Xét phương trình \(2{\log _2}x = - 3.\)
a) Từ phương trình trên, hãy tính \({\log _2}x.\)
b) Từ kết quả ở câu a và sử dụng định nghĩa lôgarit, hãy tìm x.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Do 2 > 1 ⇒ hàm số y = log2x đồng biến trên D = \(\left(0;+\infty\right)\)
\(log_2x>1\\ \Rightarrow x>2\)

Khoảng giá trị của x mà đồ thị hàm số \(y=log_2x\) nằm phía trên đường thẳng y = 2 là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Tập nghiệm của bất phương trình \(log_2x>2\) là \(\left(4;+\infty\right)\)

tham khảo
a)Điều kiện \(3-x>0\) hay \(x< 3\)
\(4-log\left(3-x\right)=3log\left(3-x\right)=1\Leftrightarrow10^1=3-x\)
Vậy nghiệm của phương trình là \(x=2\) thỏa mãn điều kiện
b) Điều kiện \(x+2>0\) và \(x-1>0\) tức là \(x>1\)
\(\left(x+2\right)\left(x-1\right)=2\Rightarrow x^2+x-4=0\)
Vậy pt có nghiệm \(x=\dfrac{-1+\sqrt{17}}{2}\)

a) \({\log _{\frac{1}{2}}}\left( {x - 2} \right) = - 2\)
Điều kiện: \(x - 2 > 0 \Leftrightarrow x > 2\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là \(x = 6\).
b) \({\log _2}\left( {x + 6} \right) = {\log _2}\left( {x + 1} \right) + 1\)
Điều kiện: \(\left\{ \begin{array}{l}x + 6 > 0\\x + 1 > 0\end{array} \right. \Leftrightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}x > - 6\\x > - 1\end{array} \right. \Leftrightarrow x > - 1\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là \(x = 4\).

\(a,\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^{x-2}=\sqrt{8}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{2x-4}=\left(\dfrac{1}{2}\right)^{-\dfrac{3}{2}}\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-4=-\dfrac{3}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow2x=\dfrac{5}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\)
\(b,9^{2x-1}=81\cdot27^x\\ \Leftrightarrow3^{4x-2}=3^{4+3x}\\ \Leftrightarrow4x-2=4+3x\\ \Leftrightarrow x=6\)
c, ĐK: \(x-2>0\Rightarrow x>2\)
\(2log_5\left(x-2\right)=log_59\\
\Leftrightarrow log_5\left(x-2\right)^2=log_59\\
\Leftrightarrow\left(x-2\right)^2=3^2\\
\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x-2=3\\x-2=-3\end{matrix}\right.\\
\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=5\left(tm\right)\\x=-1\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm là x = 5.
d, ĐK: \(x-1>0\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
\(log_2\left(3x+1\right)=2-log_2\left(x-1\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow log_2\left(3x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)=2\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-2x-1=4\\ \Leftrightarrow3x^2-2x-5=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(3x-5\right)\left(x+1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{5}{3}\left(tm\right)\\x=-1\left(ktm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vậy phương trình có nghiệm \(x=\dfrac{5}{3}\)

a: \(log_2\left(mn\right)=log_2\left(2^7\cdot2^3\right)=7+3=10\)
\(log_2m+log_2n=log_22^7+log_22^3=7+3=10\)
=>\(log_2\left(mn\right)=log_2m+log_2n\)
b: \(log_2\left(\dfrac{m}{n}\right)=log_2\left(\dfrac{2^7}{2^3}\right)=7-3=4\)
\(log_2m-log_2n=log_22^7-log_22^3=7-3=4\)
=>\(log_2\left(\dfrac{m}{n}\right)=log_2m-log_2n\)
a) \(\log_2\left(mn\right)=\log_2\left(2^7.2^3\right)=\log_22^{7+3}=\log_22^{10}=10.\log_22=10.1=10\)
\(\log_2m+\log_2n=\log_22^7+\log_22^3=7\log_22+3\log_22=7.1+3.1=7+3=10\)
b) \(\log_2\left(\dfrac{m}{n}\right)=\log_2\dfrac{2^7}{2^3}=\log_22^4=4.\log_22=4.1=4\)
\(\log_2m-\log_2n=\log_22^7-\log_22^3=7.\log_22-3\log_22=7.1-3.1=4\)

a:
| x | 0,5 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 8 |
| \(y\) | -1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
b:
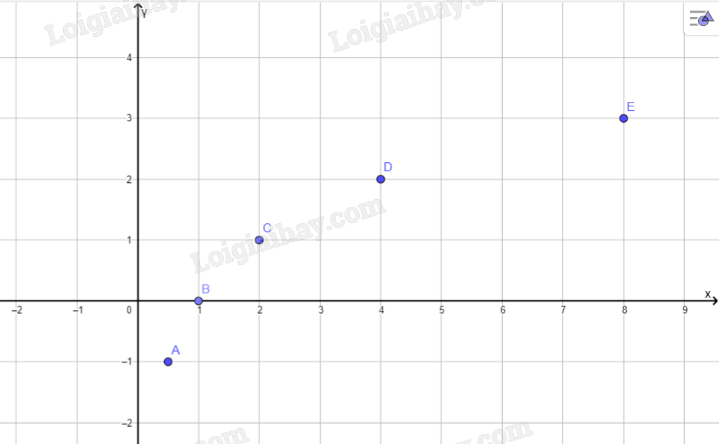
c: Tọa độ giao điểm của hàm số với trục hoành là B(2;0)
Đồ thị hàm số này ko cắt trục tung
d:
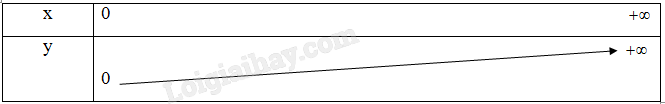
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow0^+}log_2x=0\)
\(\lim\limits_{x\rightarrow+\infty}\left(log_2x\right)=+\infty\)
=>Hàm số này đồng biến trên TXĐ của nó là D=[0;+vô cực)

a)
ĐK: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}2x-4>0\\x-1>0\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow x>1\)
\(\log_5\left(2x-4\right)+\log_{\dfrac{1}{5}}\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_5\left(2x-4\right)-\log_5\left(x-1\right)=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_5\left(\dfrac{2x-4}{x-1}\right)=\log_51\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-4}{x-1}=1\\ \Leftrightarrow2x-4=x-1\\ \Leftrightarrow x=3\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy x = 3.
b) ĐK: x > 0
\(\log_2x+\log_4x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_2x+\dfrac{1}{2}\log_2x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(1+\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\log_2x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3}{2}\log_2x=3\\ \Leftrightarrow\log_2x=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\left(tm\right)\)
Vậy x= 4
tham khảo
a)Chia cả hai vế của phương trình cho \(2\), ta được:
\(log_2x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
Vậy \(log_2x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\)
b) Áp dụng định nghĩa của logarit, ta có:
\(log_2x=-\dfrac{3}{2}\Leftrightarrow2^{-\dfrac{3}{2}}=x\)
Vậy \(x=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{4}\)