K
Khách
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.
Các câu hỏi dưới đây có thể giống với câu hỏi trên

CM
20 tháng 9 2018
Chọn D.
Để f(x) ≤ 0 thì (x + 5)(3 - x) < 0
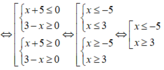
Vậy x ∈ (- ∞ ;-5] ∪ [3;+ ∞ ).

NV
Nguyễn Việt Lâm
Giáo viên
21 tháng 4 2021
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-y+m\right)^2+y^2+2\left(m+1\right)y-m^2+25\ge0\); \(\forall x;y\)
\(\Leftrightarrow y^2+2\left(m+1\right)y-m^2+25\ge0\) ;\(\forall y\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\Delta'=\left(m+1\right)^2-\left(-m^2+25\right)\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+m-12\le0\Rightarrow-4\le m\le3\)
DN
1

9 tháng 5 2020
\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{2-x}{x+1}+2=\frac{x+4}{x+1}< 0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-4< x< -1\)
1/ \(f\left(x\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow2x-4\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge2\)
2/ \(f\left(x\right)\le0\Leftrightarrow\left(x+5\right)\left(3-x\right)\le0\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge-5\\x\ge3\end{matrix}\right.\\\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\le-5\\x\le3\end{matrix}\right.\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x\ge3\\x\le-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
6/ ĐKXĐ: \(x\ne2\)
\(f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{3x-6}\le0\Leftrightarrow3x-6< 0\Leftrightarrow x< 2\)