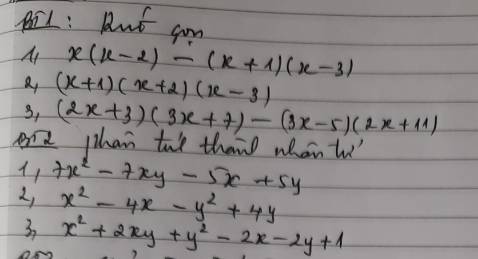
mn oi giup mik 2 bai nay dc ko aj plss mn
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Bài 1. (a) Điều kiện: \(x\ne\pm1\).
Ta có: \(A=\left(\dfrac{x-2}{x-1}-\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}+\dfrac{3}{x-1}\right):\left(1-\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}\right)\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x-2+3}{x-1}-\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}\right):\dfrac{x+1-\left(x+3\right)}{x+1}\)
\(=\left(\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-\dfrac{x+3}{x+1}\right):\dfrac{x+1-x-3}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2-\left(x+3\right)\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}:\dfrac{-2}{x+1}\)
\(=\dfrac{x^2+2x+1-x^2-2x+3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{-2}\)
\(=\dfrac{4}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{x+1}{-2}=\dfrac{2}{1-x}\)
Vậy: \(A=\dfrac{2}{1-x}\)
(b) \(A=3\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{1-x}=3\)
\(\Rightarrow1-x=\dfrac{2}{3}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{1}{3}\left(TM\right)\)
Vậy: \(x=\dfrac{1}{3}\)
Bài 2. (a) Phương trình tương đương với:
\(\dfrac{3\left(3x-2\right)}{12}+\dfrac{6\left(x+3\right)}{12}=\dfrac{4\left(x-1\right)}{12}+\dfrac{x+1}{12}\)
\(\Rightarrow3\left(3x-2\right)+6\left(x+3\right)=4\left(x-1\right)+x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow9x-6+6x+18=4x-4+x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10x=-15\Leftrightarrow x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy: Phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\left\{-\dfrac{3}{2}\right\}\).
(b) Điều kiện: \(x\ne\pm1\). Phương trình tương đương với:
\(\dfrac{2\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}+\dfrac{2\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{2x^2+2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow2\left(x+1\right)+2\left(x-1\right)=2x^2+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x+2+2x-2=2x^2+2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2-4x+2=0\Leftrightarrow2\left(x^2-2x+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2\left(x-1\right)^2=0\Rightarrow x-1=0\Leftrightarrow x=1\left(KTM\right)\)
Vậy: Phương trình có tập nghiệm \(S=\varnothing\)

\(D=\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{1}{x^2-x^4}=\dfrac{x^4}{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)}-\dfrac{1}{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^4-1}{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x^2-1\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}{x^2\left(x^2-1\right)}=\dfrac{x^2+1}{x^2}=1+\dfrac{1}{x^2}\)
do \(x\ne0,\pm1\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{x^2}>0\Rightarrow1+\dfrac{1}{x^2}>1\Rightarrow D>1\left(đpcm\right)\)
\(D=\dfrac{x^2}{x^2-1}+\dfrac{1}{x^2-x^4}\\ =\dfrac{x^4\left(1-x\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(1-x\right)x^2}+\dfrac{x-1}{x^2\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x\right)\left(x-1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x^4-x^5+x-1}{x^2\left(1-x\right)\left(1+x\right)\left(x-1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{-\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{-x^2\left(x-1\right)^2\left(x+1\right)}\\ =\dfrac{x^2+1}{x^2}>1\left(đpcm\right)\)
(x2 + 1 luôn lớn hơn x2)

3:
1: =>15x-9x+6=45-10x+25
=>6x+6=-10x+70
=>16x=64
=>x=4
2: =>x^2+4x-16-16=0
=>x^2+4x-32=0
=>(x+8)(x-4)=0
=>x=4 hoặc x=-8
3: ĐKXĐ: x<>4; x<>-4
\(PT\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x+4+\left(x+2\right)\left(x-4\right)}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}=\dfrac{5x-4}{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+4\right)}\)
=>x+4+x^2-2x-8=5x-4
=>x^2-x-4=5x-4
=>x^2-6x=0
=>x(x-6)=0
=>x=0 hoặc x=6
4: \(\Leftrightarrow5\left(4x+1\right)-x+2>=3\left(2x-3\right)\)
=>20x+5-x+2>=6x-9
=>19x+7>=6x-9
=>13x>=-16
=>x>=-16/13

1.
\(A=\dfrac{x\left(x^2+x-6\right)}{x\left(x^2-4\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x^2-4\right)+x-2}{x^2-4}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)+x-2}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2+1\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\dfrac{x+3}{x+2}\)
thay x = 98 ta được: \(A=\dfrac{101}{100}\)
2. (đkxd \(x\ne\pm1\))
\(B=\dfrac{x-1}{x+1}+\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}+\dfrac{5x}{1-x^2}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}+\dfrac{\left(x+1\right)^2}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}-\dfrac{5x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}=\dfrac{\left(x-1\right)^2+\left(x+1\right)^2-5x}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{x^2-2x+1+x^2+2x+1-5x}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{2x^2-5x+2}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{2x^2-4x-x+2}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{2x\left(x-2\right)-\left(x-2\right)}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)}{x^2-1}\)để B bằng 0 thì: \(\left(x-2\right)\left(2x-1\right)=0\left(x^2-1\ge0\forall x\ne\pm1\right)\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=0\\2x-1=0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=2\left(tm\right)\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)

a)
Bốn cảnh của bức tranh tứ bình đó: đêm vàng trên bờ suối có ánh trăng tan, trời mưa chuyển bốn phương ngàn, bình minh cây xanh nắng gội, chiều lênh láng máu sau rừng.
b)
Hai cảnh tượng đối lập tương phản của bài thơ:
- Cảnh "đêm vàng trên bờ suối có ánh trăng tan" và cảnh "bình minh cây xanh nắng gội".
Ý nghĩa của nó: tái hiện lại cuộc sống tự do thoải mái trong rừng của chúa tể sơn lâm, lúc say mồi lúc giấc ngủ tưng bừng.

1: AD=8-2=6cm
AD/AB=6/8=3/4
AE/AC=9/12=3/4
=>AD/AB=AE/AC
2: Xét ΔADE và ΔABC có
AD/AB=AE/AC
góc A chung
=>ΔADE đồng dạng với ΔABC
3: AI là phân giác
=>IB/IC=AB/AC
=>IB/IC=AD/AE
=>IB*AE=AD*IC


2:
1: =7x(x-y)-5(x-y)
=(x-y)(7x-5)
2: =(x^2-y^2)-(4x-4y)
=(x-y)(x+y)-4(x-y)
=(x-y)(x+y-4)
3: =(x^2+2xy+y^2)-(2x+2y)+1
=(x+y)^2-2(x+y)+1
=(x+y-1)^2