Tìm x sao cho giá trị của biểu thức \(\frac{5-2x}{6}\)là số dương.
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


Để giá trị biểu thức 5 – 2x là số dương
⇔ 5 – 2x > 0
⇔ -2x > -5 (Chuyển vế và đổi dấu hạng tử 5)
⇔ 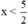 (Chia cả hai vế cho -2 < 0, BPT đổi chiều)
(Chia cả hai vế cho -2 < 0, BPT đổi chiều)
Vậy 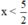

a) Để giá trị biểu thức 5 – 2x là số dương
<=> 5 – 2x > 0
<=> -2x > -5 ( Chuyển vế và đổi dấu hạng tử 5 )
\(\Leftrightarrow x< \frac{5}{2}\)( Chia cả 2 vế cho -2 < 0 ; BPT đổi chiều )
Vậy : \(x< \frac{5}{2}\)
b) Để giá trị của biểu thức x + 3 nhỏ hơn giá trị biểu thức 4x - 5 thì:
x + 3 < 4x – 5
<=< x – 4x < -3 – 5 ( chuyển vế và đổi dấu các hạng tử 4x và 3 )
<=> -3x < -8
\(\Leftrightarrow x>\frac{8}{3}\)( Chia cả hai vế cho -3 < 0, BPT đổi chiều).
Vậy : \(x>\frac{8}{3}\)
c) Để giá trị của biểu thức 2x +1 không nhỏ hơn giá trị của biểu thức x + 3 thì:
2x + 1 ≥ x + 3
<=> 2x – x ≥ 3 – 1 (chuyển vế và đổi dấu các hạng tử 1 và x).
<=> x ≥ 2.
Vậy x ≥ 2.
d) Để giá trị của biểu thức x2 + 1 không lớn hơn giá trị của biểu thức (x - 2)2 thì:
x2 + 1 ≤ (x – 2)2
<=> x2 + 1 ≤ x2 – 4x + 4
<=> x2 – x2 + 4x ≤ 4 – 1 ( chuyển vế và đổi dấu hạng tử 1; x2 và – 4x).
<=> 4x ≤ 3
\(\Leftrightarrow x\le\frac{3}{4}\)( Chia cả 2 vế cho 4 > 0 )
Vậy : \(x\le\frac{3}{4}\)

A/ Theo đề ta có \(\frac{x}{2}-\frac{x-5}{10}\) không âm
\(\Rightarrow\frac{x}{2}-\frac{x-5}{10}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{5x}{10}-\frac{x-5}{10}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{5x-x+5}{10}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{4x+5}{10}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow4x+5\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow4x\ge-5\)
\(\Rightarrow x\ge-\frac{5}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow S=\left\{x\in R;x\ge-\frac{5}{4}\right\}\)
B/ theo đề ta có \(\frac{2x-3}{8}-\frac{x-5}{12}\) không dương
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x-3}{8}-\frac{x-5}{12}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3\left(2x-3\right)}{24}-\frac{2\left(x-5\right)}{24}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{6x-9}{24}-\frac{2x-10}{24}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{6x-9-2x+10}{24}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{4x-1}{24}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow4x-1\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow4x\le1\)
\(\Rightarrow x\le\frac{1}{4}\)
\(\Rightarrow S=\left\{x\in R;x\le\frac{1}{4}\right\}\)

Bài 1:
a) Vì giá trị của biểu thức \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\) không nhỏ hơn giá trị của biểu thức \(\frac{3x+3}{6}\) nên \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\) \(\ge\) \(\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
TH1: \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\) = \(\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
=> (3x-2)6 = (3x+3)4
18x -12= 12x+12
=> x = 4
TH2: \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\) > \(\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
=> (3x-2)6 > (3x+3)4
18x-12> 12x+12
=> x \(\ge\) 5
b) Vì ( x+1)2 \(\ge\) 0; (x-1)2 \(\ge\) 0 mà (x+1) luôn lớn hơn (x-1) với mọi x nên không có giá trị của x thỏa mãn (x+1)2 nhỏ hơn (x-1)2
c) Phần c bạn cũng xét tương tự như phần a
TH1: \(\frac{2x-3}{35}+\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}=\frac{x^2}{7}-\frac{2x-3}{5}\)
TH2: \(\frac{2x-3}{35}+\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}<\frac{x^2}{7}-\frac{2x-3}{5}\)

a: \(\dfrac{2x-2}{3}>=\dfrac{x+3}{6}\)
=>4x-4>=x+3
=>3x>=7
=>x>=7/3
b: (x+3)^2<(x-2)^2
=>6x+9<4x-4
=>2x<-13
=>x<-13/2
c: \(\dfrac{2x-3}{3}-x< =\dfrac{2x-3}{5}\)
=>2/3x-1-x<=2/5x-3/5
=>-11/15x<2/5
=>x>-6/11

Answer:
a) \(\frac{5x}{2x+2}+1=\frac{6}{x+1}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{5x}{2\left(x+1\right)}+\frac{2\left(x+1\right)}{2\left(x+1\right)}=\frac{12}{2\left(x+1\right)}\)
\(\Rightarrow5x+2x+2-12=0\)
\(\Rightarrow7x-10=0\)
\(\Rightarrow x=\frac{10}{7}\)
b) \(\frac{x^2-6}{x}=x+\frac{3}{2}\left(ĐK:x\ne0\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2-6=x^2+\frac{3}{2}x\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3}{2}x=-6\)
\(\Rightarrow x=-4\)
c) \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\ge\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3\left(3x-2\right)-2\left(3x+3\right)}{12}\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow9x-6-6x-6\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x-12\ge0\)
\(\Rightarrow x\ge4\)
d) \(\left(x+1\right)^2< \left(x-1\right)^2\)
\(\Rightarrow x^2+2x+1< x^2-2x+1\)
\(\Rightarrow4x< 0\)
\(\Rightarrow x< 0\)
e) \(\frac{2x-3}{35}+\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}\le\frac{x^2}{7}-\frac{2x-3}{5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{2x-3+5\left(x^2-2x\right)}{35}\le\frac{5x^2-7\left(2x-3\right)}{35}\)
\(\Rightarrow2x-3+5x^2-10x\le5x^2-14x+21\)
\(\Rightarrow6x\le24\)
\(\Rightarrow x\le4\)
f) \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\le\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3\left(3x-2\right)-2\left(3x+3\right)}{12}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow9x-6-6x-6\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x\le12\)
\(\Rightarrow x\le4\)

a) \(ĐKXĐ:\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne\pm2\\x\ne-\frac{13}{6}\end{cases}}\)
Đặt \(A=\left(\frac{1+2x}{4+2x}-\frac{x}{3x-6}+\frac{2x^2}{12-3x^2}\right)\cdot\frac{24-12x}{6+13x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\left(\frac{1+2x}{2\left(x+2\right)}-\frac{x}{3\left(x-2\right)}-\frac{2x^2}{3\left(x^2-4\right)}\right)\cdot\frac{12\left(2-x\right)}{6+13x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{3\left(2x^2-3x-2\right)-2\left(x^2+2x\right)-4x^2}{6\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\cdot\frac{12\left(2-x\right)}{6+13x}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{-2\left(6x^2-9x-6-2x^2-4x-4x^2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(6+13x\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{-2\left(-6-13x\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(6+13x\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow A=\frac{2}{x+2}\)
b) Để biểu thức nhận giá trị dương
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{2}{x+2}>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x+2>0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-2\)
Vậy để biểu thức có giá trị dương thì \(x>-2\)
Theo đề bài ta có :
\(\frac{5-2x}{6}>0\) ( vì biểu thức là số dương )
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(5-2x>0\) ( nhân 2 vế cho 6 )
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(2x< 5\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\)\(x< \frac{5}{2}\)
Vậy \(x< \frac{5}{2}\) thì biểu thức \(\frac{5-2x}{6}\) là số dương
Chúc bạn học tốt ~