Biết rằng phương trình
log 2 2 x - 3 log 2 x + 1 = 0
có hai nghiêm phân biệt. Gọi hai nghiệm đó là x1, x2.
Giá trị của tích x1x2 bằng:
A. 8
B. 6
C. 2
D. 9
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) \(x^2+2\left(m-1\right)x-6m-7=0\)\(0\)
\(\left(a=1;b=2\left(m-1\right);b'=m-1;c=-6m-7\right)\)
\(\Delta'=b'^2-ac\)
\(=\left(m-1\right)^2-1.\left(-6m-7\right)\)
\(=m^2-2m+1+6m+7\)
\(=m^2+4m+8\)
\(=m^2+2.m.2+2^2+4\)
\(=\left(m+2\right)^2+4>0,\forall m\)
Vì \(\Delta'>0\) nên phương trình ( 1 ) luôn có 1 nghiệm phân biệt với mọi m

Chọn C.
Điều kiện: 5x – 1 > 0 hay x > 0
Phương trình đã cho tương đương:
log2( 5x - 1) [log2( 5x - 1) + 1] = 2
Đặt t = log2(5x - 1), khi đó phuơng trình trở thành: t(t + 1) = 2
Suy ra t = 1 hoặc t = -2
Với t =1 ta có log2(5x - 1) = 1 nên 5x – 1 = 2; x = log53
Với t = -2ta có log2(5x - 1) = - 2 nên 5x – 1 = 2-2; x = log5(5/4)
Mặt khác x1 > x2 suy ra 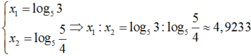

\(\Delta=1-4\left(-m-2\right)\ge0\Leftrightarrow m\ge-\dfrac{9}{4}\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=-1\\x_1x_2=-m-2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2-x_1x_2-2x_2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1\left(x_1+x_2\right)-2x_1x_2-2x_2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-x_1-2\left(-m-2\right)-2x_2=16\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1+2x_2=2m-12\)
\(\Rightarrow x_1+x_2+x_2=2m-12\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-1+x_2=2m-12\Rightarrow x_2=2m-11\Rightarrow x_1=-1-x_2=-2m+10\)
Lại có: \(x_1x_2=-m-2\)
\(\Rightarrow\left(-2m+10\right)\left(2m-11\right)=-m-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-43m+108=0\Rightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=4\\m=\dfrac{27}{4}\end{matrix}\right.\)

a, \(\Delta'=\left(-m\right)^2-1\left(-1\right)=m^2+1>0\)
Vậy phương trình đã cho luôn có hai nghiệm phân biệt x1 và x2
b, Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=2m\\x_1x_2=-1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x^2_1+x^2_2-x_1x_2=7\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-3x_1x_2=7\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(2m\right)^2-3\left(-1\right)=7\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2+3=7\\ \Leftrightarrow4m^2=4\\ \Leftrightarrow m^2=1\\ \Leftrightarrow m=\pm1\)

\(\Delta'=1-4\left(m+1\right)=-4m-3>0\Rightarrow m< -\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Theo hệ thức Viet: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=1\\x_1x_2=m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1^2+x_1x_2=7-3x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1\left(x_1+x_2\right)=7-3x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1=7-3x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1+x_2=7-2x_2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1=7-2x_2\Rightarrow x_2=3\Rightarrow x_1=1-x_2=-2\)
Thế vào \(x_1x_2=m+1\Rightarrow-6=m+1\Rightarrow m=-7\)

3:
\(\Delta=\left(2m-1\right)^2-4\left(-2m-11\right)\)
=4m^2-4m+1+8m+44
=4m^2+4m+45
=(2m+1)^2+44>=44>0
=>Phương trình luôn có hai nghiệm pb
|x1-x2|<=4
=>\(\sqrt{\left(x_1+x_2\right)^2-4x_1x_2}< =4\)
=>\(\sqrt{\left(2m-1\right)^2-4\left(-2m-11\right)}< =4\)
=>\(\sqrt{4m^2-4m+1+8m+44}< =4\)
=>0<=4m^2+4m+45<=16
=>4m^2+4m+29<=0
=>(2m+1)^2+28<=0(vô lý)

a, Thay m=0 vào pt ta có:
\(x^2-x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow\) pt vô nghiệm
b, Để pt có 2 nghiệm thì \(\Delta\ge0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(-1\right)^2-4.1\left(m+1\right)\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow1-4m-4\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow-3-4m\ge0\\ \Leftrightarrow4m+3\le0\\ \Leftrightarrow m\le-\dfrac{3}{4}\)
Theo Vi-ét:\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x_1+x_2=1\\x_1x_2=m+1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(x_1x_2\left(x_1x_2-2\right)=3\left(x_1+x_2\right)\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x_1x_2\right)^2-2x_1x_2=3.1\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(m+1\right)^2-2\left(m+1\right)-3=0\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m+1=3\\m+1=-1\end{matrix}\right.\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}m=2\left(ktm\right)\\m=-2\left(tm\right)\end{matrix}\right.\)
Chọn A.