Tìm x để
a) A=\(\dfrac{x^2+3x-1}{x+2}\) có giá trị là số nguyên (x ϵ Z)
b) B=\(\dfrac{x^2+x+3}{x+1}\) có giá trị là số nguyên (x ϵ Z)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bổ sung phần c và d luôn:
c, C = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{2}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5(x2 - 1) = 2(2x2 + 3)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 5x2 - 5 = 4x2 + 6
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = 11
\(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 - 11 = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) (x - \(\sqrt{11}\))(x + \(\sqrt{11}\)) = 0
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-\sqrt{11}=0\\x+\sqrt{11}=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\\x=-\sqrt{11}\left(TM\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
d, Ta có: \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{2x^2+3}\) = \(\dfrac{x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}-\dfrac{5}{2}}{2\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) = \(\dfrac{1}{2}\) - \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\)
C nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\dfrac{5}{4\left(x^2+\dfrac{3}{2}\right)}\) nguyên \(\Leftrightarrow\) 5 \(⋮\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\))
\(\Leftrightarrow\) 4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) \(\in\) Ư(5)
Xét các TH:
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-1}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{1}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -5 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-11}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{11}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = 1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-5}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{5}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
4(x2 + \(\dfrac{3}{2}\)) = -1 \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 = \(\dfrac{-7}{4}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\) x2 + \(\dfrac{7}{4}\) = 0 (Vô nghiệm)
Vậy không có giá trị nào của x \(\in\) Z thỏa mãn C \(\in\) Z
Chúc bn học tốt! (Ko bt đề sai hay ko nữa :v)

a,A = \(\dfrac{3}{x-1}\)
A \(\in\) Z \(\Leftrightarrow\) 3 ⋮ \(x-1\) ⇒ \(x-1\) \(\in\) { -3; -1; 1; 3}
\(x\) \(\in\) { -2; 0; 2; 4}
b, B = \(\dfrac{x-2}{x+3}\)
B \(\in\) Z \(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x-2\) \(⋮\) \(x+3\) ⇒ \(x+3-5\) \(⋮\) \(x+3\)
⇒ 5 \(⋮\) \(x+3\)
\(x+3\) \(\in\){ -5; -1; 1; 5}
\(x\) \(\in\) { -8; -4; -2; 2}
a.\(A=\dfrac{3}{x-1}\)có giá trị là 1 số nguyên khi \(3\) ⋮ \(x-1.\)
\(\Rightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm3\right\}.\)
Ta có bảng:
| \(x-1\) | \(1\) | \(-1\) | \(3\) | \(-3\) |
| \(x\) | \(2\) | \(0\) | \(4\) | \(-2\) |
| TM | TM | TM | TM |
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-2;0;2;4\right\}.\)
b.\(B=\dfrac{x-2}{x+3}\)có giá trị là 1 số nguyên khi \(x-2\) ⋮ \(x+3.\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(x+3\right)-5⋮x+3.\)
Mà x+3 ⋮ x+3 \(\Rightarrow\) Ta cần: \(-5⋮x+3\Rightarrow x+3\inƯ\left(-5\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm5\right\}.\)
Ta có bảng:
| \(x+3\) | \(1\) | \(-1\) | \(5\) | \(-5\) |
| \(x\) | \(-2\) | \(-4\) | \(2\) | \(-8\) |
| TM | TM | TM | TM |
Vậy \(x\in\left\{-8;-4;-2;2\right\}.\)

a: Sửa đề: \(A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}-3}\)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=0\\x\ne9\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để A là số nguyên thì \(\sqrt{x}+1⋮\sqrt{x}-3\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}-3+4⋮\sqrt{x}-3\)
=>\(4⋮\sqrt{x}-3\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}-3\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}\in\left\{4;2;5;1;7;-1\right\}\)
=>\(\sqrt{x}\in\left\{4;2;5;1;7\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{16;4;25;1;49\right\}\)
b: 
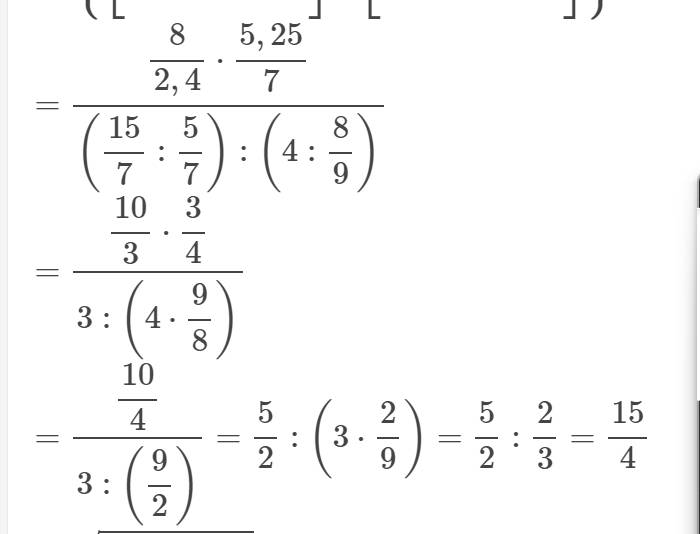

\(a,P=\dfrac{2x^2+2x+2+2x-1+x^2+6x+2}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\\ P=\dfrac{3x^2+10x+3}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+x+1\right)}\)

a) \(Q=\) \(\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{x+2\sqrt{x}+1}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{x-1}\right).\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}}\left(x>0;x\ne1\right)\)
\(Q=\left(\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)^2}-\dfrac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\right).\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(Q=\dfrac{\left(\sqrt{x}+2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)-\left(\sqrt{x}-2\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)^2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}.\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(Q=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{x}-2-x+\sqrt{x}+2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)^2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}.\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(Q=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)^2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}.\dfrac{\sqrt{x}+1}{\sqrt{x}}\)
\(Q=\dfrac{2}{\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\) \(=\dfrac{2}{x-1}\) \(\left(đpcm\right)\).
b) Để \(Q\in Z\) <=> \(\dfrac{2}{x-1}\in Z\) <=> \(x-1\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
Ta có bảng sau:
| x -1 | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 |
| x | 2(TM) | 0(ko TM) | 3(TM) | -1(koTM) |
Vậy để biểu thức Q nhận giá trị nguyên thì \(x\in\left\{2;3\right\}\)

a) Ta có: \(A=\left(\dfrac{2}{\sqrt{x}-3}+\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}}{x-4\sqrt{x}+3}\right):\dfrac{2\left(x-2\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\sqrt{x}-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)+2\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}:\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{4\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\cdot\dfrac{1}{2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-1}{\left(\sqrt{x}-3\right)\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)^2}\)

a)ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge0\\x\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{2\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{2\sqrt{x}-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}-\dfrac{2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{x+\sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}+2-2}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{x-\sqrt{x}}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)}{\left(\sqrt{x}-1\right)\left(\sqrt{x}+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+1}\)
b) \(x=9\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{3}{3+1}=\dfrac{3}{4}\)
\(x=7-4\sqrt{3}\Rightarrow A=\dfrac{\sqrt{7-4\sqrt{3}}}{\sqrt{7-4\sqrt{3}}+1}=\dfrac{\sqrt{7-2\sqrt{12}}}{\sqrt{7-2\sqrt{12}}+1}=\dfrac{\sqrt{4-2\sqrt{3}\sqrt{4}+3}}{\sqrt{4-2\sqrt{3}\sqrt{4}+3}+1}=\dfrac{2-\sqrt{3}}{2-\sqrt{3}+1}=\dfrac{2-\sqrt{3}}{3-\sqrt{3}}=\dfrac{\left(2-\sqrt{3}\right)\left(3+\sqrt{3}\right)}{\left(3-\sqrt{3}\right)\left(3+\sqrt{3}\right)}=\dfrac{3-\sqrt{3}}{6}\)
a: ĐểA nguyên thì x^2+2x+x+2-3 chia hết cho x+2
=>-3 chia hết cho x+2
=>x+2 thuộc {1;-1;3;-3}
=>x thuộc {-1;-3;1;-5}
b: B nguyên khi x^2+x+3 chia hết cho x+1
=>3 chia hết cho x+1
=>x+1 thuộc {1;-1;3;-3}
=>x thuộc {0;-2;2;-4}