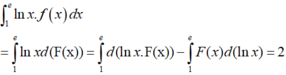Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(I=\int\limits^e_1x^2.ln^2x.\dfrac{1}{x\left(lnx+1\right)^2}dx\)
Đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=x^2ln^2x\\dv=\dfrac{1}{x\left(lnx+1\right)^2}dx\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=2x.lnx\left(lnx+1\right)\\v=-\dfrac{1}{lnx+1}\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I=-\dfrac{x^2ln^2x}{lnx+1}|^e_1+\int\limits^e_12x.lnxdx=-\dfrac{e^2}{2}+I_1\)
Xét \(I_1\), đặt \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}u=lnx\\dv=2xdx\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}du=\dfrac{dx}{x}\\v=x^2\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Rightarrow I_1=x^2lnx|^e_1-\int\limits^e_1xdx=...\)

= 1 / e . ( t/p từ 1->e ( e.lnx / ( x + 1 ) ) dx
= 1 / e . ( tp từ 1->e ( ln(x+1) / ( x + 1 ) ) dx < e.lnx = ln ( x + 1 ) mà >
= 1 / e . ( tp từ 1->e ( ln(x+1) d ( ln ( x + 1 ) )
= 1 / e . ( 1 /2 . ln^2 (( x + 1 )) |1->e )
= ( ln^2 (( e + 1 )) - ln2 ) / 2e
\(I=\int_1^e\dfrac{\ln x}{x}dx=\int_1^e\ln x.d(\ln x)=\dfrac{(\ln x)^2}{2}|_1^e=...\)

Cách làm cơ bản của dạng này:
Cho hàm số y=f(x) liên tục trên R\ {0; -1} thỏa mãn f(1) =-2ln2 và\(x\left(x+1\right)f'\left(x\right)+f\left(x\right)=x^... - Hoc24
https://hoc24.vn/cau-hoi/cho-ham-so-y-fx-lien-tuc-tren-left02right-thoa-man-cac-dieu-kien-f2-1-va-intlimits2-0fleftxrightdxintlimits2-0leftf.3001074942942 giúp luôn câu này nữa ạ

a) Với điều kiện x > 0, ta có phương trình
e 2 . e ln x = x + 3
⇔ e 2 .x = x + 3
⇔x( e 2 − 1) = 3
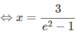
(thỏa mãn điều kiện)
b) Tương tự câu a), x = e 2
c) Với điều kiện x > 3 ta có:
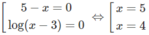

Chọn C
Ta có
I = 4 ∫ 1 e x ( 1 + ln x ) d x = 2 ∫ 1 e ( 1 + ln x ) d ( x 2 ) = 2 1 + ln x x 2 | 1 e - ∫ 1 e x 2 . 1 x d x = 2 2 e 2 - 1 - e 2 2 + 1 2 = 3 e 2 - 1
Nên a=3; b=-1 nên M=5.

Với điều kiện x > 1 ta có phương trình:
ln(4x + 2) = ln[x(x − 1)]
⇔ 4x + 2 = x 2 – x ⇔ x 2 – 5x – 2 = 0
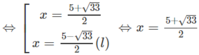

Với điều kiện x > 0, ta có phương trình
e 2 . e lnx = x + 3
⇔ e 2 .x = x + 3
⇔x( e 2 − 1) = 3
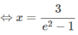
(thỏa mãn điều kiện)