
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


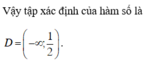

ĐKXĐ:
a. \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x-1\ge0\\x-3\ne0\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x\ge1\\x\ne3\end{matrix}\right.\) \(\Rightarrow D=[1;+\infty)\backslash\left\{3\right\}\)
b. \(D=R\)
c. \(x+3>0\Rightarrow x>-3\Rightarrow D=\left(-3;+\infty\right)\)
d. \(\left|x-2\right|\ge0\Rightarrow x\in R\Rightarrow D=R\)

a) Hàm \(y = 2{x^3} + 3x + 1\) là hàm đa thức nên có tập xác định \(D = \mathbb{R}\)
b) Biểu thức \(\frac{{x - 1}}{{{x^2} - 3x + 2}}\)có nghĩa khi \({x^2} - 3x + 2 \ne 0 \Leftrightarrow x \ne 1\)và \(x \ne 2\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số đã cho là \(D = \mathbb{R}/\left\{ {1;2} \right\}\)
c) Biểu thức \(\sqrt {x + 1} + \sqrt {1 - x} \) có nghĩa khi \(x + 1 \ge 0\) và \(1 - x \ge 0\), tức là \( - 1 \le x \le 1\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số đã cho là \(D = \left[ { - 1;1} \right]\)

Hàm số xác định \(\Leftrightarrow\left(m-2\right)x^2-2\left(m-3\right)x+m-1\ge0\)
Đặt \(f\left(x\right)=\left(m-2\right)x^2-2\left(m-3\right)x+m-1\ge0\)
\(f\left(x\right)\ge0,\forall x\in R\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}a>0\\\Delta\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m-2>0\\\left[-2\left(m-3\right)\right]^2-4\left(m-2\right)\left(m-1\right)\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}m>2\\4\left(m^2-6m+9\right)-4\left(m^2-3m+2\right)\le0\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow4m^2-24m+36-4m^2+12m-8\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-12m+28\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow m\le\dfrac{7}{3}\)
\(KL:m\in(2;\dfrac{7}{3}]\)

a) Biểu thức \(4{x^2} - 1\) có nghĩa với mọi \(x \in \mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số này là \(D = \mathbb{R}\)
b) Biểu thức \(f(x)\) có nghĩa khi và chỉ khi \({x^2} + 1 \ne 0,\)tức là với mọi \(x \in \mathbb{R}\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số này là \(D = \mathbb{R}\)
c) Biểu thức \(f(x)\) có nghĩa khi và chỉ khi \(\frac{1}{x}\) có nghĩa, tức là khi \(x \ne 0,\)
Vậy tập xác định của hàm số này là \(D = \mathbb{R}{\rm{\backslash }}\{ 0\} \)


a) \(y = \frac{1}{{{x^2} - x}}\) xác định \( \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - x \ne 0 \Leftrightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}x \ne 0\\x \ne 1\end{array} \right.\)
Tập xác định \(D = \mathbb{R}\backslash \left\{ {0;1} \right\}\)
b) \(y = \sqrt {{x^2} - 4x + 3} \) xác định \( \Leftrightarrow {x^2} - 4x + 3 \ge 0 \Leftrightarrow \left\{ \begin{array}{l}x \ge 3\\x \le 1\end{array} \right.\)
Tập xác định \(D = \left( { - \infty ;1} \right] \cup \left[ {3; + \infty } \right)\)
c) \(y = \frac{1}{{\sqrt {x - 1} }}\) xác định \( \Leftrightarrow x - 1 > 0 \Leftrightarrow x > 1\)
Tập xác định \(D = \left( {1; + \infty } \right)\)

\(y=\sqrt{x+3+2\sqrt{x+2}}+\sqrt{2-x^2+2\sqrt{1-x^2}}\)
\(=\sqrt{x+2+2\sqrt{x+2}+1}+\sqrt{1-x^2+2\cdot\sqrt{1-x^2}\cdot1+1}\)
\(=\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{x+2}+1\right)^2}+\sqrt{\left(\sqrt{1-x^2}+1\right)^2}\)
\(=\left|\sqrt{x+2}+1\right|+\left|\sqrt{1-x^2}+1\right|\)
ĐKXĐ: \(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x+2>=0\\1-x^2>=0\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>\(\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-2\\x^2< =1\end{matrix}\right.\Leftrightarrow\left\{{}\begin{matrix}x>=-2\\-1< =x< =1\end{matrix}\right.\)
=>-1<=x<=1
TXĐ là D=[-1;1]