Mn cho em xin lời giải bài này ạ..... Em cảm ơn mn nhiều ạ
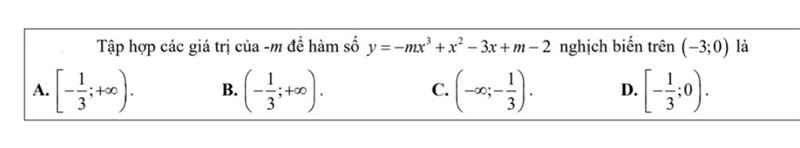
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Từ đồ thị ta thấy \(f'\left(x\right)>0\) trên các khoảng \(\left(-1;1\right)\) và \(\left(3;+\infty\right)\)
\(f'\left(x\right)< 0\) trên \(\left(-\infty;-1\right)\) và \(\left(1;3\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Hàm nghịch biến trên (1;3)

Đặt \(x=\sqrt[3]{\sqrt[]{50}+7}-\sqrt[3]{\sqrt[]{50}-7}\)
\(x^3=14-3\sqrt[3]{\left(\sqrt[]{50}+7\right)\left(\sqrt[]{50}-7\right)}\left(\sqrt[3]{\sqrt[]{50}+7}-\sqrt[3]{\sqrt[]{50}-7}\right)\)
\(x^3=14-3x\)
\(x^3+3x-14=0\)
\(\left(x-2\right)\left(x^2+2x+7\right)=0\)
\(x=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\dfrac{m}{n}=2\)
\(\Rightarrow\) Hiển nhiên tồn tại vô số m, n nguyên thỏa mãn đẳng thức trên

a: Δ=(m-2)^2-4(m-4)
=m^2-4m+4-4m+16
=m^2-8m+20
=m^2-8m+16+4
=(m-2)^2+4>=4>0
=>Phương trình luôn có 2 nghiệm pb
b: x1^2+x2^2
=(x1+x2)^2-2x1x2
=(m-2)^2-2(m-4)
=m^2-4m+4-2m+8
=m^2-6m+12
=(m-3)^2+3>=3
Dấu = xảy ra khi m=3

\(a,\dfrac{x}{9}=\dfrac{5}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=9\cdot\dfrac{5}{3}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=15\\ b,\dfrac{17}{x}=\dfrac{85}{105}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=17\cdot\dfrac{105}{85}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=21\\ c,\dfrac{x}{8}+\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{7}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{x}{8}=\dfrac{1}{2}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\\ d,\dfrac{3}{x-7}=\dfrac{27}{135}\\ \Leftrightarrow x-7=15\\ \Leftrightarrow x=22\)
\(e,\dfrac{75}{20-x}=\dfrac{3}{2}\times10\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{75}{20-x}=15\\ \Leftrightarrow20-x=5\\ \Leftrightarrow x=15\\ f,\left(x-50\%\right)\times\dfrac{5}{3}=\dfrac{7}{4}-0,5\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right)\times\dfrac{5}{3}=\dfrac{5}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{1}{2}=\dfrac{3}{4}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{4}\\ g,\left(\dfrac{2}{15}+\dfrac{3}{35}+\dfrac{2}{63}\right):x=\dfrac{1}{18}\\ \Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2}{9}:x=\dfrac{1}{18}\\ \Leftrightarrow x=4\)
\(h,\left[\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right):6+4\right]\times\dfrac{2}{3}=0,6\times\dfrac{40}{6}\\ \Leftrightarrow\left[\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right):6+4\right]\times\dfrac{2}{3}=4\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right):6+4=6\\ \Leftrightarrow\left(x-\dfrac{1}{2}\right):6=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x-\dfrac{1}{2}=12\\ \Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{25}{2}\)

\(y=\dfrac{sinx-cosx}{sinx+cosx}\Rightarrow y'=\dfrac{\left(sinx-cosx\right)'.\left(sinx+cosx\right)-\left(sinx+cosx\right)'.\left(sinx-cosx\right)}{\left(sinx+cosx\right)^2}\)
Dễ thấy : \(\left(sinx-cosx\right)'=cosx+sinx\)
\(\left(sinx+cosx\right)'=cosx-sinx\)
Suy ra : \(y'=\dfrac{\left(sinx+cosx\right)^2+\left(sinx-cosx\right)^2}{\left(sinx+cosx\right)^2}=\dfrac{2}{\left(sinx+cosx\right)^2}\)

3.15:
EF vuông góc MH
NP vuông góc MH
Do đó: EF//NP
3.17:
góc yKH+góc H=180 độ
mà hai góc này là hai góc ở vị trí trong cùng phía
nên Ky//Hx

3.
Từ BBT ta thấy hàm đồng biến trên các khoảng \(\left(-\infty;-1\right)\) và \(\left(1;+\infty\right)\)
B đúng
4.
Từ BBT ta thấy hàm đồng biến trên các khoảng \(\left(-\infty;-1\right)\) và \(\left(0;1\right)\)
A đúng
1.
B sai (thiếu điều kiện \(f'\left(x\right)=0\) tại hữu hạn điểm)
\(y'=-3mx^2+2x-3\)
Hàm nghịch biến trên khoảng đã cho khi với mọi \(x\in\left(-3;0\right)\) ta có:
\(-3mx^2+2x-3\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x-3\le3mx^2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{2x-3}{3x^2}\le m\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge\max\limits_{\left(-3;0\right)}\left(\dfrac{2x-3}{3x^2}\right)\)
Xét hàm \(f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2x-3}{3x^2}\Rightarrow f'\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2\left(3-x\right)}{3x^3}< 0;\forall x\in\left(-3;0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow f\left(x\right)>f\left(-3\right)=-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow m\ge-\dfrac{1}{3}\)
CHọn B