
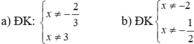
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

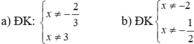

Bài 1:
a) x≠2x≠2
Bài 2:
a) x≠0;x≠5x≠0;x≠5
b) x2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5xx2−10x+25x2−5x=(x−5)2x(x−5)=x−5x
c) Để phân thức có giá trị nguyên thì x−5xx−5x phải có giá trị nguyên.
=> x=−5x=−5
Bài 3:
a) (x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45)(x+12x−2+3x2−1−x+32x+2)⋅(4x2−45)
=(x+12(x−1)+3(x−1)(x+1)−x+32(x+1))⋅2(2x2−2)5=(x+12(x−1)+3(x−1)(x+1)−x+32(x+1))⋅2(2x2−2)5
=(x+1)2+6−(x−1)(x+3)2(x−1)(x+1)⋅2⋅2(x2−1)5=(x+1)2+6−(x−1)(x+3)2(x−1)(x+1)⋅2⋅2(x2−1)5
=(x+1)2+6−(x2+3x−x−3)(x−1)(x+1)⋅2(x−1)(x+1)5=(x+1)2+6−(x2+3x−x−3)(x−1)(x+1)⋅2(x−1)(x+1)5
=[(x+1)2+6−(x2+2x−3)]⋅25=[(x+1)2+6−(x2+2x−3)]⋅25
=[(x+1)2+6−x2−2x+3]⋅25=[(x+1)2+6−x2−2x+3]⋅25
=[(x+1)2+9−x2−2x]⋅25=[(x+1)2+9−x2−2x]⋅25
=2(x+1)25+185−25x2−45x=2(x+1)25+185−25x2−45x
=2(x2+2x+1)5+185−25x2−45x=2(x2+2x+1)5+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+25+185−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+25+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+2+185−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+2+185−25x2−45x
=2x2+4x+205−25x2−45x=2x2+4x+205−25x2−45x
c) tự làm, đkxđ: x≠1;x≠−1

Câu 1 :
a) ĐKXĐ : \(\hept{\begin{cases}x+1\ne0\\2x-6\ne0\end{cases}}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne-1\\x\ne3\end{cases}}\)
b) Để \(P=1\Leftrightarrow\frac{4x^2+4x}{\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-6\right)}=1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{4x^2+4x-\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-6\right)}{\left(x+1\right)\left(2x-6\right)}=0\)
\(\Rightarrow4x^2+4x-2x^2+4x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2+8x+6=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2+4x+4-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(x+2-1\right)\left(x+2+1\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x+1=0\\x+3=0\end{cases}}\) \(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}x=-1\left(KTMĐKXĐ\right)\\x=-3\left(TMĐKXĐ\right)\end{cases}}\)
Vậy : \(x=-3\) thì P = 1.

a. ĐK \(\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x+5\ne0\end{cases}\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x\ne0\\x\ne-5\end{cases}}}\)
b. \(A=\frac{x^2+2x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x^2+2x\right)+2\left(x-5\right)\left(x+5\right)+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
\(=\frac{x\left(x+5\right)\left(x-1\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x-1}{2}\)
Để \(A=1\Rightarrow\frac{x-1}{2}=1\Rightarrow x=3\)
Để \(A=-3\Rightarrow\frac{x-1}{2}=-3\Rightarrow x=-5\)
Vậy với x=3 thì A=1 ; với x=-5 thì A=-3

a)=3x2(x+2)/x2(x+2)+(x+2)
=3x2(x+2)/(x+2)(x2+1)
Để phân thức được xác định thì (x+2)(x2+1) khác 0
X2+1 >0
x+20
x2
b) theo câu a
ta có:
=3x2(x+2)/(x+2)(x2+1)
=3x2/x2+1=2
=3x2=(x2+1)2
=3x2=2x2+2
=x2=2
x=

\(\frac{x^2+2x}{2x+10}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x^2+2x}{2\left(x+5\right)}+\frac{x-5}{x}+\frac{50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\)
\(=\frac{x\left(x^2+2x\right)+2\left(x+5\right)\left(x-5\right)+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x^3+2x^2+2x^2-50+50-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x^3+4x^2-5x}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\)
\(=\frac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x^2+4x-5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x^2-1+4\left(x-1\right)\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}\)
a/ Để biểu thức xác đinh => 2x(x+5) khác 0 => x khác 0 và x khác -5
b/ Gọi biểu thức là A. Rút gọn A ta được:
\(A=\frac{x\left(x-1\right)\left(x+5\right)}{2x\left(x+5\right)}=\frac{x-1}{2}\left(x\ne0;x\ne-5\right)\)
A=1 => x-1=2 => x=3
c/ A=-1/2 <=> x-1=-1 => x=0
d/ A=-3 <=> x-1=-6 => x=-5

a) A=3x+22(x−1)−3(2x+1)
Gía trị phân thức A được xác định khi 2 (x - 1) - 3 (2x + 1) \(\ne0\)
=> Nếu tìm được x khi phân thức A = 0 thì sẽ tìm được điều kiện của x để giá trị phân thức A được xác định.
Ta có phương trình:
2 (x - 1) - 3 (2x + 1) \(=0\)
hay 2x - 2 - 6x - 3 = -4x - 5 = 0
=> x = (0 + 5) : (-4) = \(\dfrac{-5}{4}\)
Vậy x \(\ne\dfrac{-5}{4}\) thì giá trị phân thức A
=3x+22(x−1)−3(2x+1)được xác định.
b) \(B=\dfrac{0,5\left(x+3\right)-2}{1,2\left(x+0,7\right)-4\left(0,6x+0,9\right)}\)
Gía trị phân thức B được xác định khi 1,2 (x + 0,7) - 4 (0,6x + 0,9) \(\ne\) 0
=> Nếu tìm được x khi phân thức B = 0 thì sẽ tìm được điều kiện của x để giá trị phân thức B được xác định.
Ta có phương trình:
1,2 (x + 0,7) - 4 (0,6x + 0,9) = 0
hay 1,2x + 0,84 - 2,4x - 3,6 = -1,2x - 2,76 = 0
=> x = (0 + 2,76) : (-1,2) = \(\dfrac{-23}{10}=-2,3\)
Vậy x \(\ne0\) thì giá trị phân thức B
=0,5(x+3)−21,2(x+0,7)−4(0,6x+0,9)được xác định.
Sửa lại:
a) \(A=\dfrac{3x+2}{2\left(x-1\right)-3\left(2x+1\right)}\)
Gía trị phân thức A được xác định khi 2 (x - 1) - 3 (2x + 1) ≠0
=> Nếu tìm được x khi phân thức A = 0 thì sẽ tìm được điều kiện của x để giá trị phân thức A được xác định.
Ta có phương trình:
2 (x - 1) - 3 (2x + 1) =0
hay 2x - 2 - 6x - 3 = -4x - 5 = 0
=> x = (0 + 5) : (-4) = \(\dfrac{-5}{4}=-1,25\)
Vậy x ≠ \(-1,25\) thì giá trị phân thức A được xác định.
b) \(B=\dfrac{0,5\left(x+3\right)-2}{1,2\left(x+0,7\right)-4\left(0,6x+0,9\right)}\)
Gía trị phân thức B được xác định khi 1,2 (x + 0,7) - 4 (0,6x + 0,9) ≠ 0
=> Nếu tìm được x khi phân thức B = 0 thì sẽ tìm được điều kiện của x để giá trị phân thức B được xác định.
Ta có phương trình:
1,2 (x + 0,7) - 4 (0,6x + 0,9) = 0
hay 1,2x + 0,84 - 2,4x - 3,6 = -1,2x - 2,76 = 0
=> x = (0 + 2,76) : (-1,2) = \(\dfrac{-23}{10}\)=−2,3
Vậy x ≠ -2,3 thì giá trị phân thức B được xác định.

b, P=x+2x+3−5x2+3x−2x−6+12−xP=x+2x+3−5x2+3x−2x−6+12−x
=x+2x+3−5(x+3)(x−2)−1x−2=x+2x+3−5(x+3)(x−2)−1x−2
=(x+2)(x−2)(x+3)(x−2)−5(x+3)(x−2)−x+3(x+3)(x−2)=(x+2)(x−2)(x+3)(x−2)−5(x+3)(x−2)−x+3(x+3)(x−2)
=x2−4−5−x−3(x+3)(x−2)=x2−x−12(x+3)(x−2)=x2−4−5−x−3(x+3)(x−2)=x2−x−12(x+3)(x−2)
=x2−4x+3x−12(x+3)(x−2)=x2−4x+3x−12(x+3)(x−2)
=(x−4)(x+3)(x+3)(x−2)=x−4x−2=(x−4)(x+3)(x+3)(x−2)=x−4x−2
c, Để P=−34P=−34
⇔x−4x−2=−34⇔x−4x−2=−34
⇔4(x−4)=−3(x−2)⇔4(x−4)=−3(x−2)
⇔4x−16+3x−6=0⇔4x−16+3x−6=0
⇔7x−22=0⇔7x−22=0
⇔x=227⇔x=227
d, Để P có giá trị nguyên
⇔x−4⋮x−2⇔x−4⋮x−2
⇔(x−2)−2⋮x−2⇔(x−2)−2⋮x−2
⇔2⋮x−2⇔x−2∈Ư(2)={1;−1;2;−2}⇔2⋮x−2⇔x−2∈Ư(2)={1;−1;2;−2}
| x−2x−2 | 1 | -1 | 2 | -2 |
| x | 3 | 1 | 4 | 0 |
e,
x2−9=0x2−9=0
⇒x2=9⇒[x=3x=−3⇒x2=9⇒[x=3x=−3
Với x=3,có :
x−4x−2=3−43−2=−11=−1x−4x−2=3−43−2=−11=−1
Với x=-3,có :
x−4x−2=−3−4−3−2=75x−4x−2=−3−4−3−2=75

a) ĐKXĐ: \(^{x^3+2x^2+x+2}\)khác 0
=> x^2(x+2)+(x+2) Khác 0
=> (x^2+1)(x+2) khác 0
=> x^2 khác -1(vô lý) và x khác -2
Vậy x khác -2 thì biểu thức A được xác định
b)\(A=\frac{3x^3+6x^2}{x^3+2x^2+x+2}=\frac{3x^2\left(x+2\right)}{x^2\left(x+2\right)+\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(=\frac{3x^2\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x^2+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}=\frac{3x^2}{x^2+1}\)
Để A=2 thì \(\frac{3x^2}{x+2}=2\)=>\(3x^2=2\left(x^2+1\right)=>3x^2=2x^2+2\)
\(=>x^2=2=>x=\sqrt{2}\)(Thỏa mãn điều kiện xác định)

a, ĐKXĐ: \(\hept{\begin{cases}x^3+1\ne0\\x^9+x^7-3x^2-3\ne0\\x^2+1\ne0\end{cases}}\)
b, \(Q=\left[\left(x^4-x+\frac{x-3}{x^3+1}\right).\frac{\left(x^3-2x^2+2x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)}{x^9+x^7-3x^2-3}+1-\frac{2\left(x+6\right)}{x^2+1}\right]\)
\(Q=\left[\frac{\left(x^3+1\right)\left(x^4-x\right)+x-3}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}.\frac{\left(x-1\right)\left(x+1\right)\left(x^2-x+1\right)}{\left(x^7-3\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}+1-\frac{2\left(x+6\right)}{x^2+1}\right]\)
\(Q=\left[\left(x^7-3\right).\frac{\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x^7-3\right)\left(x^2+1\right)}+1-\frac{2\left(x+6\right)}{x^2+1}\right]\)
\(Q=\frac{x-1+x^2+1-2x-12}{x^2+1}\)
\(Q=\frac{\left(x-4\right)\left(x+3\right)}{x^2+1}\)

Bài 1:
a) Để giá trị của phân thức A được xác định <=> \(7x^2+7x\ne0\) <=> \(7x.\left(x+1\right)\ne0\)<=> \(x\ne0\)và \(x\ne-1\)
=> Để giá trị của phân thức A được xác định thì x phải khác -1 và 0.
b) Để phân thức A = 0 => x - 3 = 0 => x = 3 (thỏa mãn đkxd)
=> Để giá trị phân thức A = 0 thì x = 3
Bạn viết z chắc mỏi tay lắm. Mik sẽ giải cho bạn b3 nhé
a) \(2x^3-12x^2+18x=2x.\left(x^2-6x+9\right)=2x.\left(x-3\right)^2\)
b) \(16y^2-4x^2-12x-9=16y^2-\left(4x^2+12x+9\right)=16y^2-\left(2x+3\right)^2\)
\(=\left(4y+2x+3\right).\left(4y-2x-3\right)\)