Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

a: Để A là số nguyên thì
x^3-2x^2+4 chia hết cho x-2
=>\(x-2\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2;4;-4\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{3;1;4;0;6;-2\right\}\)
b: Để B là số nguyên thì
\(3x^3-x^2-6x^2+2x+9x-3+2⋮3x-1\)
=>\(3x-1\in\left\{1;-1;2;-2\right\}\)
=>\(x\in\left\{\dfrac{2}{3};0;1;-\dfrac{1}{3}\right\}\)

a, \(\dfrac{6}{2x+1}\Rightarrow2x+1\inƯ\left(6\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2;\pm3;\pm6\right\}\)
| 2x + 1 | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 | 3 | -3 | 6 | -6 |
| 2x | 0 | -2 | 1 | -3 | 2 | -4 | 5 | -7 |
| x | 0 | -1 | 1/2 ( loại ) | -3/2 ( loại ) | 1 | -2 | 5/2 ( loại ) | -7/2 ( loại ) |
c, \(\dfrac{x-3}{x-1}=\dfrac{x-1-2}{x-1}=1-\dfrac{2}{x-1}\Rightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(2\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm2\right\}\)
| x - 1 | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 |
| x | 2 | 0 | 3 | -1 |
tương tự ....

\(a,ĐK:x^2-1=\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\ne0\Leftrightarrow x\ne\pm1\\ \dfrac{3x+3}{x^2-1}=\dfrac{3\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}=\dfrac{3}{x-1}=2\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1=\dfrac{3}{2}\Leftrightarrow x=\dfrac{5}{2}\left(tm\right)\\ b,\dfrac{3}{x-1}\in Z\\ \Leftrightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(3\right)=\left\{-3;-1;1;3\right\}\\ \Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{-2;0;2;4\right\}\left(tm\right)\)

phân thức được xác định ⇔ x2 - 1 ≠ 0 ⇔ x ≠ \(\left\{-1;1\right\}\)
\(\dfrac{3x+3}{x^2-1}=-2\)
=> 3x + 3 = -2x2 + 2
=> 2x2 + 3x + 1 = 0
=> (2x+1)(x+1) = 0
=> x = -1/2 (thỏa mãn) hoặc x = -1 (loại)
Vậy, để phân thức có giá trị bằng –2 thì x = -1/2.
\(\dfrac{3x+3}{x^2-1}\)=\(\dfrac{3\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}\) (x khác -1 và x khác 1)
= \(\dfrac{3}{x-1}\)
=> Phân thức ban đầu có giá trị nguyên ⇔ 3 chia hết cho x-1
=> x-1 ∈\(\left\{-3;-1;1;3\right\}\)
=> x ∈\(\left\{-2;0;2;4\right\}\)
Vậy, để phân thức có giá trị là số nguyên.thì x ∈\(\left\{-2;0;2;4\right\}\).

a) ĐKXĐ: \(x\notin\left\{1;-1\right\}\)
b) Ta có: \(\dfrac{3x+3}{x^2-1}\)
\(=\dfrac{3\left(x+1\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x-1\right)}\)
\(=\dfrac{3}{x-1}\)
Để phân thức có giá trị bằng -2 thì \(\dfrac{3}{x-1}=-2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1=\dfrac{-3}{2}\)
hay \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
Vậy: Để phân thức có giá trị bằng -2 thì \(x=-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c) Để phân thức có giá trị là số nguyên thì \(3⋮x-1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1\inƯ\left(3\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x-1\in\left\{1;-1;3;-3\right\}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\in\left\{2;0;4;-2\right\}\)
Kết hợp ĐKXĐ, ta được:
\(x\in\left\{2;0;4;-2\right\}\)
Vậy: Để phân thức có giá trị là số nguyên thì \(x\in\left\{2;0;4;-2\right\}\)

để \(\frac{7}{x^2-x+1}\in Z\Leftrightarrow x^2-x+1\inƯ_7=\left\{\pm1;\pm7\right\}\)
nếu \(x^2-x+1=-7\Leftrightarrow x^2-x+8=0\left(vo nghiem\right)\)
nếu \(x^2-x+1=-1\Leftrightarrow x^2-x +2=0\left(vo nghiem\right)\)
nếu \(x^2-x+1=1\Leftrightarrow x^2-x=0\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=1\\x=0\end{cases} }\)
nếu \(x^2-x+1=7\Leftrightarrow x^2-x-6=0\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x=3\\x=-2\end{cases} }\)
vậy \(x\in\left\{-2,0,1,3\right\}\)
Để \(\frac{7}{x^2-x+1}\)ta có : \(x^2-x+1=x^2-x+\frac{1}{4}+\frac{3}{4}=\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\)
hay \(7⋮\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\inƯ\left(7\right)=\left\{\pm1;\pm7\right\}\)
Xét từng trường hợp :
TH1 : \(\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}=1\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=\frac{1}{4}\Leftrightarrow x-\frac{1}{2}=\pm\frac{1}{2}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x_1=\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}=1;x_2=-\frac{1}{2}+\frac{1}{2}=0\)( chọn )
TH2 : \(\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}=-1\Leftrightarrow\left(x-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=-\frac{7}{4}\)ko thỏa mãn
tương tự 2 trường hợp còn lại

ĐKXĐ : x2 - 6x + 9 \(\ne\)0
<=> x \(\ne\)3
a) A = 0
=> 3x2 - 11x + 6 = 0
<=> 3x2 - 9x - 2x + 6 = 0
<=> 3x(x - 3) - 2(x - 3) = 0
<=> (3x - 2)(x - 3) = 0
<=> \(\orbr{\begin{cases}x=\frac{2}{3}\left(tm\right)\\x=3\left(\text{loại}\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy x = 2/3 thì A = 0
b) Ta có A = \(\frac{3x^2-11x+6}{x^2-6x+9}=3+\frac{7x-21}{x^2-6x+9}=3+\frac{7}{x-3}\)
Để : A \(\inℤ\Leftrightarrow7⋮x-3\Leftrightarrow x-3\inƯ\left(7\right)\Leftrightarrow x-3\in\left\{1;7;-1;-7\right\}\)
Lập bảng xét các trường hợp
| x - 3 | 1 | 7 | -1 | -7 |
| x | 4(tm) | 10(tm) | 2(tm) | -4(tm) |
Vậy \(x\in\left\{4;10;2;-4\right\}\)thì A \(\inℤ\)
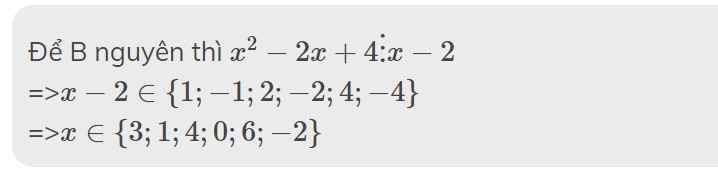
x^3-3x^2-11x+8/ x-5