Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a) Các phương trình phản ứng xảy ra là:
\(C+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}CO_2\)
\(S+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}SO_2\)
\(4P+5O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2P_2O_5\)
b) Các phương trình phản ứng xảy ra là:
\(4Na+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2Na_2O\)
\(2Zn+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2ZnO\)
\(4Al+3O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2Al_2O_3\)
\(3Fe+2O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}Fe_3O_4\)
\(2Cu+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2CuO\)
c) Các phương trình phản ứng xảy ra là:
\(2CO+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2CO_2\)
\(2NO+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2NO_2\)
\(CH_4+3O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}CO_2+2H_2O\)
\(2C_2H_6+7O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}4CO_2+6H_2O\)
\(C_3H_8+5O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}3CO_2+4H_2O\)
a)
\(C+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}CO_2\\ S+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}SO_2\\ 4P+5O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2P_2O_5\)
b)
\(4Na+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2Na_2O\\ 2Zn+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2ZnO\\ 4Al+3O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2Al_2O_3\\ 3Fe+2O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}Fe_3O_4\\ 2Cu+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2CuO\)
c)
\(2CO+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2CO_2\\ 2NO+O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}2NO_2\\ CH_4+2O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}CO_2+2H_2O\\ 2C_2H_6+7O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}4CO_2+6H_2O\\ C_3H_8+5O_2\xrightarrow[]{t^o}3CO_2+4H_2O\)

S + O2 ➝ SO2 ( thuộc loại oxit axit , SO2: lưu huỳnh đioxit)
P + O2 ➝ P2O5 ( thuộc loại oxit axit , P2O5: đi phôtpho pentaoxit)
C + O2➝ CO2 ( thuộc loại oxit axit , CO2 : cacbon đioxit )
Si + O2 ➝ SiO2( thuộc loại oxit axit , SiO2: silic đioxit )
Cu + O2 ➝ Cu2O(thuộc loại oxit bazo , Cu2O: đồng (1) oxit )
Na + O2➝ Na2O( thuộc loại oxit bazo , Na2O: natri oxit)
Fe + O2➝ Fe3O4(thuộc loại oxit bazo , Fe3O4: oxit sắt từ)
Al + O2 ➝ Al2O3(thuộc loại oxit bazo , Al2O3: nhôm oxit)
Mg + O2➝ MgO(thuộc loại oxit bazo , Mg : magie oxit)
CH4 + O2 ➝ CO2 + H2O (thuộc loại oxit axit , CH4: khí metan
H2O: nước
Chúc bạn học tốt

C + O2 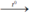 CO2. Cacbon đioxit.
CO2. Cacbon đioxit.
4P + 5O2 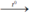 2P2O5. Điphotpho pentaoxit.
2P2O5. Điphotpho pentaoxit.
2H2 + O2 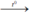 2H2O. Nước.
2H2O. Nước.
4Al + 3O2 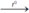 2Al2O3. Nhôm oxit.
2Al2O3. Nhôm oxit.

a)\(CH4+2O2-->CO2+2H2O\)
\(n_{CH4}=\frac{3,2}{16}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(n_{O2}=2n_{CH4}=0,4\left(mol\right)\)
\(V_{O2}=0,4.22,4=8,96\left(l\right)\)
b)\(n_{CO2}=n_{CH4}=0,2\left(mol\right)\)
\(m_{CO2}=0,2.44=8,8\left(g\right)\)
15: Đốt cháy 4,6 g một hợp chất bằng oxi thu được 8,8g CO2 và 5,4g H2O. Khối lượng oxi đã tham gia phản ứng:
a) 9,6g b) 8,6g c)10g d) 9,8g
16:
\(C3H8+5O2-->3CO2+4H2O\)
Thiếu bài 17
a) C+O2--------->CO2
S+O2------------->SO2
4P+5O2--------->2P2O5
b) 4Na+O2------->2Na2O
2Zn+O2---------->2ZnO
4Al+3O2----->2Al2O3
3Fe+2O2-------->Fe3O4
2Cu+O2--------->2CuO
c)2 CO+O2------>2CO2
2NO+O2--->2NO2
CH4+2O2------>CO2+2H2O
C2H6+7/2O2------>2CO2+3H2O
C3H8+5O2---------->3CO2+4H2O

Bài 8:
\(V_{O_2}=20.100=2000\left(ml\right)=2\left(l\right)\\ a,PTHH:2KMnO_4\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)K_2MnO_4+MnO_2+O_2\\ n_{O_2}=\dfrac{2}{22,4}=\dfrac{5}{56}\left(mol\right)\\ n_{O_2\left(p.ứ\right)}=\dfrac{5}{56}.90\%=\dfrac{9}{112}\left(mol\right)\\ n_{KMnO_4\left(dùng\right)}=\dfrac{9}{112}.2=\dfrac{9}{56}\left(mol\right)\\ \Rightarrow m_{KMnO_4}=\dfrac{9}{56}.158=\dfrac{711}{28}\left(g\right)\\ b,2KClO_3\rightarrow\left(t^o,xt\right)2KCl+3O_2\\ n_{KClO_3}=\dfrac{2}{56}.\dfrac{2}{3}=\dfrac{1}{42}\left(mol\right)\\ m_{KClO_3}=122,5.\dfrac{1}{42}=\dfrac{35}{12}\left(g\right)\)
Bài 1:
\(C+O_2\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)CO_2\)
Tên sản phẩm: Cacbon dioxit/ Khí cacbonic
\(4P+5O_2\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)2P_2O_5\)
Tên sản phẩm: Điphotpho pentaoxit
\(2H_2+O_2\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)2H_2O\)
Tên sản phẩm: Nước
\(4Al+3O_2\rightarrow\left(t^o\right)2Al_2O_3\)
Tên sản phẩm: Nhôm oxit

a. 2Al + 6HCl -> 2AlCl3 + 3H2 (Phản ứng thế)
b. CH4 + 2O2 -> (t°) CO2 + 2H2O (Phản ứng thế)
c. 3Fe + 2O2 -> (t°) Fe3O4 (Phản ứng hóa hợp)
d. Fe3O4 + 4H2 -> (t°) 3Fe + 4H2O (Phản ứng oxi hóa - khử )
e. 2Zn + O2 -> (t°) 2ZnO (Phản ứng hóa hợp)
f. CuO + H2 -> (t°) Cu + H2O (Phản ứng oxi hóa - khử)
g. 2KMnO4 -> (t°) K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2 (Phản ứng phân hủy)
h. Fe + H2SO4 -> FeSO4 + H2 (Phản ứng thế)
a: \(2Al+6HCl\rightarrow2AlCl_3+3H_2\)
b: \(CH_4+2O_2\rightarrow CO_2+2H_2O\)
c: \(3Fe+2O_2\rightarrow Fe_3O_4\)
d: \(Fe_3O_4+4H_2\rightarrow3Fe+4H_2O\)

1)
3Fe + 2O2 -to-> Fe3O4
C + O2 -to-> CO2
4P + 5O2 -to-> 2P2O5
4Al + 3O2 -to-> 2Al2O3
2Cu + O2 -to-> 2CuO
2Zn + O2 -to-> 2ZnO
S + O2 -to-> SO2
4Na + O2 -to-> 2Na2O
2Ba + O2 -to-> 2BaO
CH4 + 2O2 -to-> CO2 + 2H2O
C2H5OH + 3O2 -to-> 2CO2 + 3H2O
NO + 1/2O2 -to-> NO2
CO + 1/2O2 -to-> CO2
b)
2KClO3 -to-> 2KCl + 3O2
2KMnO4 -to-> K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2
\(a)\\ 3Fe + 2O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} Fe_3O_4\\ C + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} CO_2\\ 4P + 5O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2P_2O_5\\ 4Al + 3O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2Al_2O_3\\ 2Cu + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CuO\\ 2Zn + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2ZnO\\ S + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} SO_2\\ 4Na + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2Na_2O\\ 2Ba + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2BaO\)
\(CH_4 + 2O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} CO_2 + 2H_2O\\ C_2H_5OH + 3O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CO_2 + 3H_2O\\ 2NO + O_2 \to 2NO_2\\ 2CO + O_2 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2CO_2\\ b)\\ 2KClO_3 \xrightarrow{t^o} 2KCl + 3O_2\\ 2KMnO_4 \xrightarrow{t^o} K_2MnO_4 + MnO_2 + O_2\)
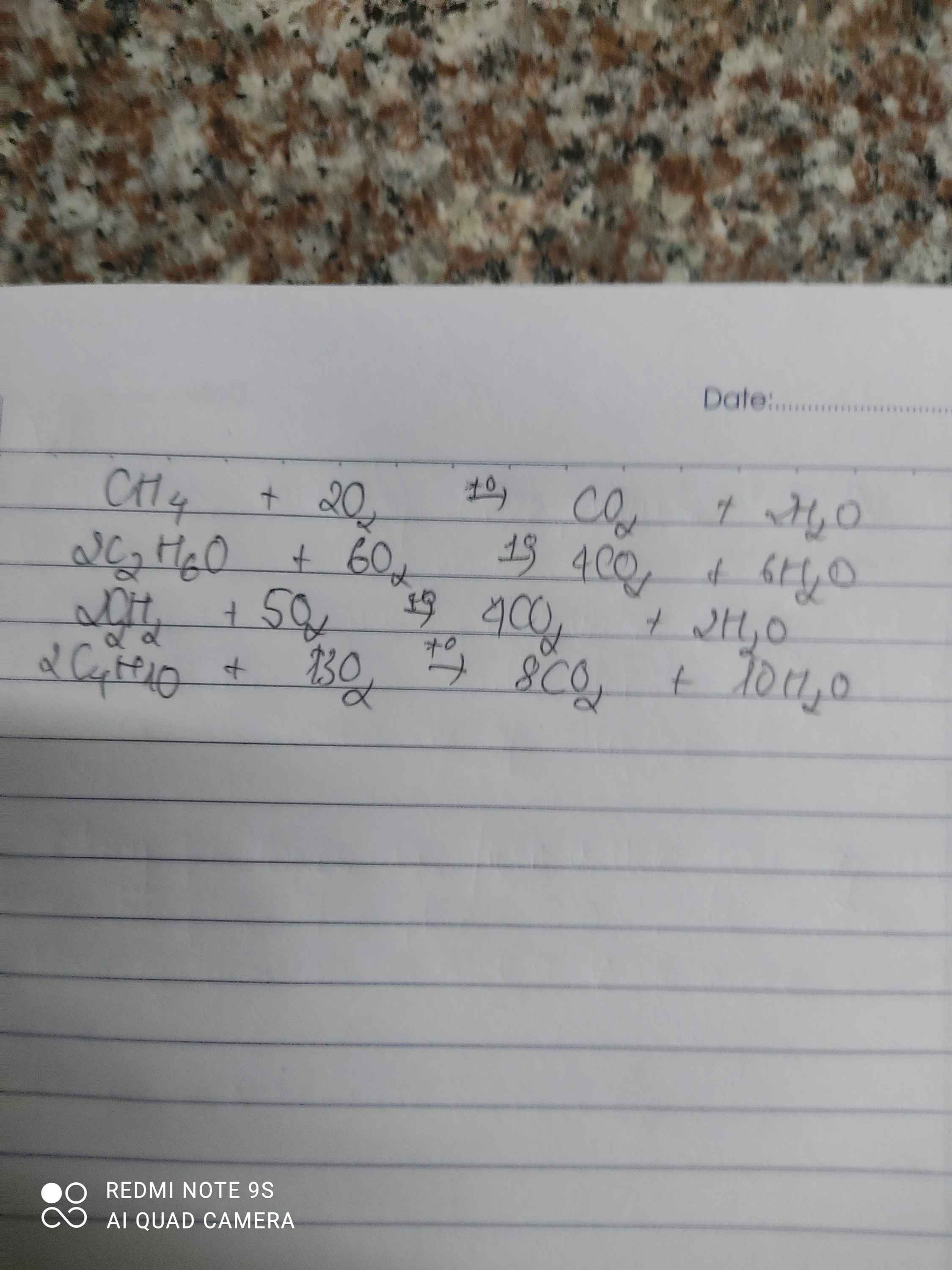
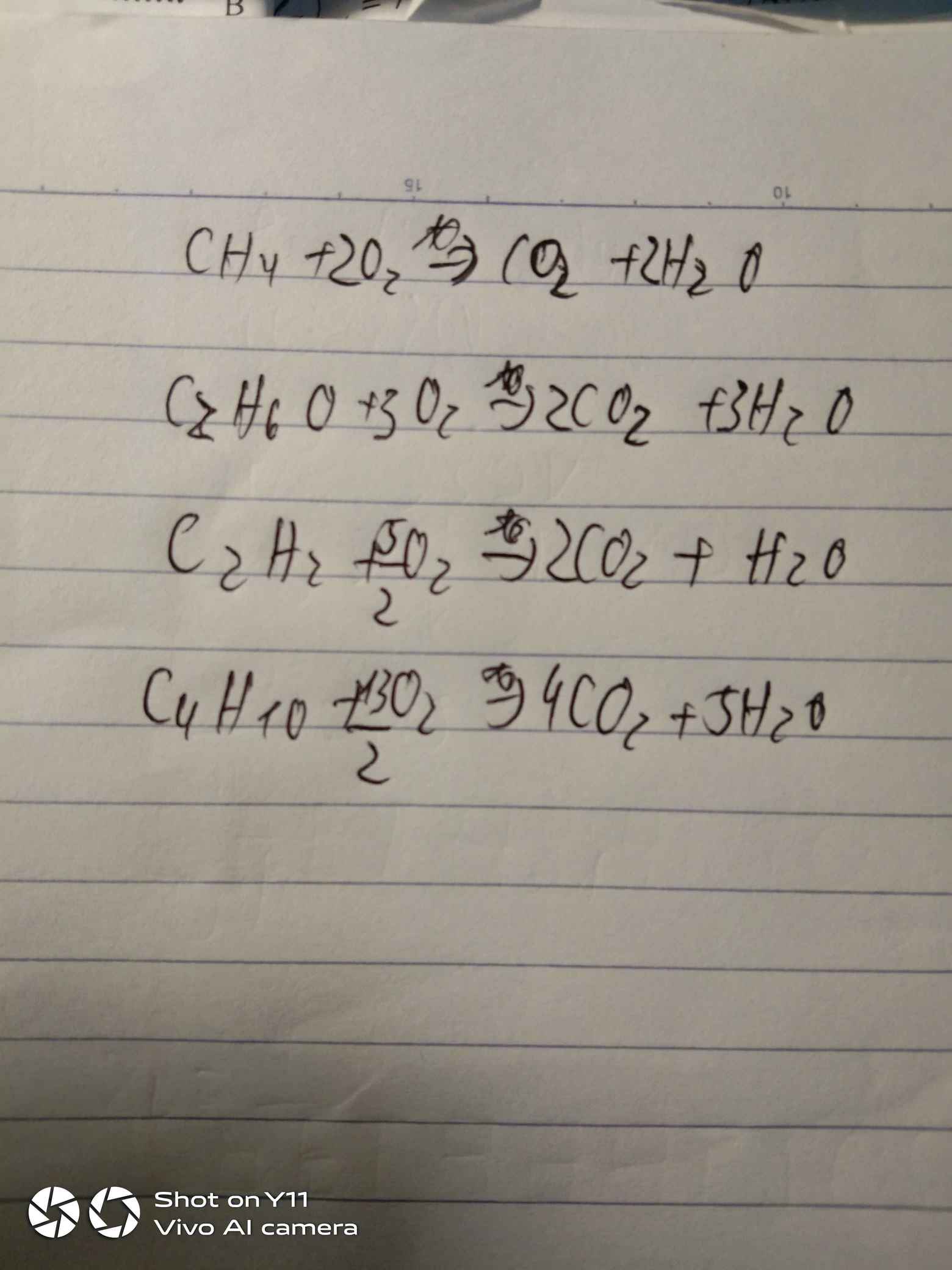
C+O2-->CO2
S+O2-->SO2
P+O2--->P2O5
Na+O2-->Na2O
Zn+O2-->ZnO
Fe+O2--->Fe3O4
Cu+O2-->CuO