow m+1=\dfrac{1}{3}\Rightarrow m=-\dfrac{2}{3}\)

1. Áp dụng quy tắc L'Hopital
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\sqrt{x+1}-1}{f\left(0\right)-f\left(x\right)}=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0}\dfrac{\dfrac{1}{2\sqrt{x+1}}}{-f'\left(0\right)}=-\dfrac{1}{6}\)
2.
\(g'\left(x\right)=2x.f'\left(\sqrt{x^2+4}\right)=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\f'\left(\sqrt{x^2+4}\right)=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=0\\\sqrt{x^2+4}=1\\\sqrt{x^2+4}=-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
2 pt cuối đều vô nghiệm nên \(g'\left(x\right)=0\) có đúng 1 nghiệm

1.
\(f'\left(x\right)=3x^2-6mx+3\left(2m-1\right)\)
\(f'\left(x\right)-6x=3x^2-3.2\left(m+1\right)x+3\left(2m-1\right)>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2\left(m+1\right)x+2m-1>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-2x-1>2m\left(x-1\right)\)
Do \(x>2\Rightarrow x-1>0\) nên BPT tương đương:
\(\dfrac{x^2-2x-1}{x-1}>2m\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2-2}{x-1}>2m\)
Đặt \(t=x-1>1\Rightarrow\dfrac{t^2-2}{t}>2m\Leftrightarrow f\left(t\right)=t-\dfrac{2}{t}>2m\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(t\right)\) với \(t>1\) : \(f'\left(t\right)=1+\dfrac{2}{t^2}>0\) ; \(\forall t\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)\) đồng biến
\(\Rightarrow f\left(t\right)>f\left(1\right)=-1\Rightarrow\) BPT đúng với mọi \(t>1\) khi \(2m< -1\Rightarrow m< -\dfrac{1}{2}\)
2.
Thay \(x=0\) vào giả thiết:
\(f^3\left(2\right)-2f^2\left(2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow f^2\left(2\right)\left[f\left(2\right)-2\right]=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}f\left(2\right)=0\\f\left(2\right)=2\end{matrix}\right.\)
Đạo hàm 2 vế giả thiết:
\(-3f^2\left(2-x\right).f'\left(2-x\right)-12f\left(2+3x\right).f'\left(2+3x\right)+2x.g\left(x\right)+x^2.g'\left(x\right)+36=0\) (1)
Thế \(x=0\) vào (1) ta được:
\(-3f^2\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)-12f\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)+36=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow f^2\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)+4f\left(2\right).f'\left(2\right)-12=0\) (2)
Với \(f\left(2\right)=0\) thế vào (2) \(\Rightarrow-12=0\) ko thỏa mãn (loại)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(2\right)=2\)
Thế vào (2):
\(4f'\left(2\right)+8f'\left(2\right)-12=0\Leftrightarrow f'\left(2\right)=1\)
\(\Rightarrow A=3.2+4.1\)

\(f\left(-1\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1^-}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1^-}\left(2-ax\right)=2+a\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1^+}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow-1^+}\left(x^2-bx+2\right)=3+b\)
\(f\left(1\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^+}\left(4x+a\right)=4+a\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}f\left(x\right)=\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow1^-}\left(x^2-bx+2\right)=3-b\)
Hàm liên tục trên R khi và chỉ khi:
\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2+a=3+b\\4+a=3-b\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a=0\\b=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
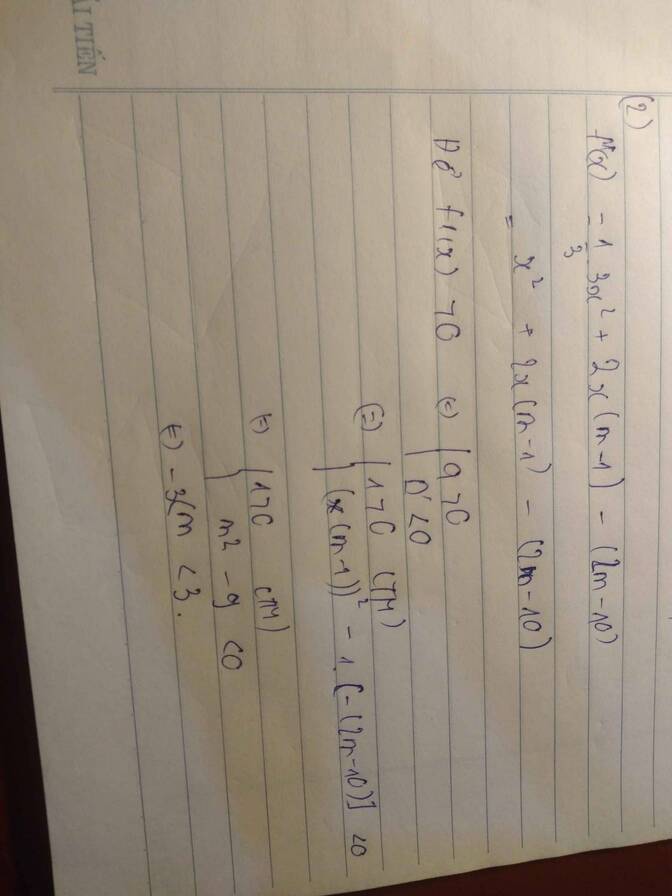
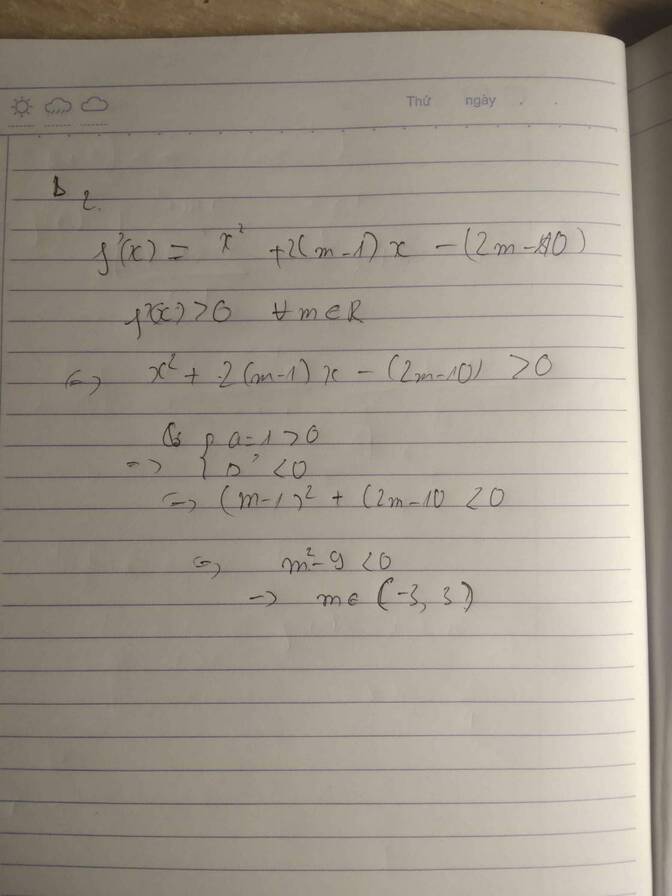
\(\Leftrightarrow\left|x^2-4\left|x\right|+2\right|=m\) (1) có 8 nghiệm phân biệt
Đặt \(x^2-4\left|x\right|+2=t\) (2)
Từ đồ thị của hàm \(y=x^2-4\left|x\right|+2\) ta thấy:
- Với \(t< -2\Rightarrow\) (2) vô nghiệm
- Với \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}t=-2\\t>2\end{matrix}\right.\Rightarrow\) (2) có 2 nghiệm
- Với \(-2< t< 2\Rightarrow\) (2) có 4 nghiệm
- Với \(t=2\Rightarrow\) (2) có 3 nghiệm
Khi đó (1) trở thành: \(\left|t\right|=m\) (3) có tối đa 2 nghiệm
\(\Rightarrow\)Phương trình đã cho có 8 nghiệm pb khi và chỉ khi (3) có 2 nghiệm t phân biệt thỏa mãn \(-2< t< 2\)
\(\Rightarrow0< m< 2\)
Không có phương án nào đúng