Tìm các giá trị của a sao cho biểu thức sau có giá trị bằng 2: 3 a - 1 3 a + 1 + a - 3 a + 3
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

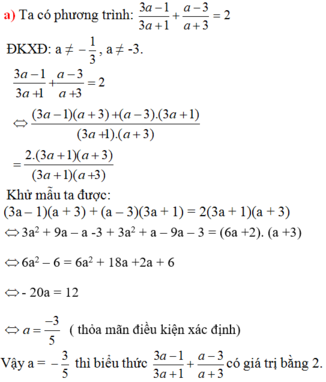

Bài 2:
(1 + x)3 + (1 - x)3 - 6x(x + 1) = 6
<=> x3 + 3x2 + 3x + 1 - x3 + 3x2 - 3x + 1 - 6x2 - 6x = 6
<=> -6x + 2 = 6
<=> -6x = 6 - 2
<=> -6x = 4
<=> x = -4/6 = -2/3
Bài 3:
a) (7x - 2x)(2x - 1)(x + 3) = 0
<=> 10x3 + 25x2 - 15x = 0
<=> 5x(2x - 1)(x + 3) = 0
<=> 5x = 0 hoặc 2x - 1 = 0 hoặc x + 3 = 0
<=> x = 0 hoặc x = 1/2 hoặc x = -3
b) (4x - 1)(x - 3) - (x - 3)(5x + 2) = 0
<=> 4x2 - 13x + 3 - 5x2 + 13x + 6 = 0
<=> -x2 + 9 = 0
<=> -x2 = -9
<=> x2 = 9
<=> x = +-3
c) (x + 4)(5x + 9) - x2 + 16 = 0
<=> 5x2 + 9x + 20x + 36 - x2 + 16 = 0
<=> 4x2 + 29x + 52 = 0
<=> 4x2 + 13x + 16x + 52 = 0
<=> 4x(x + 4) + 13(x + 4) = 0
<=> (4x + 13)(x + 4) = 0
<=> 4x + 13 = 0 hoặc x + 4 = 0
<=> x = -13/4 hoặc x = -4

T a c ó : A = B ⇔ ( x + 2 ) ( x – 2 ) + 3 x 2 = ( 2 x + 1 ) 2 + 2 x ⇔ x 2 – 4 + 3 x 2 = 4 x 2 + 4 x + 1 + 2 x ⇔ x 2 + 3 x 2 – 4 x 2 – 4 x – 2 x = 1 + 4 ⇔ - 6 x = 5 ⇔ x = - 5 / 6 V ậ y v ớ i x = - 5 / 6 t h ì A = B .

T a c ó : A = B ⇔ ( x – 3 ) ( x + 4 ) – 2 ( 3 x – 2 ) = ( x – 4 ) 2 ⇔ x 2 + 4 x – 3 x – 12 – 6 x + 4 = x 2 – 8 x + 16 ⇔ x 2 – x 2 + 4 x – 3 x – 6 x + 8 x = 16 + 12 – 4 ⇔ 3 x = 24 ⇔ x = 8 V ậ y v ớ i x = 8 t h ì A = B

ĐKXĐ của phương trình : \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x\ne-\frac{1}{3}\\x\ne-3\end{cases}}\)
\(\frac{3a-1}{3a+1}+\frac{a-3}{a+3}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(3a-1\right)\left(a+3\right)+\left(a-3\right)\left(3a+1\right)=2\left(3a+1\right)\left(a+3\right)\)\(\Leftrightarrow3a^2+8a-3+3a^2-8a-3=2\left(3a^2+10a+3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow6a^2-6-6a^2-20a-6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-20a-12=0\Leftrightarrow a=\frac{-12}{20}=-\frac{3}{5}\)(NHẬN)
vậy tập nghiệm của phương trình là : S = { -3/5 }
Tk mk nka !!! Th@nks !!

a: Để \(\dfrac{3x-2}{4}\) không nhỏ hơn \(\dfrac{3x+3}{6}\) thì \(\dfrac{3x-2}{4}>=\dfrac{3x+3}{6}\)
=>\(\dfrac{6\left(3x-2\right)}{24}>=\dfrac{4\left(3x+3\right)}{24}\)
=>18x-12>=12x+12
=>6x>=24
=>x>=4
b: Để \(\left(x+1\right)^2\) nhỏ hơn \(\left(x-1\right)^2\) thì \(\left(x+1\right)^2< \left(x-1\right)^2\)
=>\(x^2+2x+1< x^2-2x+1\)
=>4x<0
=>x<0
c: Để \(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\) không lớn hơn \(\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\) thì
\(\dfrac{2x-3}{35}+\dfrac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}< =\dfrac{x^2}{7}-\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\)
=>\(\dfrac{2x-3+5x\left(x-2\right)}{35}< =\dfrac{5x^2-7\cdot\left(2x-3\right)}{35}\)
=>\(2x-3+5x^2-10x< =5x^2-14x+21\)
=>-8x-3<=-14x+21
=>6x<=24
=>x<=4

T a c ó : A = B ⇔ ( x + 1 ) 3 – ( x – 2 ) 3 = ( 3 x – 1 ) ( 3 x + 1 ) ⇔ x 3 + 3 x 2 + 3 x + 1 – x 3 + 6 x 2 – 12 x + 8 = 9 x 2 – 1 ⇔ x 3 – x 3 + 3 x 2 + 6 x 2 – 9 x 2 + 3 x – 12 x = - 1 – 1 – 8 ⇔ - 9 x = - 10 ⇔ x = 10 / 9 V ậ y v ớ i x = 10 / 9 t h ì A = B .

T a c ó : A = B ⇔ ( x – 1 ) ( x 2 + x + 1 ) – 2 x = x ( x – 1 ) ( x + 1 ) ⇔ x 3 – 1 – 2 x = x ( x 2 – 1 ) ⇔ x 3 – 1 – 2 x = x 3 – x ⇔ x 3 – x 3 – 2 x + x = 1 ⇔ - x = 1 ⇔ x = - 1 V ậ y v ớ i x = - 1 t h ì A = B

