Cho hai số thực dương x, y thỏa mãn điều kiện . Giá trị nhỏ nhất của biểu thức P = x.y là:
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


3: \(P=\dfrac{x}{\left(x+y\right)+\left(x+z\right)}+\dfrac{y}{\left(y+z\right)+\left(y+x\right)}+\dfrac{z}{\left(z+x\right)+\left(z+y\right)}\le\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\dfrac{x}{x+y}+\dfrac{x}{x+z}\right)+\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\dfrac{y}{y+z}+\dfrac{y}{y+x}\right)+\dfrac{1}{4}\left(\dfrac{z}{z+x}+\dfrac{z}{z+y}\right)=\dfrac{3}{2}\).
Đẳng thức xảy ra khi x = y = x = \(\dfrac{1}{3}\).

Đáp án B.
Từ giả thiết, suy ra
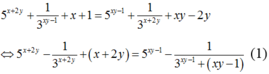
Xét hàm số f ( t ) = 5 t - 1 3 t + t trên ℝ .
Đạo hàm f ' ( t ) = 5 t . ln 5 - ln 3 3 t + 1 > 0 , ∀ t ∈ ℝ ⇒ hàm số f ( t ) luôn đồng biến trên ℝ .
Suy ra
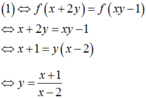
Do y > 0 nên x + 1 x - 2 > 0 ⇔ [ x > 2 x < - 1 . Mà x > 0 nên x > 2 .
Từ đó T = x + y = x + x + 1 x - 2 . Xét hàm số g ( x ) = x + x + 1 x - 2 trên 2 ; + ∞ .
Đạo hàm
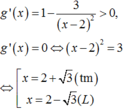
Lập bảng biến thiên của hàm số trên 2 ; + ∞ , ta thấy min g ( x ) = g ( 2 + 3 ) = 3 + 2 3 .
Vậy T m i n = 3 + 2 3 khi x = 2 + 3 và x = 1 + 3 .

Ta có \(x+y\le1\Leftrightarrow1-x\ge y>0\Leftrightarrow0< x< 1\)
Giả sử \(x^2-\dfrac{3}{4x}-\dfrac{x}{y}\le-\dfrac{9}{4}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4x^2+9\le\dfrac{3}{x}+\dfrac{4x}{y}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x}{1-x}+\dfrac{3}{x}\ge4x^2+9\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x^2+3\left(1-x\right)-x\left(4x^2+9\right)\left(1-x\right)}{x\left(1-x\right)}\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{4x^4-4x^3+13x^2-12x+3}{x\left(1-x\right)}\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{\left(x^2+3\right)\left(2x-1\right)^2}{x\left(1-x\right)}\ge0\)
Vì \(x>0;1-x>0\) nên BĐT trên luôn đúng
Vậy ta được đpcm
Dấu \("="\Leftrightarrow x=y=\dfrac{1}{2}\)

\(3xy=x+y+1\ge3\sqrt[3]{xy}\Rightarrow xy\ge1\)
\(4xy=xy+x+y+1=x\left(y+1\right)+\left(y+1\right)=\left(x+1\right)\left(y+1\right)\)
\(P=\frac{1}{x\left(y+1\right)}+\frac{1}{y\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{2xy+x+y}{4\left(xy\right)^2}=\frac{5xy-1}{4\left(xy\right)^2}\)
Xét hiệu: \(P-1=\frac{5xy-1}{4x^2y^2}-1=\frac{\left(4xy-1\right)\left(1-xy\right)}{4x^2y^2}\le0\) với mọi \(xy\ge1\)
Vậy \(P\le1\)hay max P = 1.
Dẫu "=" xảy ra <=> x = y = 1.
Áp dụng BĐT Cauchy ta có: \(3xy\ge2\sqrt{xy}+1\Leftrightarrow xy\ge1\)
Áp dụng BĐT Cauchy ta có:
\(P=\frac{1}{x\left(y+1\right)}+\frac{1}{y\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{5xy-1}{xy\left(x+1\right)\left(y+1\right)}=\frac{5xy-1}{4\left(xy\right)^2}\), đặt t=\(\frac{1}{xy}\)
\(f\left(t\right)=\frac{5}{4}t-\frac{1}{4}t^2\)đồng biến trên (0;1] nên f(t) đạt GTLN tại t=1
Vậy GTKN của P=1 đạt được khi x=y=1

Đáp án B.
Từ giả thiết, suy ra 5 x + 2 y + 1 3 x y - 1 + x + 1 = 5 x y - 1 + 1 3 x + 2 y + x y - 2 y
⇔ 5 x + 2 y - 1 3 x + 2 y + x + 2 y = 5 x y - 1 - 1 3 x y - 1 + ( x y - 1 ) (1)
Xét hàm số f ( t ) = 5 t - 1 3 t + t trên ℝ .
Đạo hàm f ' ( t ) = 5 t . ln 5 + ln 3 3 t + 1 > 0 , ∀ t ∈ ℝ ⇒ hàm số f (t) luôn đồng biến trên ℝ .
Suy ra 1 ⇔ f ( x + 2 y ) = f ( x y - 1 ) ⇔ x + 2 y = x y - 1 ⇔ x + 1 = y ( x - 2 )
y = x + 1 x - 2
Do y > 0 nên x + 1 x - 2 > 0 ⇔ x > 2 x < - 1 . Mà x > 0 nên x > 2.
Từ đó T = x + y = x + x + 1 x - 2 . Xét hàm số g ( x ) = x + x + 1 x - 2 trên 2 ; + ∞ .
Đạo hàm g ' ( x ) = 1 - 3 x - 2 2 > 0 , g ' ( x ) = 0 ⇔ ( x - 2 ) 2 = 3
⇔ x = 2 + 3 ( t m ) x = 2 - 3 ( L ) . Lập bảng biến thiên của hàm số trên 2 ; + ∞ , ta thấy m i n g ( x ) = g ( 2 + 3 ) = 3 + 2 3 .
Vậy T m i n = 3 + 2 3 khi x = 2 + 3 và y = 1 + 3 .

Từ giả thiết ta suy ra
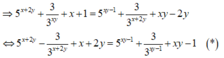
Xét hàm số f ( t ) = 5 t - 1 3 t + t với t ∈ ℝ , f ' ( t ) = 5 t . ln 5 + 3 - t . ln 3 + 1 > 0 ; ∀ t ∈ ℝ
Suy ra y= f( t) là hàm số đồng biến trên R mà từ ( * ) suy ra
f (x+ 2y) =f( xy-1) hay x+ 2y= xy-1
![]()
với x>0 suy ra y>1.
Khi đó
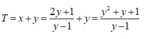
Xét hàm số
f ( y ) = y 2 + y + 1 y - 1 t r ê n 1 ; + ∞ f ' y = y 2 - 2 y - 2 y - 1 2 = 0 ⇔ y = ± 1 + 3 f 1 + 3 = 3 + 2 3 ; lim y → 1 f ( y ) = lim y → + ∞ f ( y ) = + ∞
Do đó, giá trị nhỏ nhất của hàm số là 3 + 2 3 .
Vậy kết quả là 3 + 2 3
Chọn B.

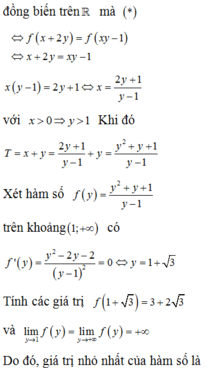

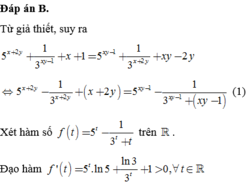
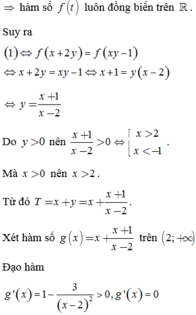

Đáp án C.
Từ giả thiết ta có
ln x + y + 1 + 3 x + y + 1 = ln 3 x y + 3.3 x y (*)
Xét f t = ln t + 3 t hàm trên 0 ; + ∞ , ta có f ' t = 1 t + 3 > , ∀ t > 0
Do đó * ⇔ x + y + 1 = 3 x y ⇔ 3 x y − 1 = x + y ≥ 2 x y ⇔ 3 xy − 2 x y − 1 ≥ 0
Suy ra x y ≥ 1 ⇒ x y ≥ 1.