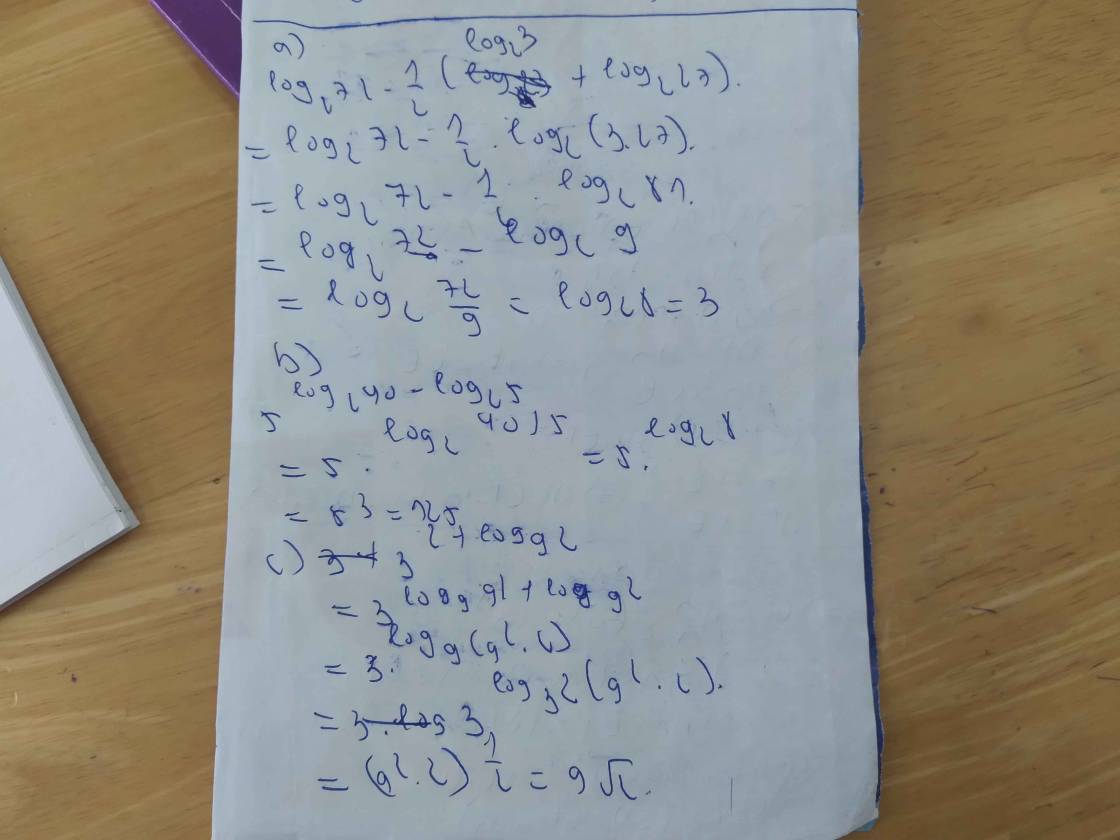\(x+x^{log_23}=x^{log_25}\)
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a,log_272-\dfrac{1}{2}\left(log_23+log_227\right)\\ =log_272-\dfrac{1}{2}log_2\left(3\cdot27\right)\\ =log_272-log_2\left(81\right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}\\ =log_272-log_29\\ =log_2\dfrac{72}{9}\\ =log_28\\ =3\)
\(b,5^{log_240-log_25}\\ =5^{log_2\dfrac{40}{5}}\\ =5^{log_28}\\ =5^3\\ =125\)
\(c,3^{2+log_92}\\ =3^{log_9\left(81\cdot2\right)}\\ =3^{\dfrac{1}{2}log_3162}\\ =\left(162\right)^{\dfrac{1}{2}}\\ =\sqrt{162}\\ =9\sqrt{2}\)

\(log_216=log_22^4=4\)
\(log_32187=log_33^7=7\)
\(log_{10}\dfrac{1}{100}=log_{10}10^{-2}=-2\)
\(log10000=log10^4=4\)
\(9^{log_312}=3^{2log_312}=3^{log_3144}=144\)
\(8^{log_25}=2^{3log_25}=2^{log_2125}=125\)
\(\left(\dfrac{1}{25}\right)^{log_5\dfrac{1}{3}}=5^{-2log_5\dfrac{1}{3}}=5^{log_59}=9\)
\(\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right)^{log_23}=2^{-2log_23}=2^{log_2\dfrac{1}{9}}=\dfrac{1}{9}\)

Ta có : \(D=\log_6\left(21,6\right)=\frac{\log_2\left(21,6\right)}{\log_26}=\frac{\log_2\frac{2^2.3^3}{5}}{\log_2\left(2.3\right)}=\frac{2+3\log_23-\log_25}{1+\log_23}=\frac{2+3a-b}{1+a}\)

Lời giải:
ĐK: \(x\in (0;+\infty)\)
\(x^{\log_29}=x^2.3^{\log_2x}-x^{\log_23}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^{2\log_23}=x^2.x^{\log_23}-x^{\log_23}=x^{\log_23+2}-x^{\log_23}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^{\log_23}(x^{\log_23}-x^2+1)=0\). Do $x\neq 0$ nên:
\(x^2-x^{\log_23}=1(*)\)
Nếu \(0< x\leq 1\Rightarrow x^2\leq 1; x^{\log_23}>0\Rightarrow x^2-x^{\log_23}< 1\) (vô lý). Do đó \(x\in (1;+\infty)\)
Đặt \(f(x)=x^2-x^{\log_23}\Rightarrow f'(x)=2x-\log_23x^{\log_23-1}\)
\(=x^{\log_23-1}(2x^{2-\log_23}-\log_23)>x^{\log_23-1}(2.1-\log_23)>0\)với mọi $x\in (1;+\infty)$ nên $f(x)$ đồng biến với mọi $x\in (1;+infty)$. Mà ở vế phải thì $1$ là hàm hằng. Do đó $(*)$ chỉ có nghiệm duy nhất.
Dễ thấy $x=2$ là nghiệm duy nhất của pt

ĐKXĐ: \(-x^2+4x+m>0\)
\(log_2\left(-x^2+4x+m\right)-log_2\left(x^2+2\right)< log_23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow log_2\left(\dfrac{-x^2+4x+m}{x^2+2}\right)< log_23\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{-x^2+4x+m}{x^2+2}< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}-x^2+4x+m>0\\-x^2+4x+m< 3x^2+6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>x^2-4x\\m< 4x^2-4x+6\end{matrix}\right.\) ; \(\forall x\in\left[1;5\right]\)
Xét hai hàm \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)=x^2-4x\\g\left(x\right)=4x^2-4x+6\end{matrix}\right.\) trên \(\left[1;5\right]\) ta được: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}f\left(x\right)_{max}=f\left(5\right)=5\\g\left(x\right)_{min}=g\left(1\right)=6\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow5\le m\le6\)
Có 2 giá trị nguyên của m

Lời giải:
a) Vì \(6^x-2^x>0\Rightarrow x>0\)
Xét \(y=6^x-2^x-32\) có \(y'=\ln 6.6^x-\ln 2.2^x>0\forall x>0\) nên hàm $y$ đồng biến trên \(x\in(0,+\infty)\).
Khi đó phương trình \(6^x-2^x=32\) có nghiệm duy nhất $x=2$
b) Có \(5^{7^x}=7^{5^x}\Leftrightarrow \log(5^{7^x})=\log (7^{5^x})\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 7^x\log 5=5^x\log 7=7^{x\frac{\log 5}{\log 7}}\log 7\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 7^{x(1-\frac{\log 5}{\log 7})}=\frac{\log 7}{\log 5}=10^{x\log 7(1-\frac{\log 5}{\log 7})}=10^{x\log(\frac{7}{5})}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\log\frac{7}{5}=\log\left ( \frac{\log 7}{\log 5} \right )\)\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{\log\left ( \frac{\log 7}{\log 5} \right )}{\log\frac{7}{5}}\)
d) ĐKXĐ:...........
\(3^x+\frac{1}{3^x}=\sqrt{8-x^2}\Leftrightarrow 9^x+\frac{1}{9^x}+2=8-x^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow 9^x+\frac{1}{9^x}+x^2=6\)
Giả sử \(x\geq 0\) . Xét hàm \(y=9^x+\frac{1}{9^x}+x^2\) có \(y'=9^x\ln 9-\frac{\ln 9}{9^x}+2x\geq 0\) nên hàm đồng biến trên \(x\in [0,+\infty)\)
Do đó PT \(9^x+\frac{1}{9^x}+x^2=6\) với $x\geq 0$ có nghiệm duy nhất \(x\approx 0,753897\)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Vì hàm \(y\) là hàm chẵn nên $-x$ cũng là nghiệm, do đó tổng kết lại PT có nghiệm là \(x\approx \pm 0,753897\)

18.
\(F\left(x\right)=\int\limits xe^{x^2}dx\)
Đặt \(t=x^2\Rightarrow xdx=\frac{1}{2}dt\)
\(\Rightarrow F\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{2}\int e^tdt=\frac{1}{2}e^t+C=\frac{1}{2}e^{x^2}+C\)
Ủa bạn có ghi nhầm đáp án A ko? Thế nào thì cả A và D đều ko phải nguyên hàm
19.
\(F\left(x\right)=\int sin^4xcosxdx=\int sin^4x.d\left(sinx\right)=\frac{1}{5}sin^5x+C\)
20.
Đặt \(4x=t\Rightarrow dx=\frac{1}{4}dt\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\Rightarrow t=0\\x=2\Rightarrow t=8\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\int\limits^2_0f\left(4x\right)dx=\int\limits^8_0\frac{1}{4}f\left(t\right)dt=\frac{1}{4}\int\limits^8_0f\left(x\right)dx=\frac{1}{4}.24=6\)
15.
\(t=cosx\Rightarrow sinx.dx=-dt\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\Rightarrow t=1\\x=\frac{\pi}{2}\Rightarrow t=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int\limits^0_1e^t\left(-dt\right)=\int\limits^1_0e^tdt\)
Nếu cần kết quả tích phân thì \(I=e-1\)
16.
\(t=x^2\Rightarrow x.dx=\frac{1}{2}dt\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\Rightarrow t=0\\x=2\Rightarrow t=4\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int\limits^4_04^t\left(\frac{1}{2}dt\right)=\frac{1}{2}\int\limits^4_04^tdt\)
17.
\(t=x^2+2x\Rightarrow\left(x+1\right)dx=\frac{1}{2}dt\) ; \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x=0\Rightarrow t=0\\x=1\Rightarrow t=3\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I=\int\limits^3_0e^t\left(\frac{1}{2}dt\right)=\frac{1}{2}\int\limits^3_0e^tdt\)

1.
\(A=3log_{2^2}\sqrt{a}-log_{2^{-1}}a^2+2log_{a^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}a\)
\(=3.\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{2}log_2a-\left(-1\right).2.log_2a+2.2.log_2a\)
\(=\dfrac{27}{4}log_2a\)
2.
\(log_{12}36=\dfrac{log_236}{log_212}=\dfrac{log_2\left(3^2.2^2\right)}{log_2\left(3.2^2\right)}=\dfrac{log_23^2+log_22^2}{log_23+log_22^2}\)
\(=\dfrac{2.log_23+2}{log_23+2}=\dfrac{2a+2}{a+2}\)
cho e hỏi tại sao \(3\log_{2^2}\sqrt{a}\) lại bằng \(3.\dfrac{1}{2}.\dfrac{1}{2}\log_2a\) và \(2\log_{a^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}a=2.2.\log_2a\)