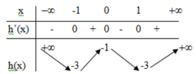
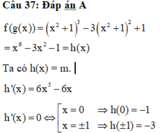Cho f(x) = \(\dfrac{1}{3}\)x3 - (m - 2)x2 - 2mx + 6. Tìm tham số m để phương trình f'(x) = 0 có 2 nghiệm x1,x2 thoả mãn: x2 - x1 = x12
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Với m=−1m=−1 thì PT f(x)=0f(x)=0 có nghiệm x=1x=1 (chọn)
Với m≠−1m≠−1 thì f(x)f(x) là đa thức bậc 2 ẩn xx
f(x)=0f(x)=0 có nghiệm khi mà Δ′=m2−2m(m+1)≥0Δ′=m2−2m(m+1)≥0
⇔−m2−2m≥0⇔m(m+2)≤0⇔−m2−2m≥0⇔m(m+2)≤0
⇔−2≤m≤0⇔−2≤m≤0
Tóm lại để f(x)=0f(x)=0 có nghiệm thì m∈[−2;0]

\(\Delta=\left(-2m\right)^2-4\left(m^2-m+1\right)\)
=4m^2-4m^2+4m-4=4m-4
Để (1) có 2 nghiệm thì 4m-4>=0
=>m>=1

\(x^3-x^2+2mx-2m=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2\left(x-1\right)+2m\left(x-1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x-1\right)\left(x^2+2m\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=1\\x^2=-2m\end{matrix}\right.\)
Để pt có 3 nghiệm \(\Rightarrow-2m>0\Rightarrow m< 0\)
a. Do vai trò 3 nghiệm như nhau, ko mất tính tổng quát giả sử \(x_1=1\) và \(x_2;x_3\) là nghiệm của \(x^2+2m=0\)
Để pt có 3 nghiệm pb \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-2m>0\\-2m\ne1\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m< 0\\m\ne-\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Khi đó: \(x_2+x_3=0\Rightarrow x_1+x_2+x_3=1\ne10\) với mọi m
\(\Rightarrow\) Không tồn tại m thỏa mãn yêu cầu
b.
Giả sử pt có 3 nghiệm, khi đó \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_2=-\sqrt{-2m}< 0< 1\\x_3=\sqrt{-2m}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Luôn có 1 nghiệm của pt âm \(\Rightarrow\) không tồn tại m thỏa mãn
Em coi lại đề bài

\(\Delta-=m^2+4m+5=\left(m+1\right)^2+1>0;\forall m\)
Pt đã cho luôn có 2 nghiệm pb với mọi m
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m\\x_1x_2=-4m-5\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\dfrac{1}{2}x_1\left(x_1+x_2\right)-\dfrac{1}{2}x_1x_2-\left(m-1\right)x_1+x_2-2m+\dfrac{33}{2}=762019\)
\(\Leftrightarrow mx_1+\dfrac{4m+5}{2}-mx_1+x_1+x_2-2m+\dfrac{33}{2}=762019\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4m+5}{2}+2m-2m+\dfrac{33}{2}=762019\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2m+19=762019\)
\(\Rightarrow m=...\)

f(x) = (m-2) x 2 - 2mx + m + 1 > 0 (*)
Với m = 2 thì bất phương trình (*) trở thành:
f(x) = -4x + 3 > 0 ⇔ x < 3/4
Vậy với m = 2 thì bất phương trình (*) có nghiệm x < 3/4 nên m = 2 (loại)
Với m ≠ 2 thì bất phương trình (*) vô nghiệm khi và chỉ khi
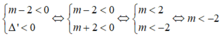
Vậy với m < -2 thì bất phương trình (*) vô nghiệm

Toi mới làm được câu 2 thoi à :( Mấy câu còn lại để rảnh nghĩ thử coi sao
\(PTHDGD:\dfrac{x+1}{x-1}=2x+m\Leftrightarrow x+1=\left(2x+m\right)\left(x-1\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+1=2x^2-2x+mx-m\Leftrightarrow2x^2+\left(m-3\right)x-m-1=0\)
De ton tai 2 diem phan biet \(\Leftrightarrow\Delta>0\Leftrightarrow\left(m-3\right)^2+8m+8>0\Leftrightarrow m^2+2m+17>0\Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)^2+16>0\forall x\)
\(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=\dfrac{3-m}{2}\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{-m-1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
Vi 2 tiep tuyen tai 2 diem x1, x2 song song voi nhau
\(\Rightarrow f'\left(x_1\right)=f'\left(x_2\right)\)
\(f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x-1-x-1}{\left(x-1\right)^2}=-\dfrac{2}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{1}{\left(x_1-1\right)^2}=\dfrac{1}{\left(x_2-1\right)^2}\Leftrightarrow x_1^2-2x_1+1=x_2^2-2x_2+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)\left(x_1+x_2\right)-2\left(x_1-x_2\right)=0\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1-x_2\right)\left(x_1+x_2-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=x_2\left(loai\right)\\x_1+x_2=2\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{3-m}{2}=2\Leftrightarrow m=-1\)

a: Khi m=2 thì pt (1) trở thành:
\(x^2-4x+3=0\)
=>(x-1)(x-3)=0
=>x=1 hoặc x=3

a) Khi \(m=1\) thì pt đã cho trở thành \(x^2-2x-10=0\) (*)
pt (*) có \(\Delta'=\left(-1\right)^2-\left(-10\right)=11>0\)
Do đó (*) có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(\left[{}\begin{matrix}x_1=\dfrac{-\left(-1\right)+\sqrt{11}}{1}=1+\sqrt{11}\\x_2=\dfrac{-\left(-1\right)-\sqrt{11}}{1}=1-\sqrt{11}\end{matrix}\right.\)
b) Xét pt đã cho \(x^2-mx-10=0\) \(\left(a=1;b=-m;c=-10\right)\)
Nhận thấy \(ac=1\left(-10\right)=-10< 0\) nên pt đã cho luôn có 2 nghiệm phân biệt \(x_1,x_2\).
Áp dụng hệ thức Vi-ét, ta có \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-\dfrac{-m}{1}=m\\x_1x_2=\dfrac{-10}{1}=-10\end{matrix}\right.\)
Ta có \(x_1^2+x_2^2=29\Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=29\Leftrightarrow m^2-2\left(-10\right)=29\)\(\Leftrightarrow m^2+20=29\Leftrightarrow m^2=9\Leftrightarrow m=\pm3\)
Vậy để pt đã cho có 2 nghiệm phân biệt thỏa mãn đề bài thì \(m=\pm3\)